The document discusses flow charts and provides examples of flow charts for simple algorithms. Some key points:
- A flow chart represents an algorithm using a diagram to show the logic and flow of a program.
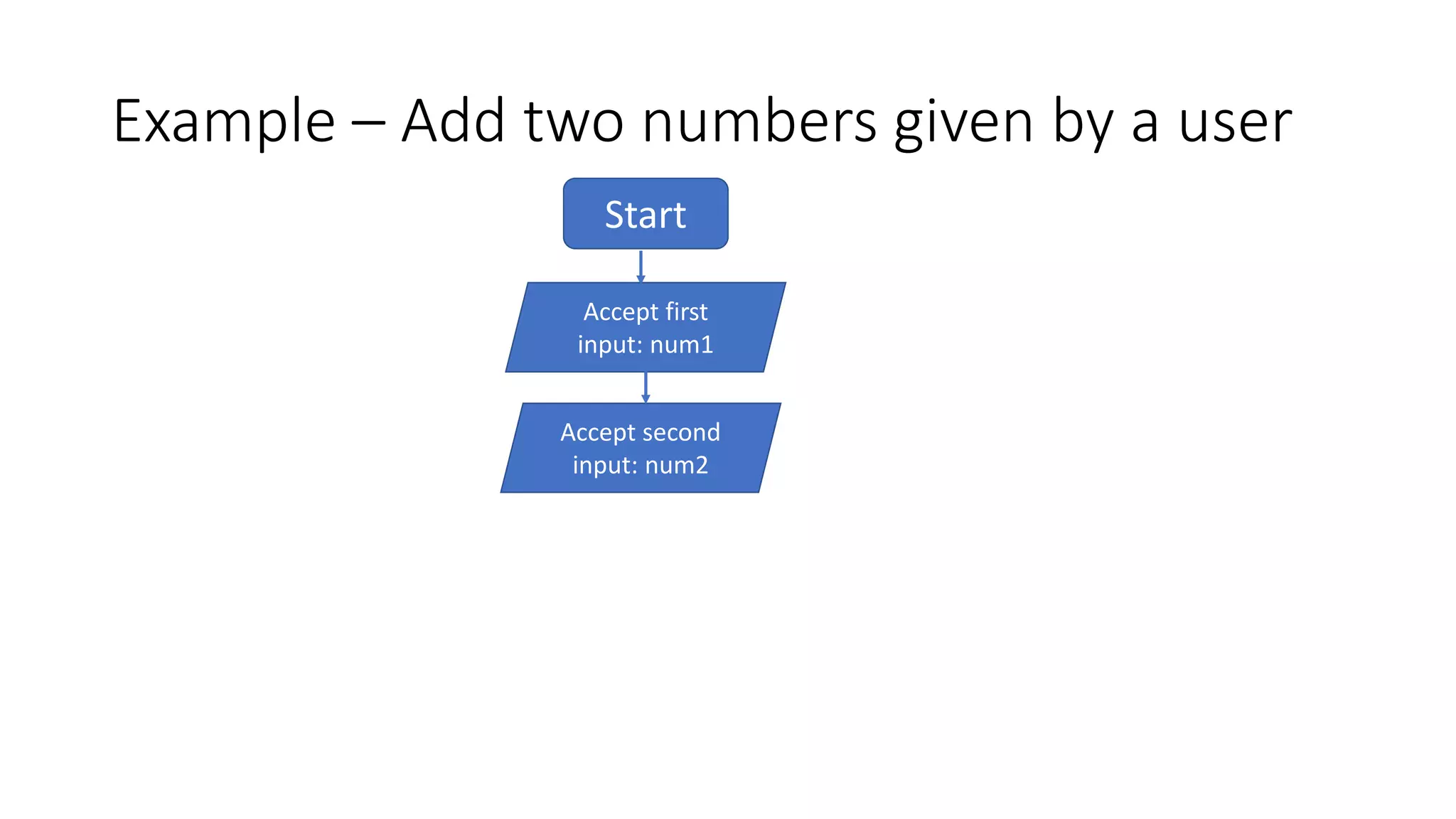
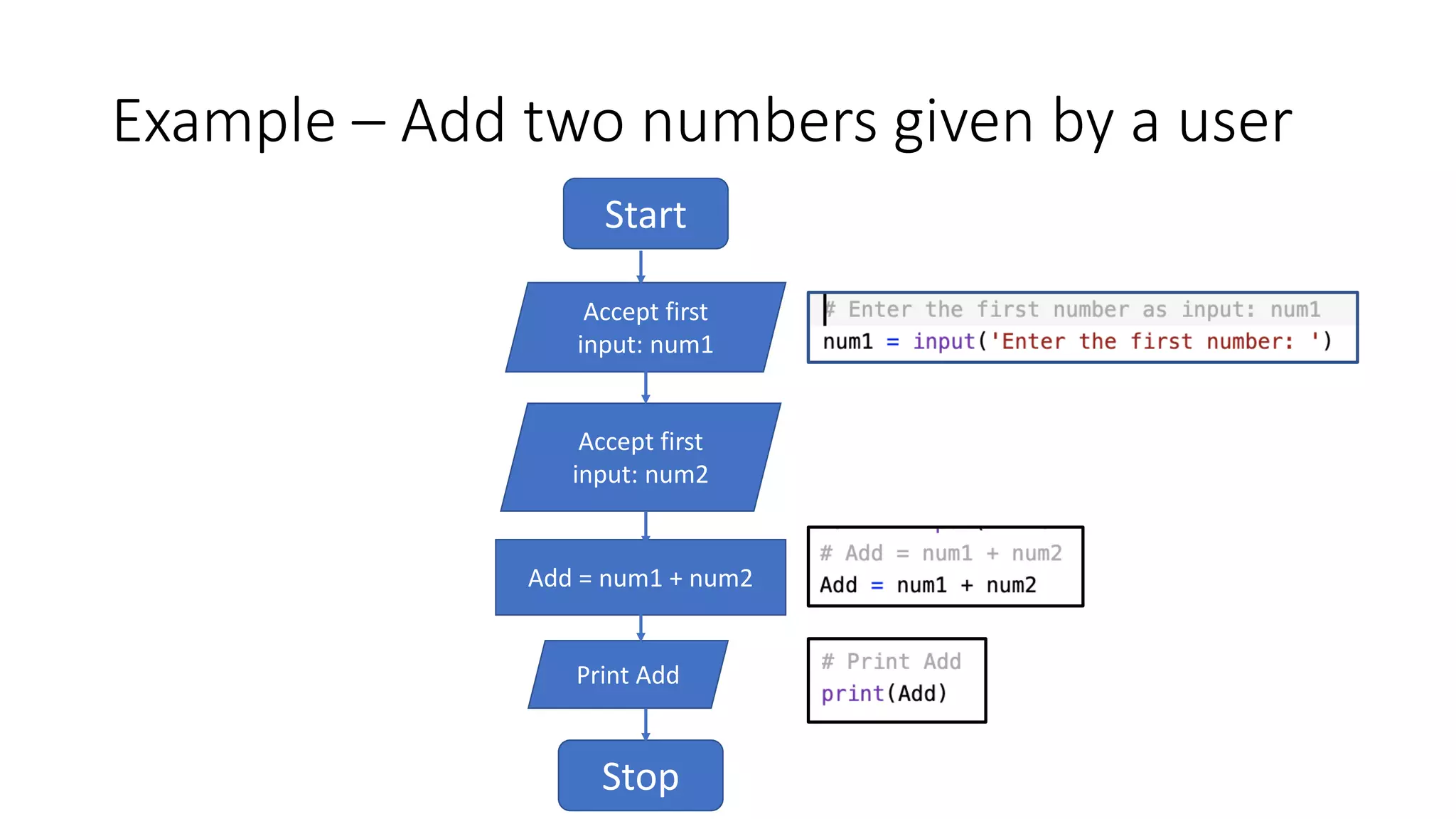
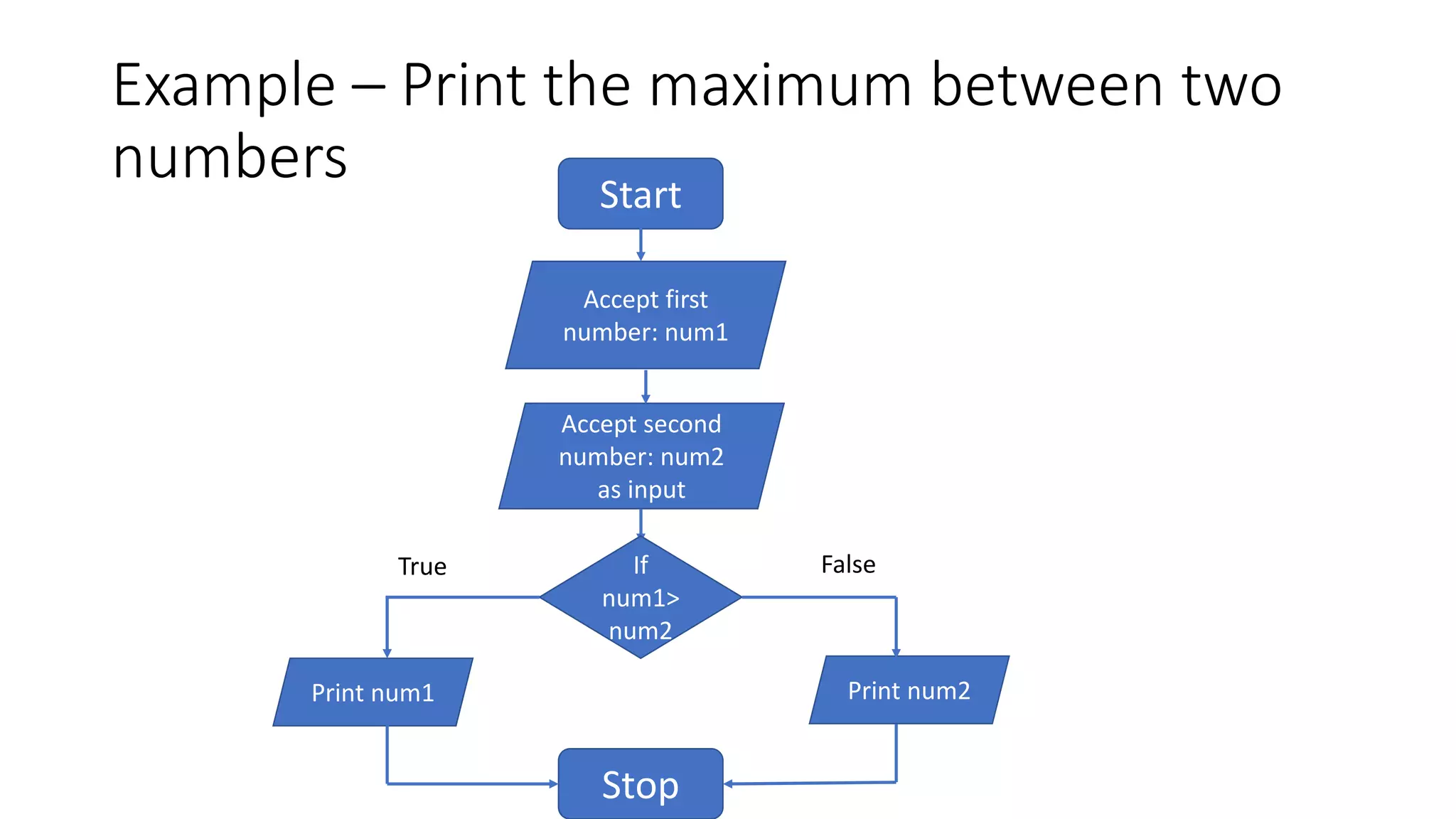
