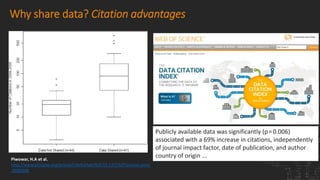
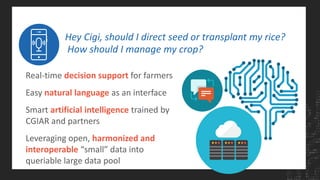
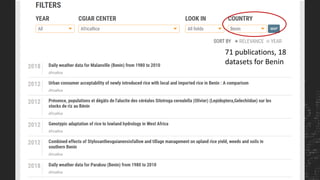
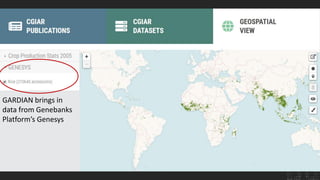
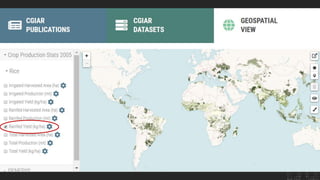
The CGIAR's Big Data Platform aims to leverage data to enhance international agricultural research and decision-making for farmers. It emphasizes data sharing for increased publication impact and promotes the FAIR principles (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) to improve data discoverability and usability. The platform also supports the development of agricultural data standards and community practices for better collaboration and innovation in data-driven research.
![Overview of CGIAR’s Big Data
Platform
Medha Devare
Sr. Research Fellow – IFPRI
[Big Data Platform Module Lead]
Ibnou Dieng
AfricaRice
February 15, 2019](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3bigdatainagriculture-ibnoudieng-190219133042/75/Overview-of-CGIAR-s-Big-Data-Platform-1-2048.jpg)