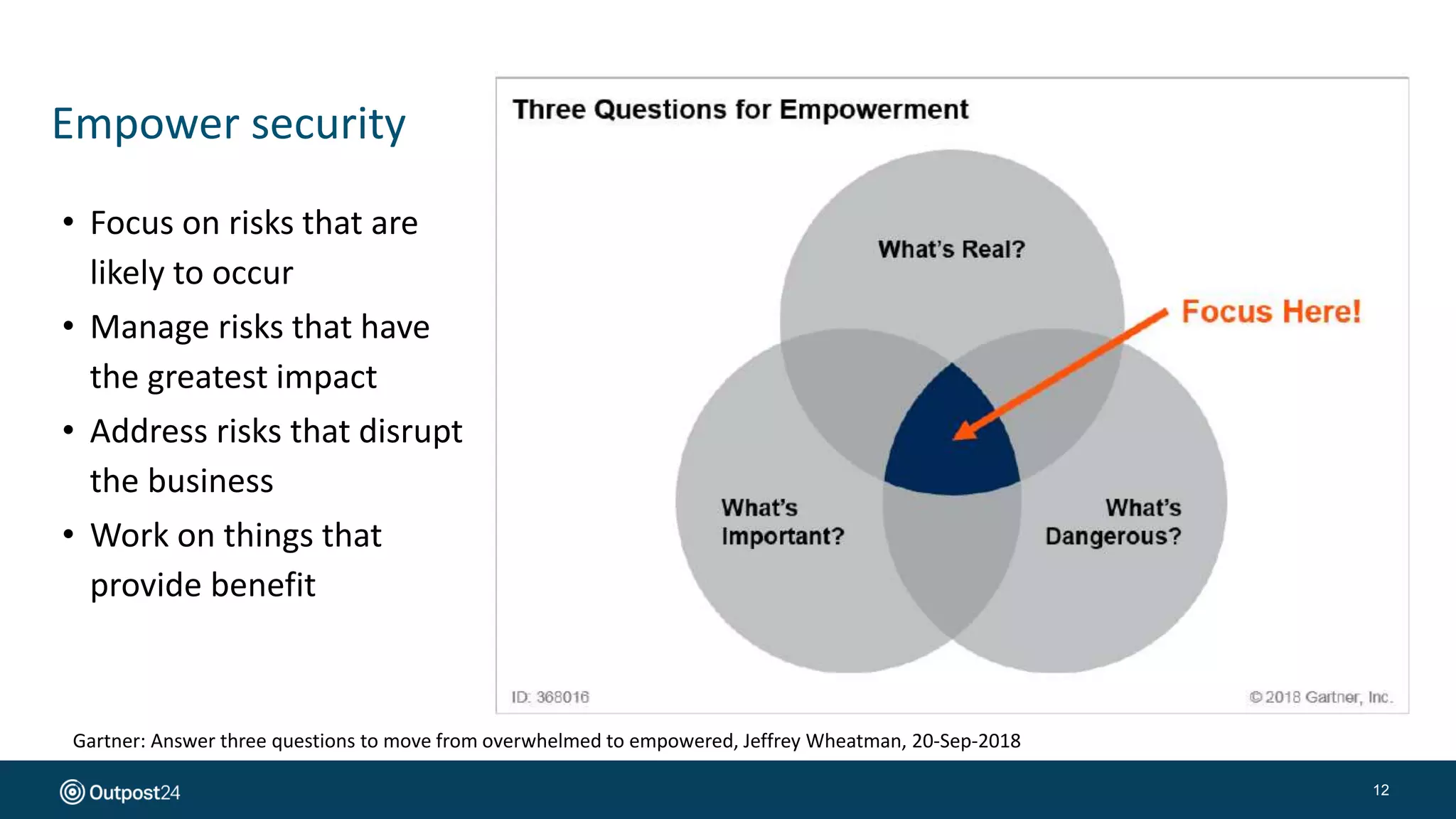
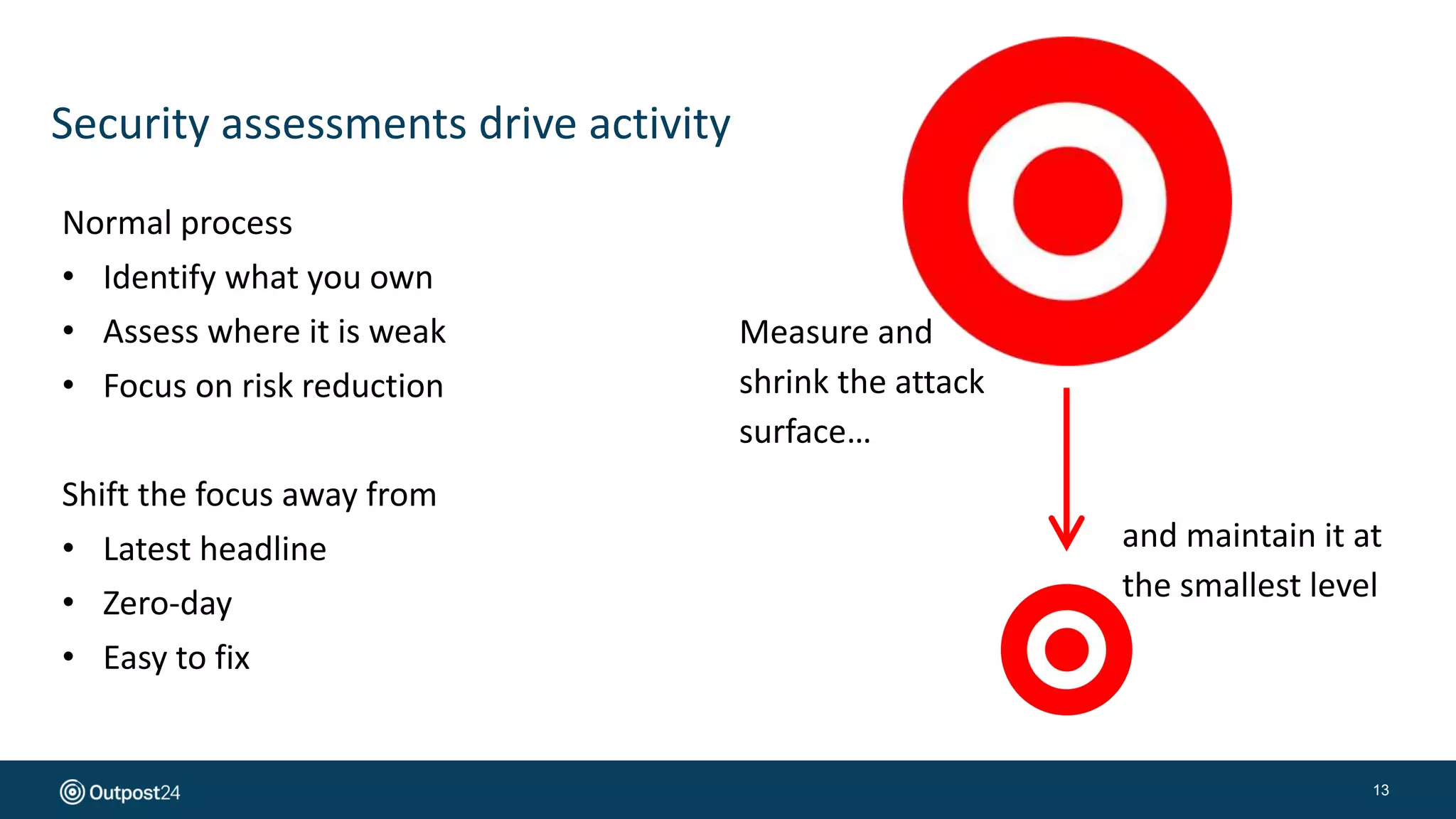
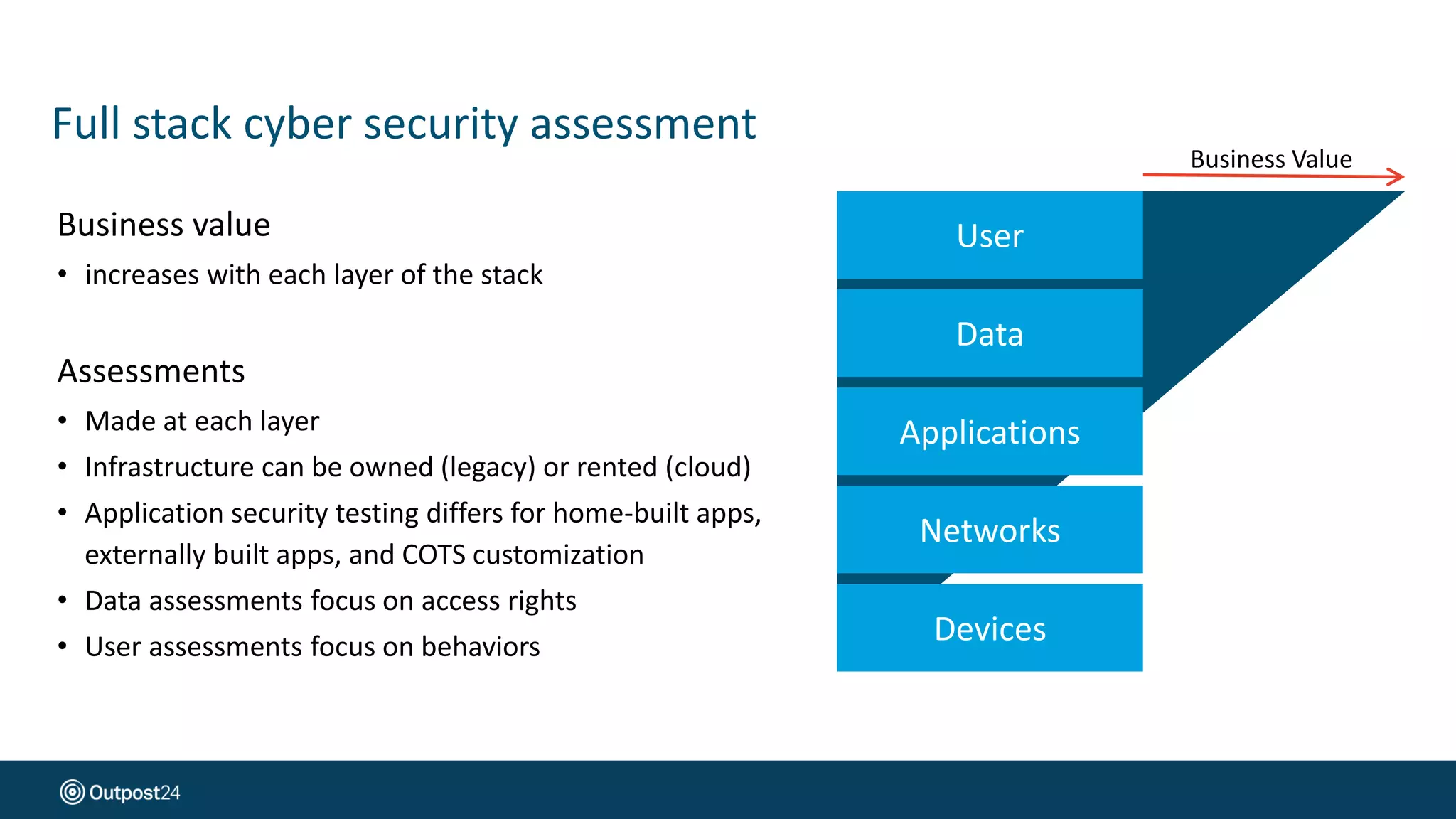