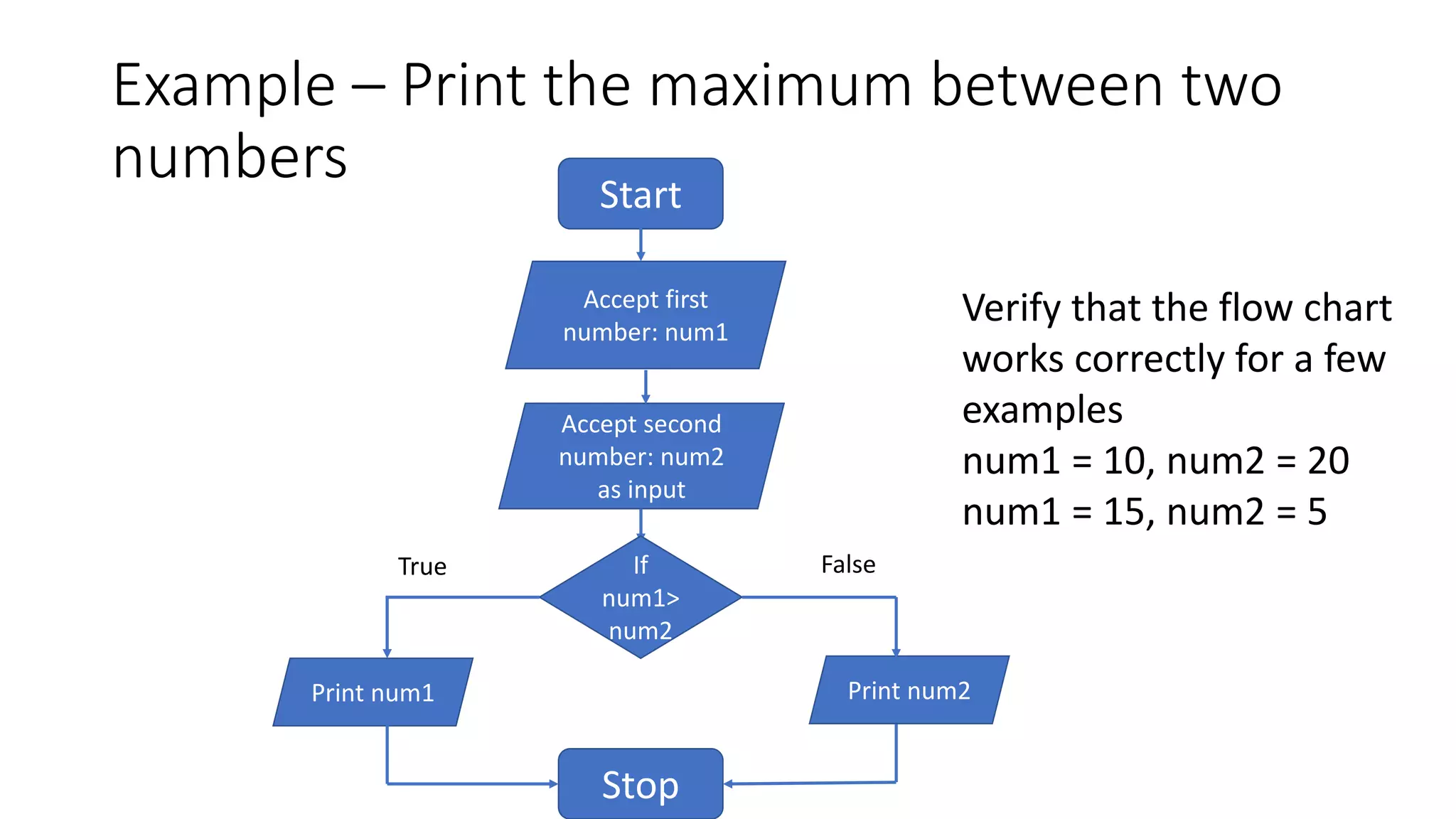
- An example flow chart is provided that takes two numbers as input, adds them, and prints the output.
