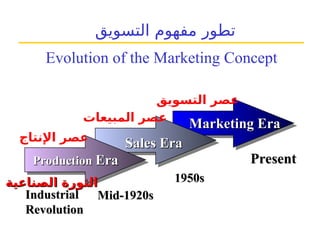
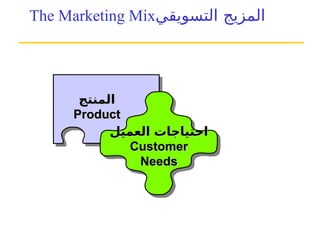
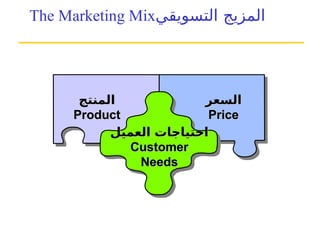
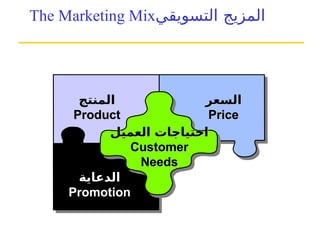
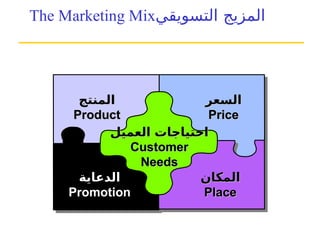
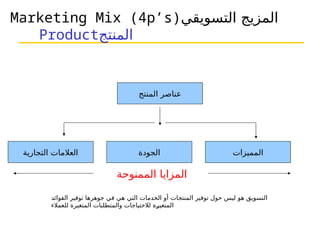
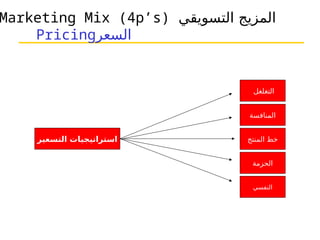
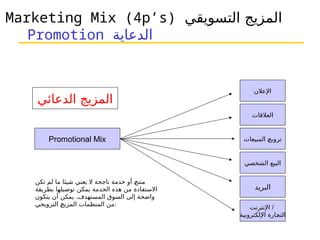
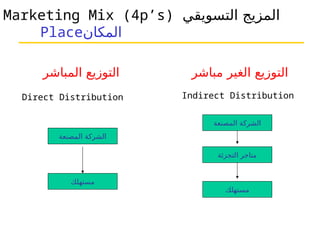
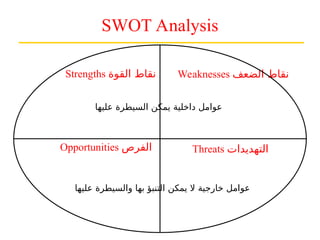
التسويق هو عملية إنشاء وتوزيع وترويج وتسعير السلع والخدمات والأفكار لتسهيل شراكات تبادلية مُرضية في بيئة ديناميكية. يركز التسويق على احتياجات المشتري، بينما يركز البيع على احتياجات البائع. تشمل استراتيجيات التسويق الرئيسية تحديد السوق المستهدف وتطوير مزيج التسويق لتحقيق الأهداف التنظيمية.