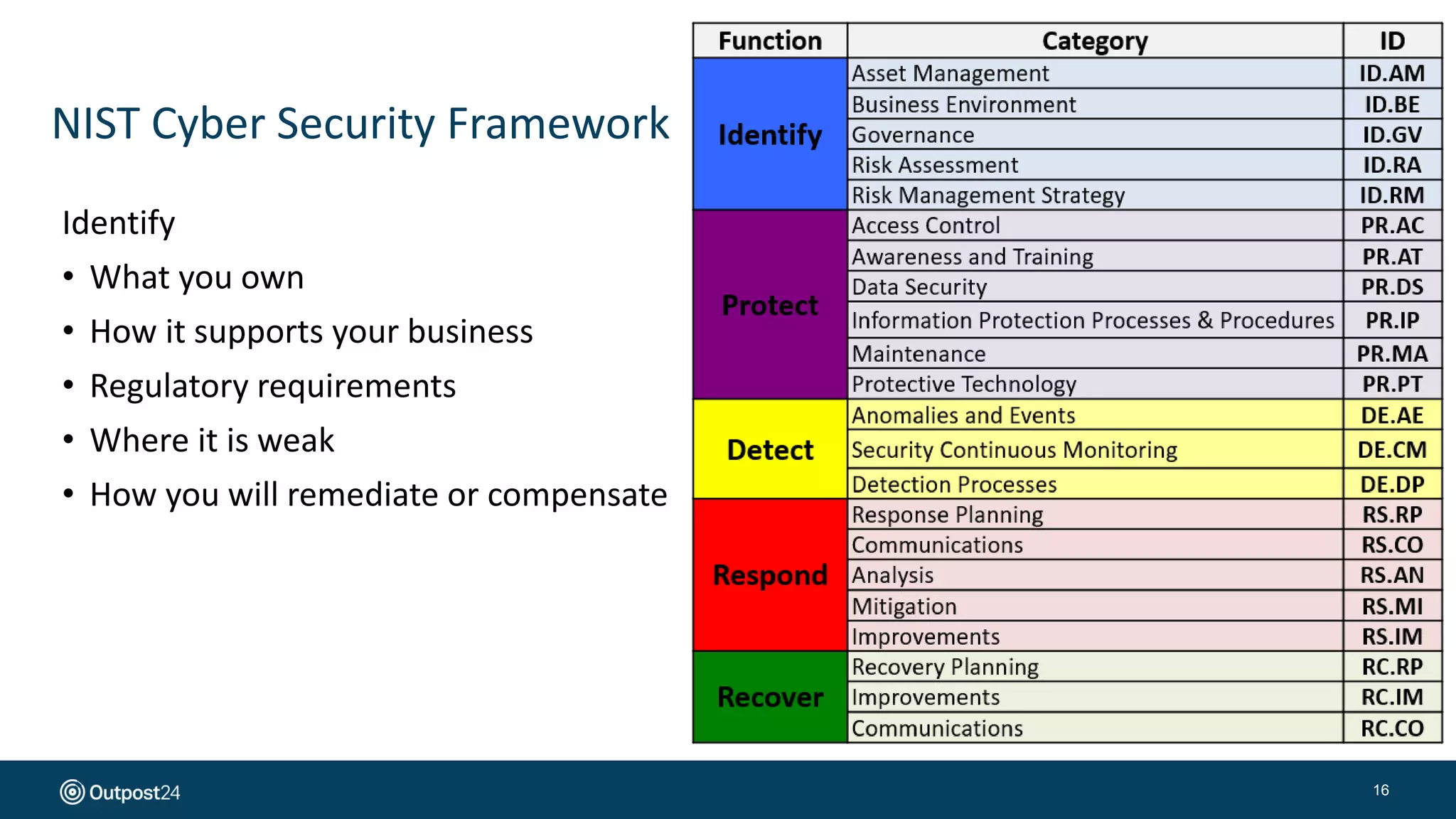
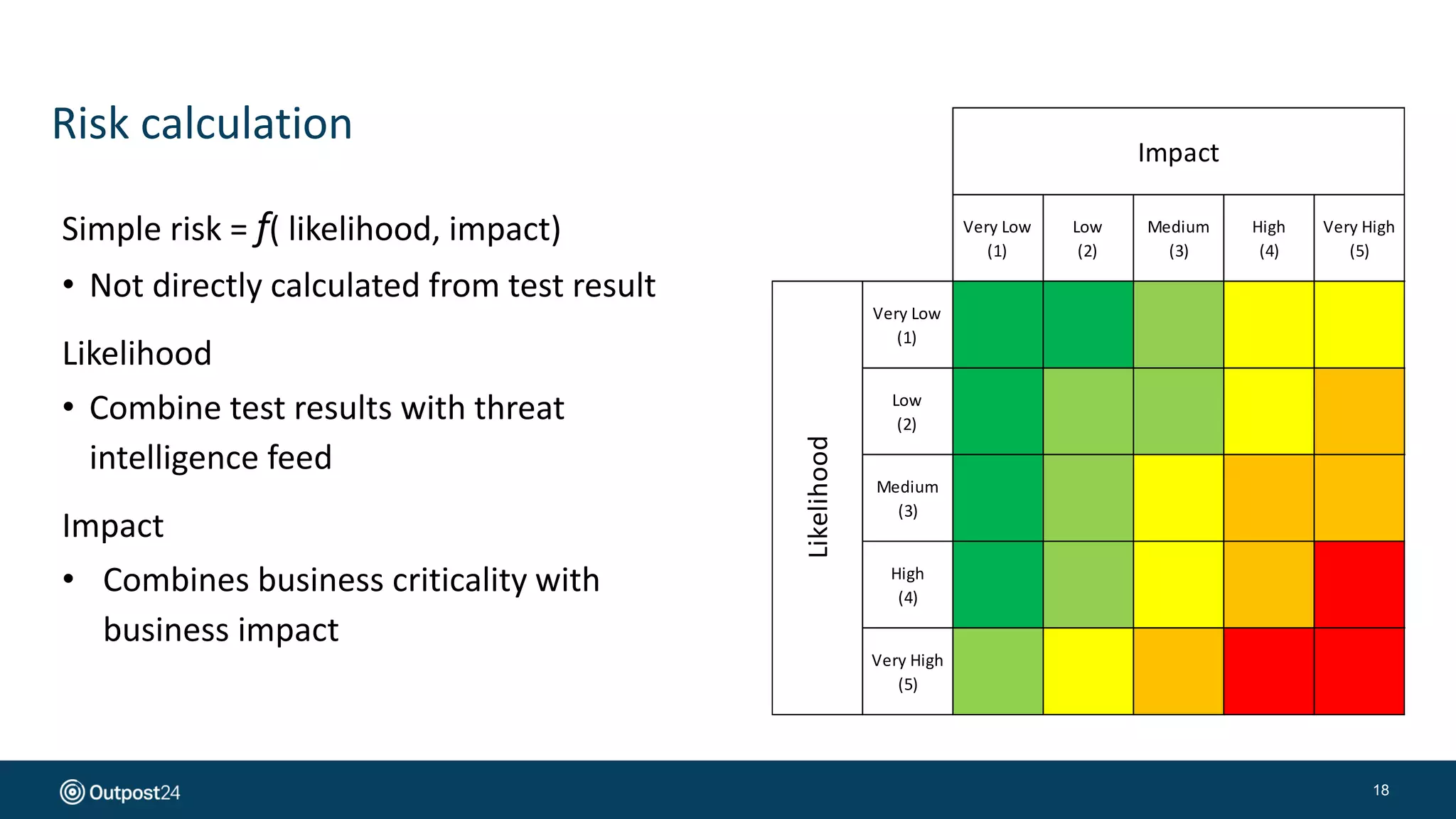
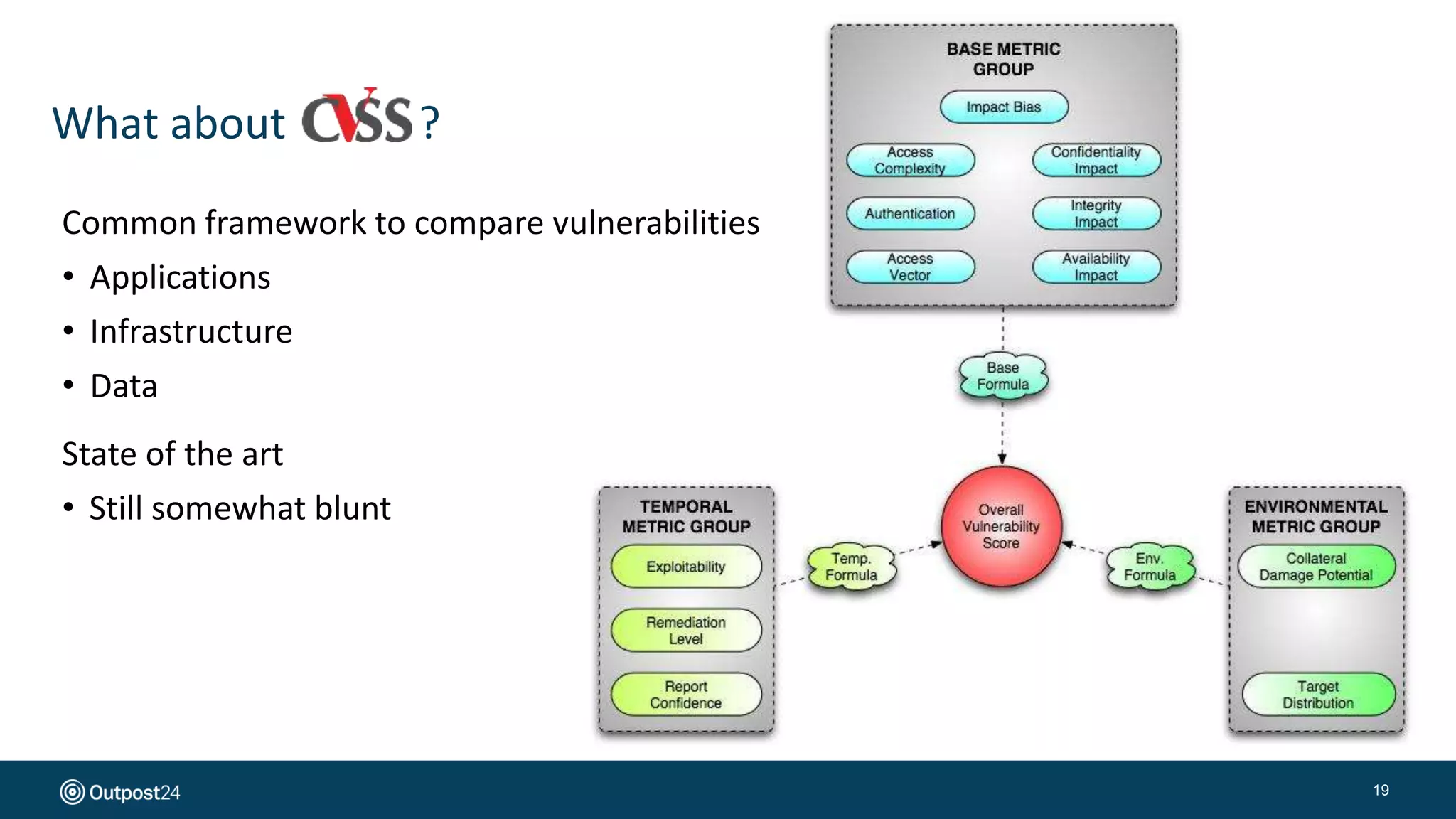