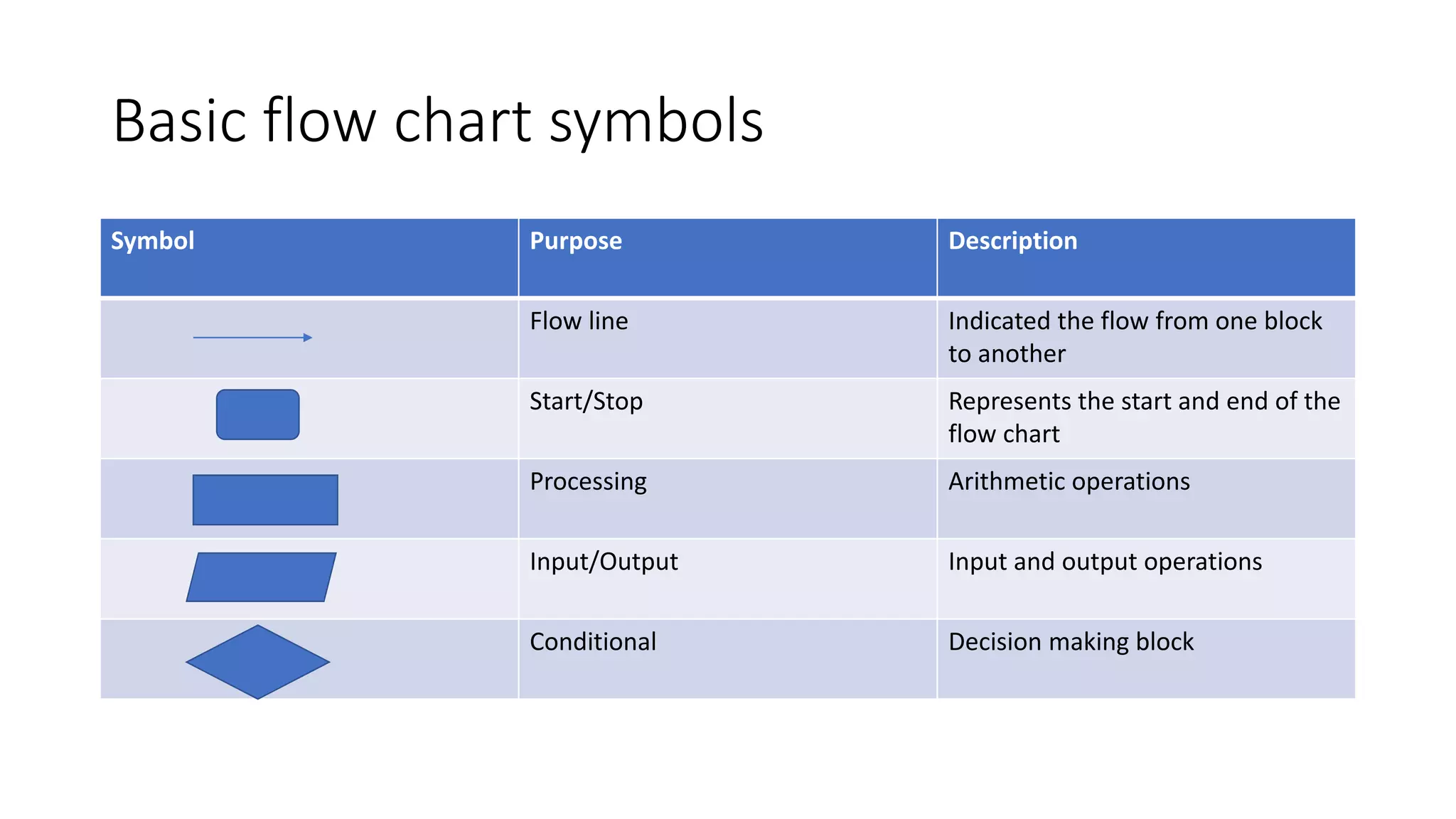
- Basic flow chart symbols are described like start/stop, processing, input/output, and conditional decision blocks.
