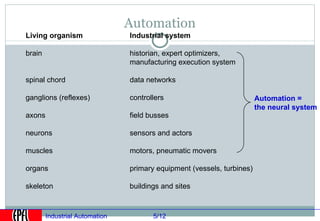
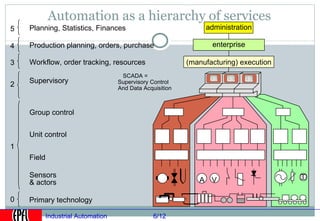
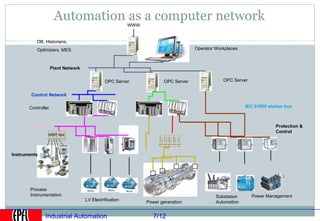
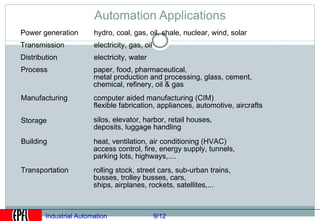
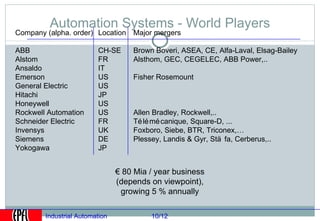
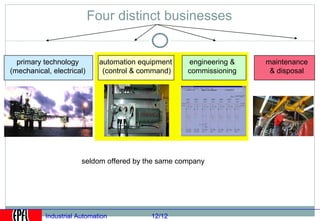
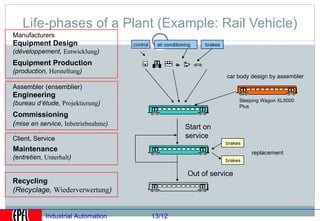
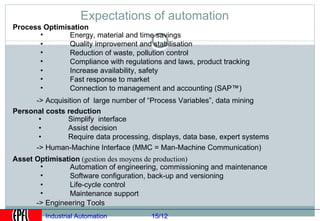
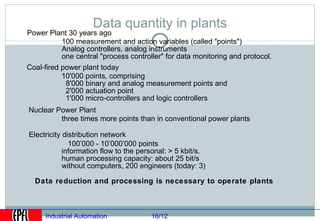
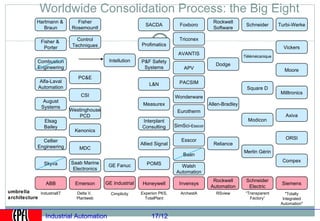
Industrial automation involves replacing human labor with machines and technology in industrial processes and manufacturing. It allows for increased efficiency, precision, and safety. Key aspects of industrial automation include open and closed loop control systems, continuous and discrete manufacturing processes, and hierarchical control architectures. Automation is widely used across various industries like power generation, manufacturing, storage and transportation to optimize processes, reduce costs, and improve quality and safety. The data needs of automated plants have grown enormously, requiring advanced computing and networking capabilities to manage all process variables.