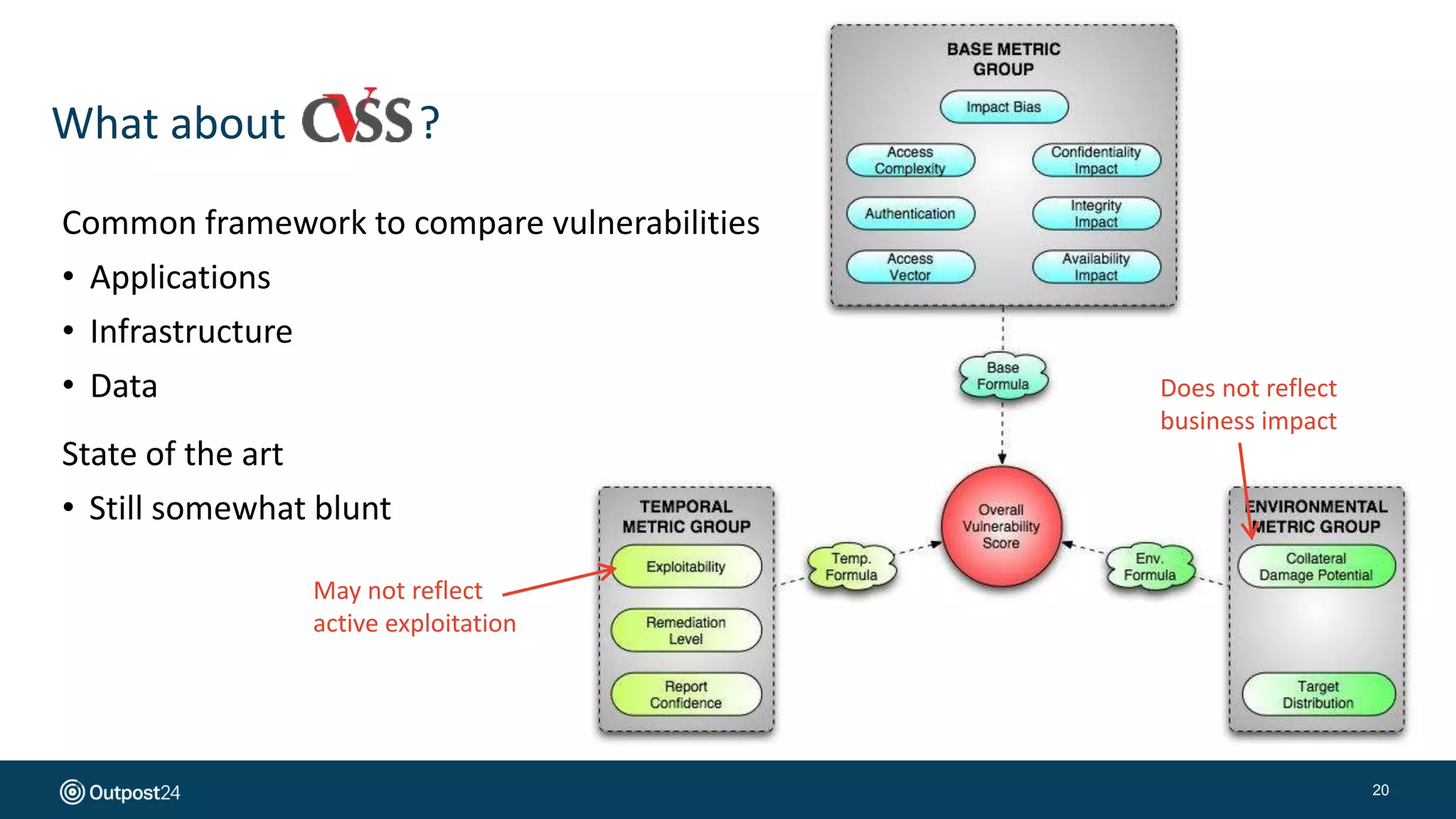
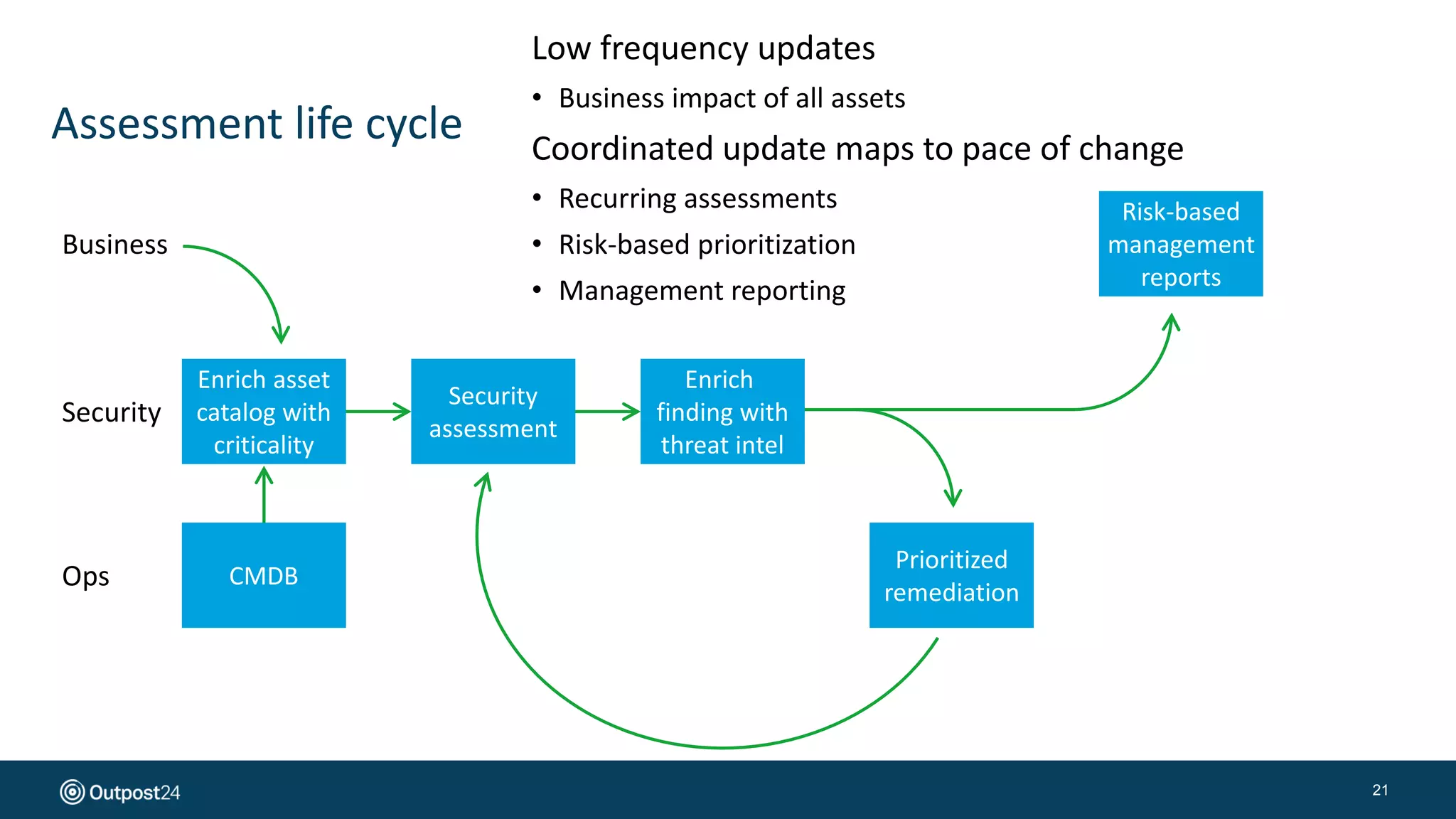
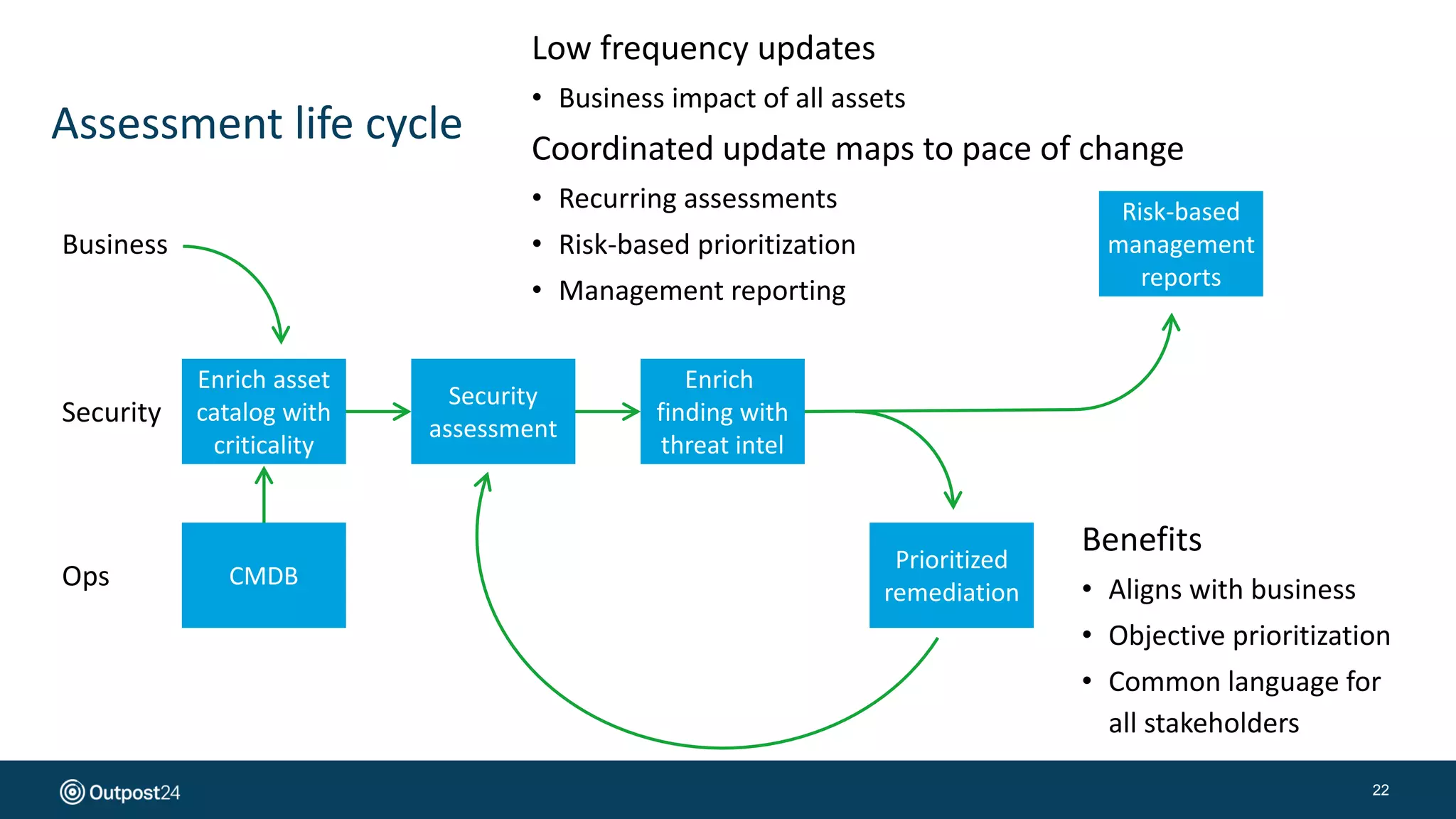