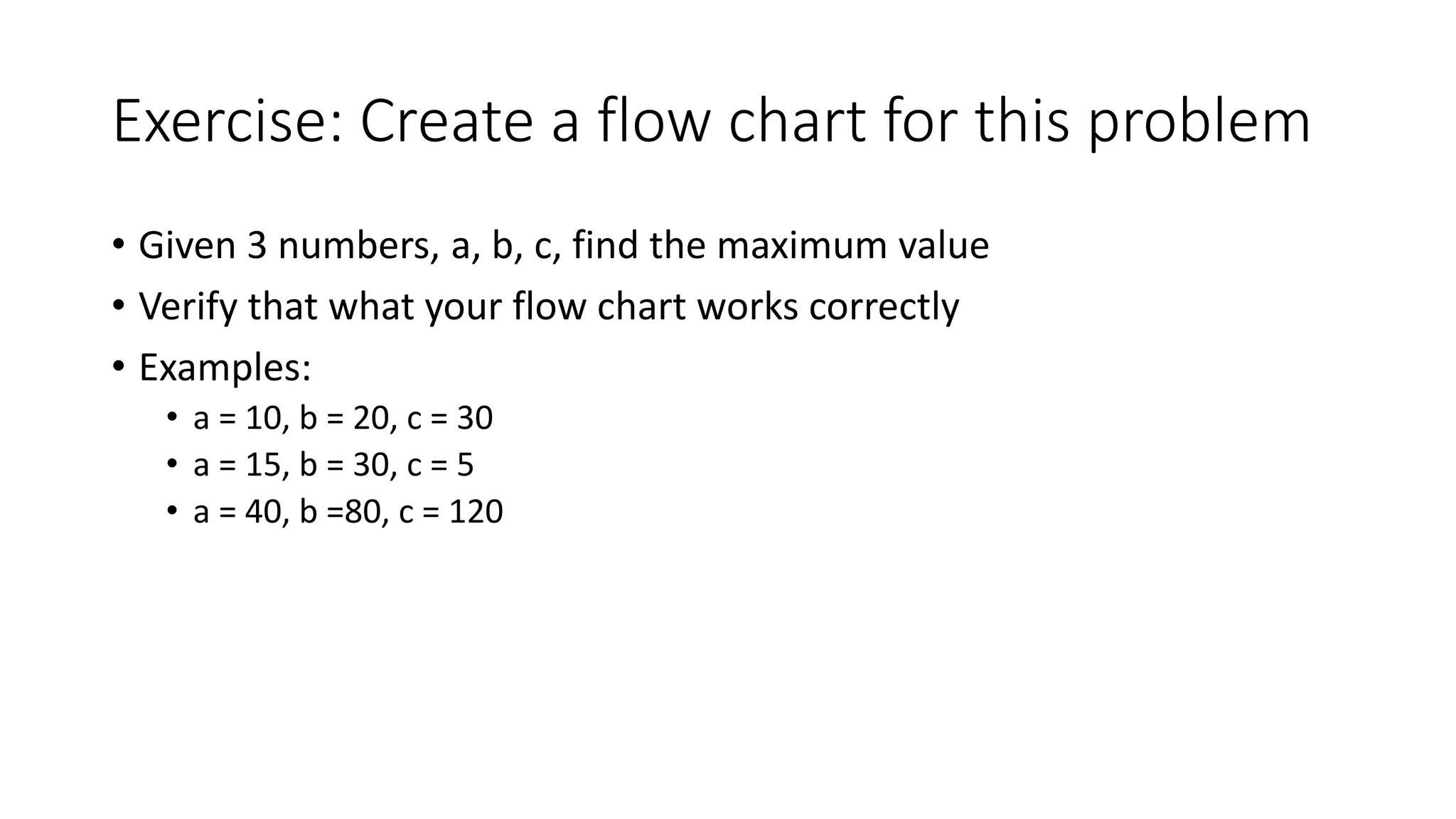
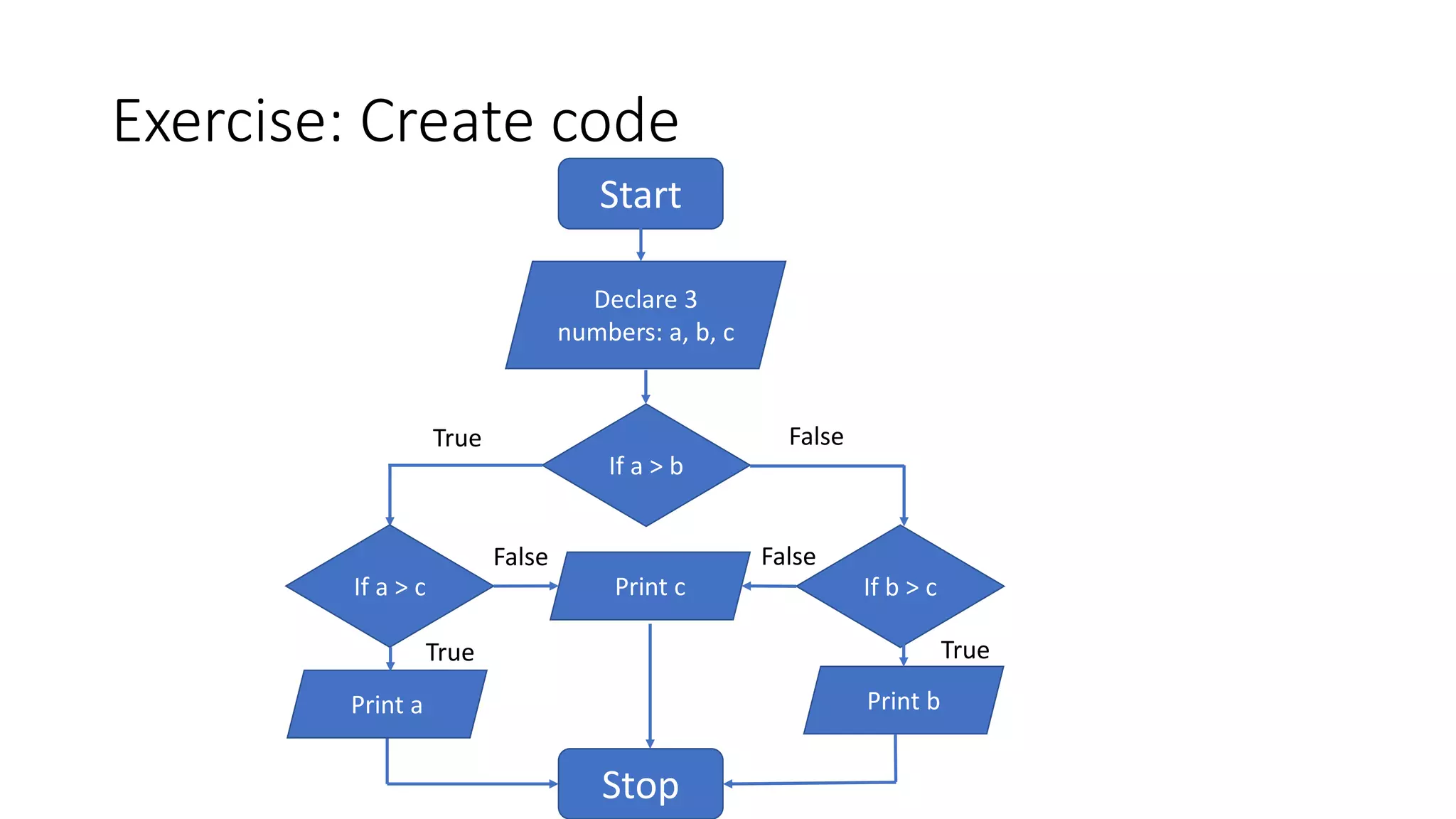
- An exercise asks the reader to create a flow chart that takes three numbers as input and finds the maximum value.
- Looping structures are discussed and an example flow chart is given to print even numbers from a list.








