Embed presentation
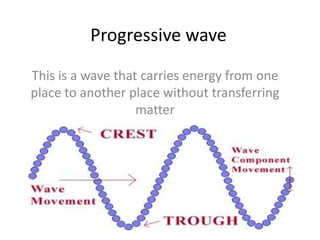

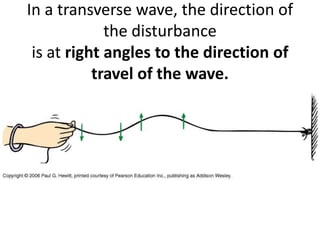
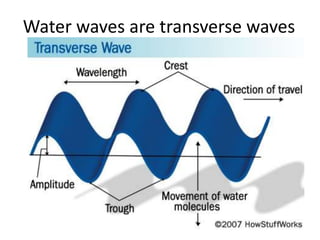
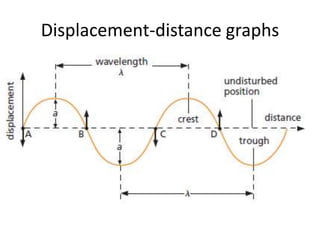

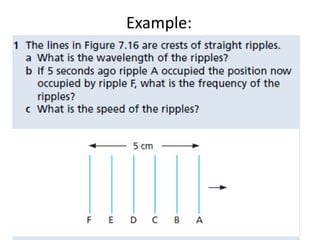
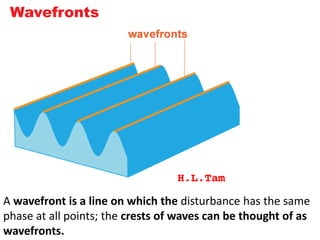
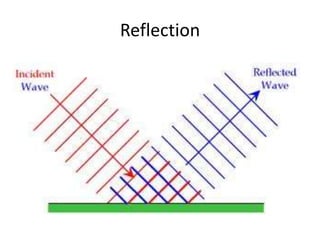
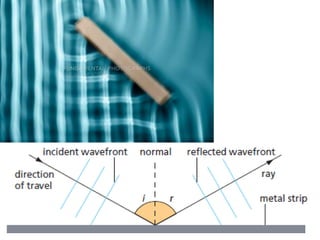
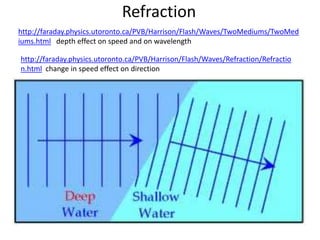

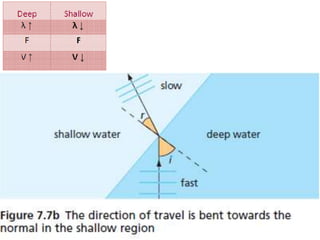
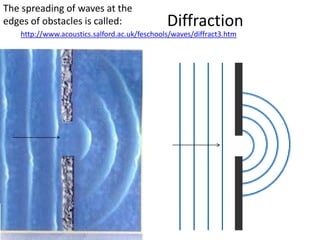
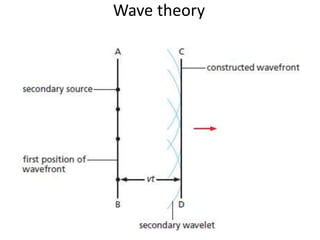
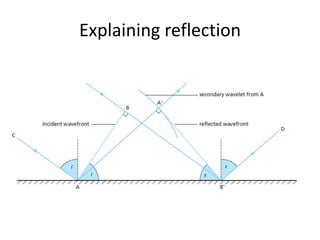
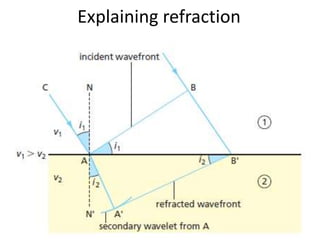
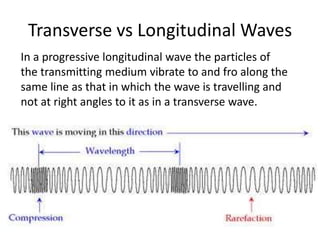
The document discusses various properties of waves including: 1. Progressive waves carry energy from one place to another without transferring matter. Transverse waves have particle disturbance perpendicular to the direction of travel, like water waves. 2. A wavefront is a line where the disturbance is in the same phase, like wave crests. Reflection and refraction occur when waves pass from one medium to another, changing speed and direction. 3. Diffraction is the spreading of waves at obstacles. Wave theory can explain reflection, refraction, and the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves where particles vibrate along or perpendicular to the direction of travel.



