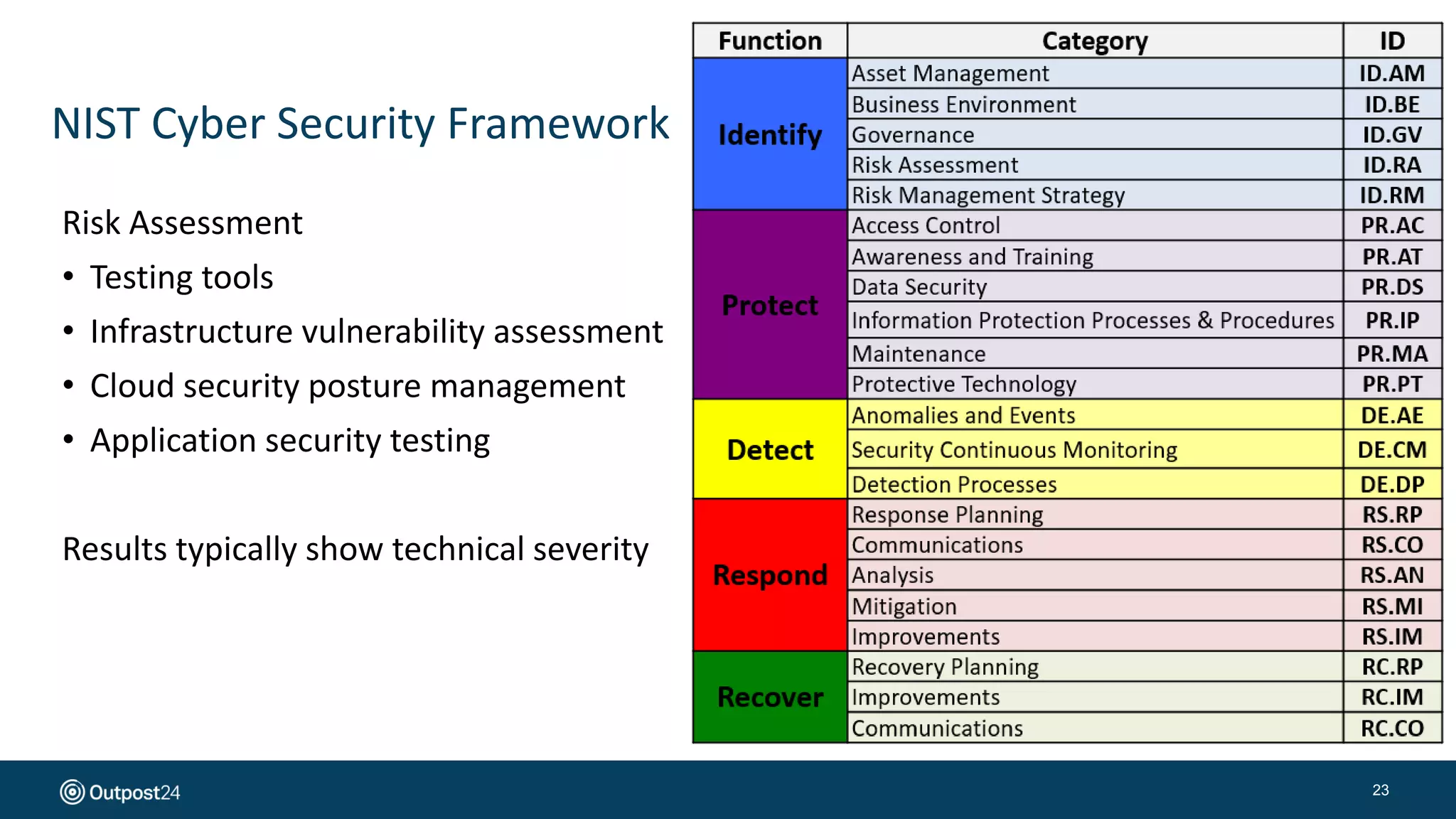
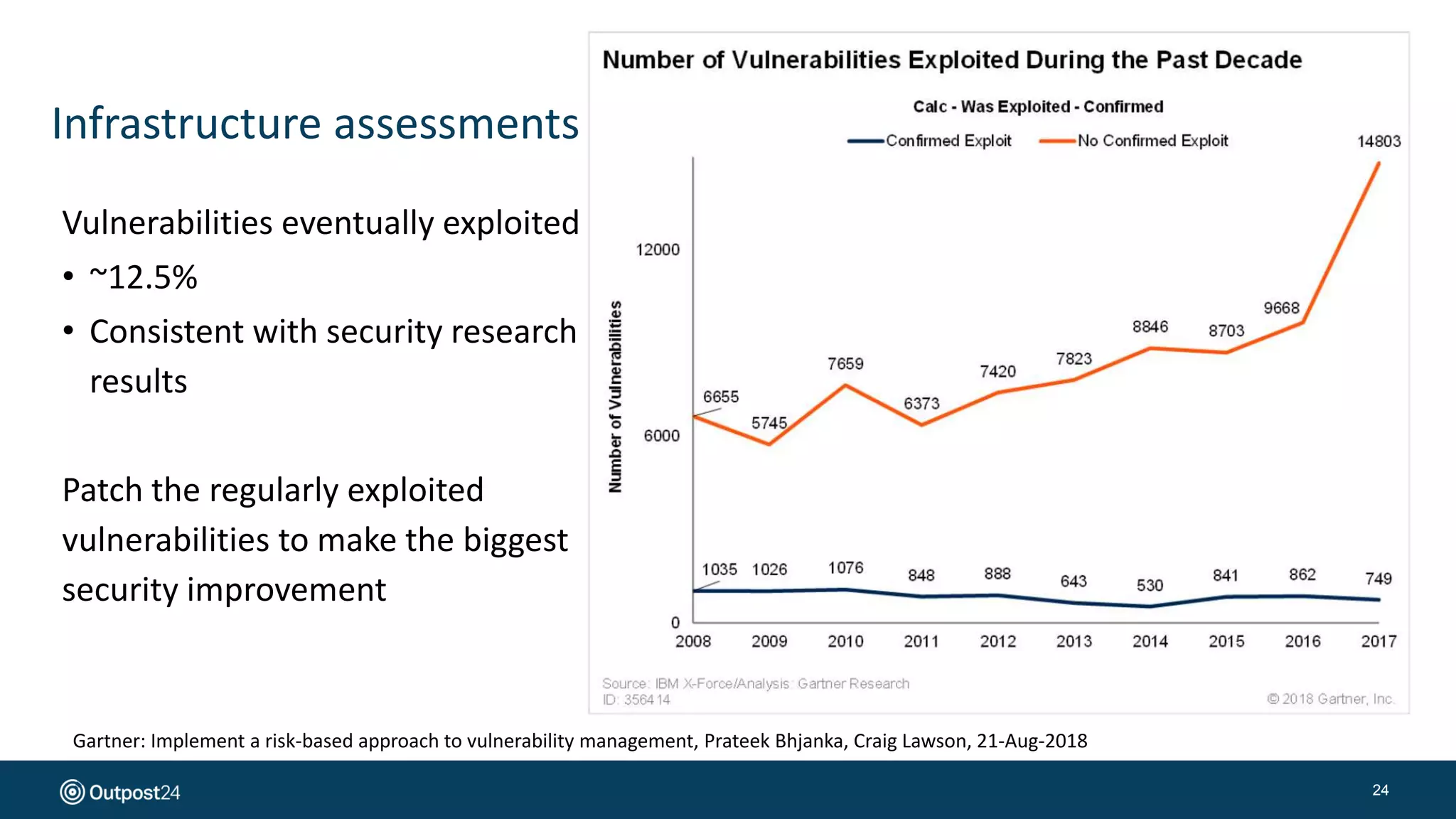