![Loops in flow chart
• Given a list list_sample = [4, 3, 2, 5, 8], print all the even numbers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pa1flowchart-200807202236/75/Pa1-flow-chart-16-2048.jpg)
![Loops in flow chart
Start
Declare list_sample [4, 3, 2, 5, 8]
Declare a variable len_list that stored the length of the list](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pa1flowchart-200807202236/75/Pa1-flow-chart-17-2048.jpg)
![Loops in flow chart
Start
Declare list_sample [4, 3, 2, 5, 8]
Declare a variable len_list that stored the length of the list](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pa1flowchart-200807202236/75/Pa1-flow-chart-18-2048.jpg)
![Loops in flow chart
Start
Declare list_sample [4, 3, 2, 5, 8]
Declare a number a=0
Declare a variable len_list that stores the length of the list
If a >
len_list
Stop a = a+1
value =
list_sample[a]
If value is
a even
number
Print value
True False
False True](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pa1flowchart-200807202236/75/Pa1-flow-chart-19-2048.jpg)
![Loops in flow chart
• Given a list list_sample = [4, 3, 2, 5, 8], print all the even numbers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pa1flowchart-200807202236/75/Pa1-flow-chart-20-2048.jpg)
![Loops in flow chart - while
• Given a list list_sample = [4, 3, 2, 5, 8], print all the even numbers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pa1flowchart-200807202236/75/Pa1-flow-chart-21-2048.jpg)
![Loops in flow chart - while
• Given a list list_sample = [4, 3, 2, 5, 8], print all the even numbers
Declare a number a=0
If a >
len_list
Stop a = a+1
value =
list_sample[a]
If value is
a even
number
Print value
True False
False True](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pa1flowchart-200807202236/75/Pa1-flow-chart-22-2048.jpg)
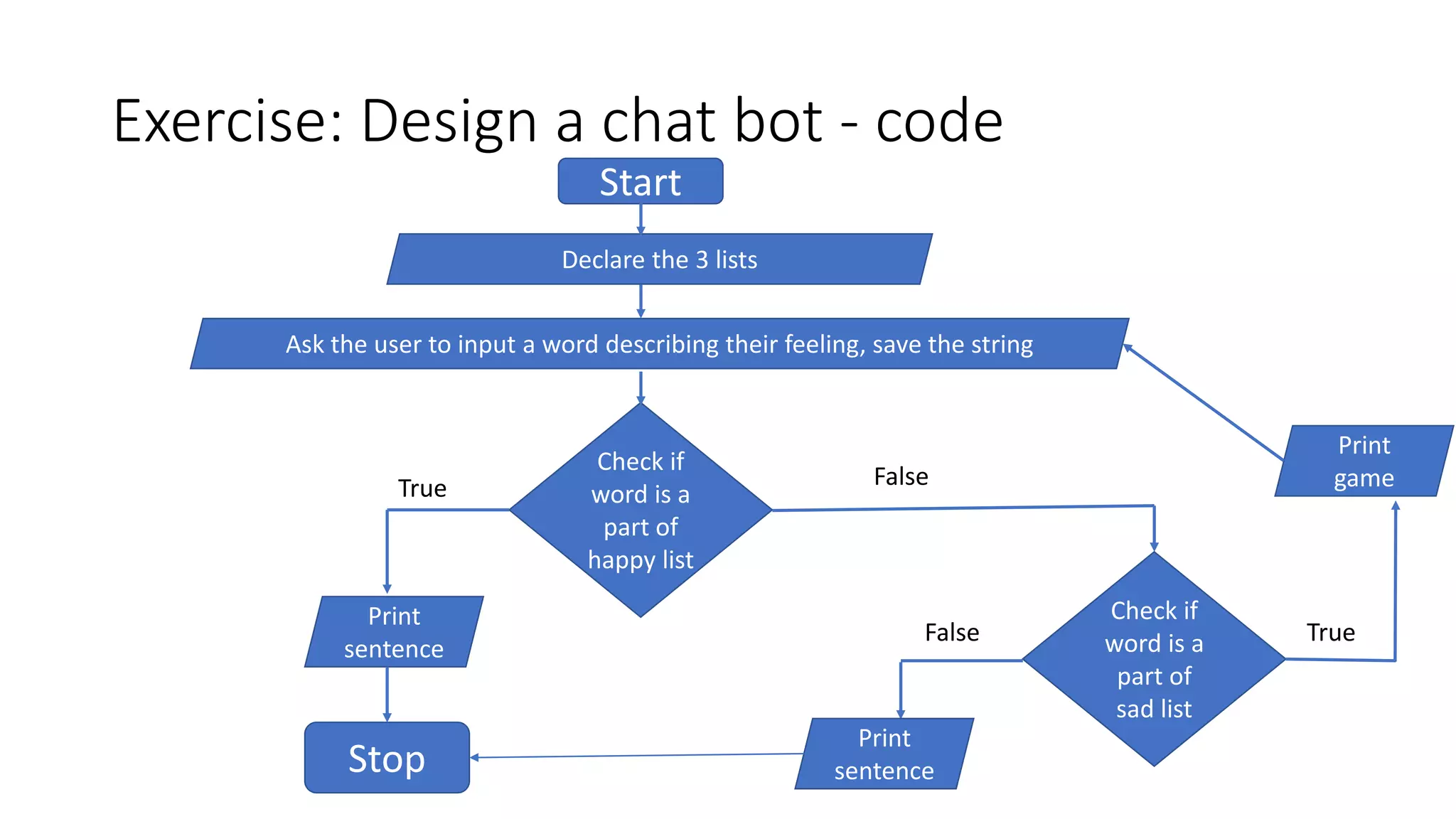
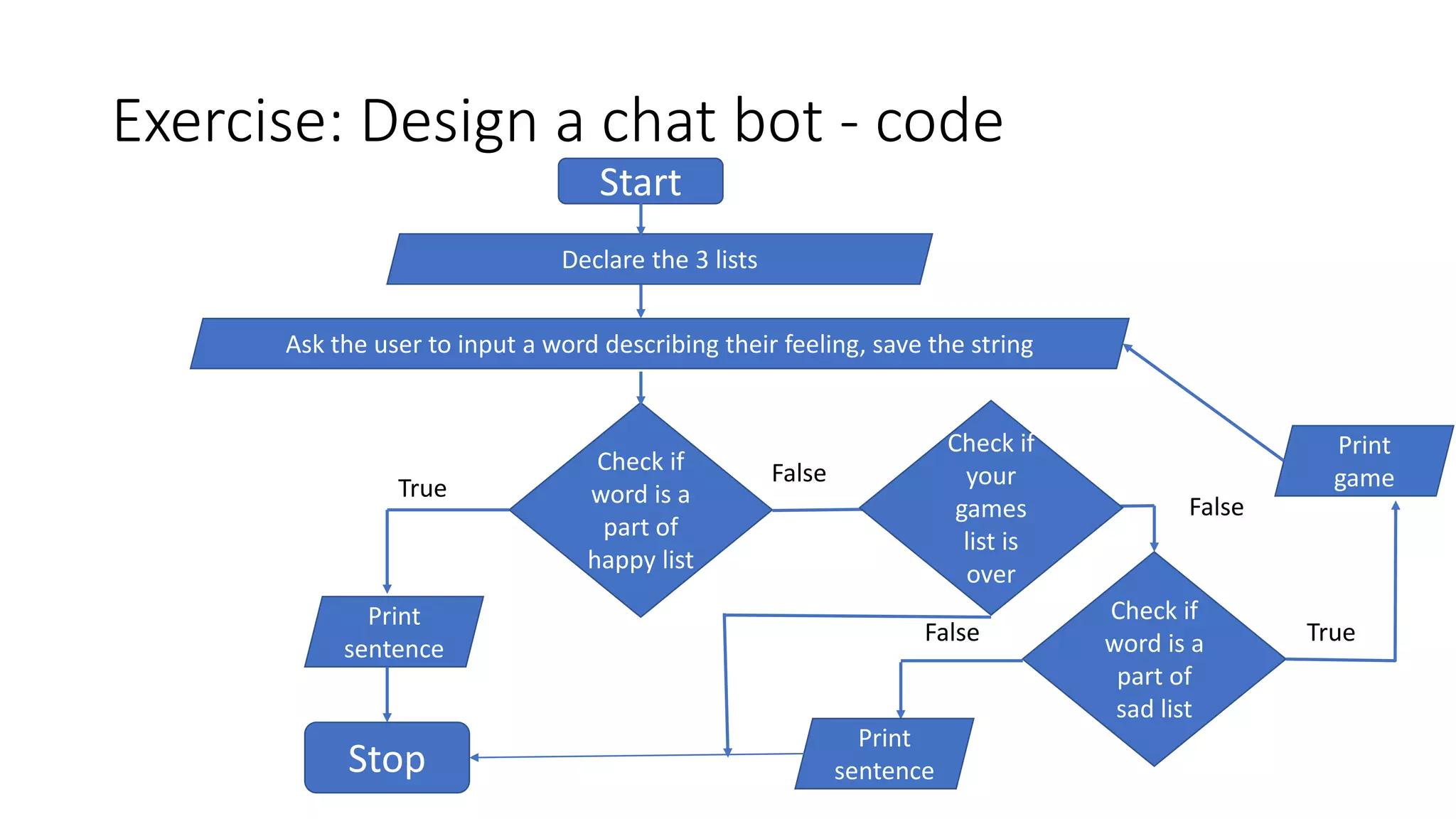
![Exercise: Design a chat bot - flowchart
• list_happy_words = [“joyful”, “happy”, “amazing”, “beautiful”]
• list_sad_words = [“sad”, “tears”, “crying”, “depressed”]
• list_games = [“tetris”, “flappy bird”, “snake”]
• Ask the user to enter a word that describes their feeling
• If the feeling they enter is one of the list_happy_words, print “Glad you are
happy” and exit.
• If the feeling they enter is one of the list_sad_words, ask the user to play
one of the games from the list list_games.
• Ask the user again how they are feeling and continue till the list of games is
exhausted.
• If you already suggested all the games and the user is still unhappy, exit.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pa1flowchart-200807202236/75/Pa1-flow-chart-23-2048.jpg)