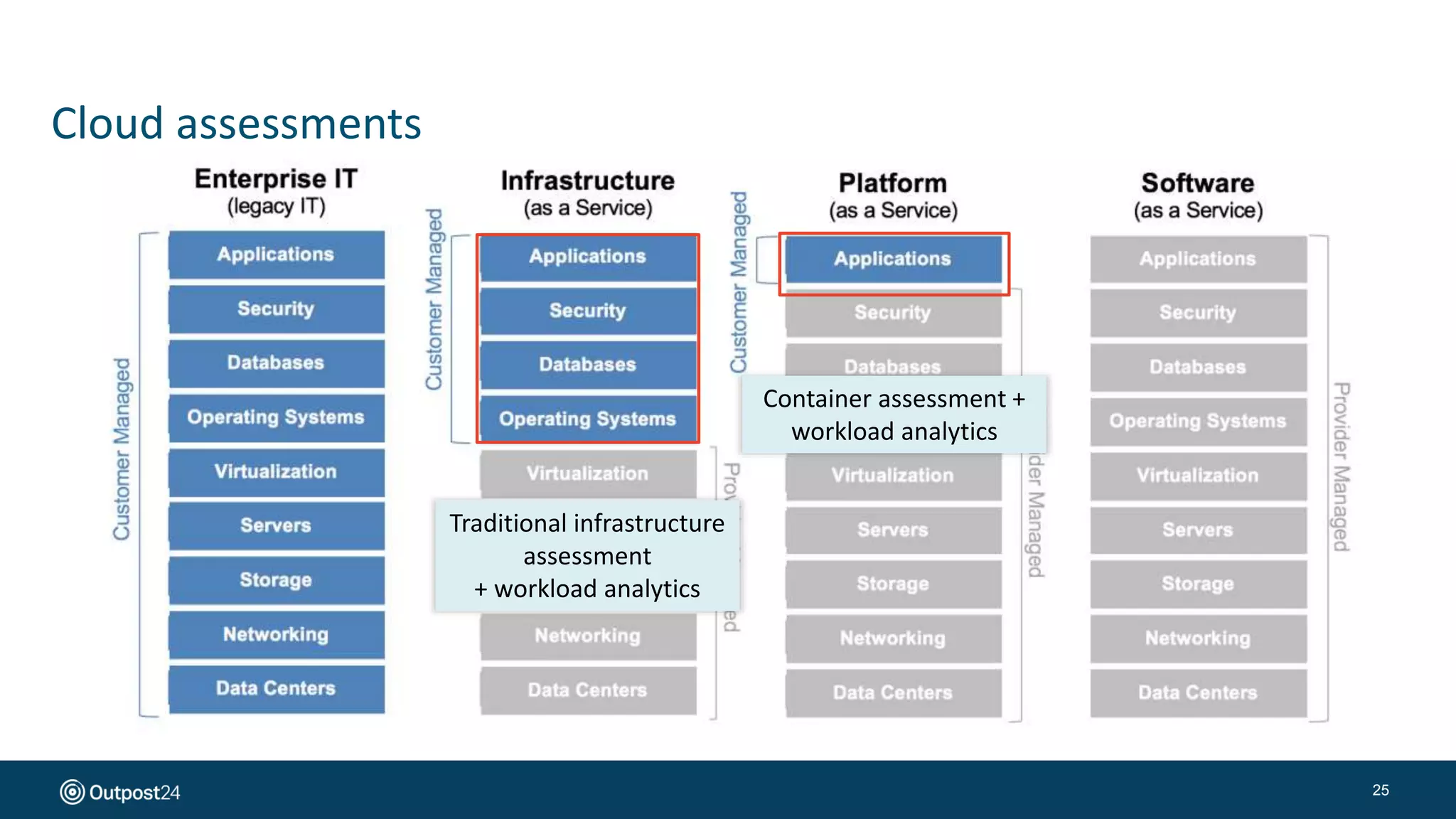
The document presents a risk-based approach to cyber security assessments, emphasizing the need to prioritize and manage risks effectively. It discusses various vulnerabilities across infrastructure, applications, and data, advocating for a comprehensive evaluation that aligns with business objectives. The document concludes with the importance of ongoing assessments and maintaining a minimized attack surface to enhance overall security posture.