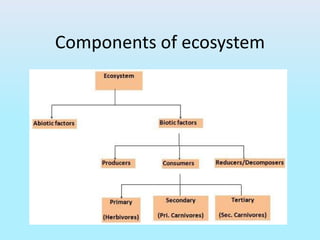
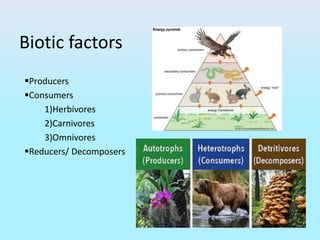
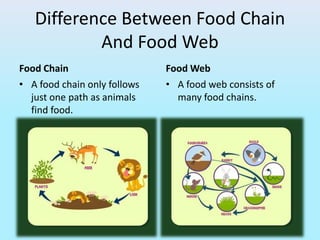
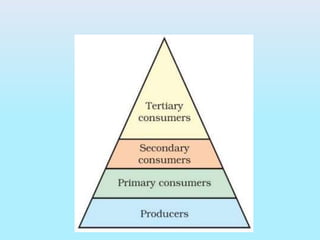
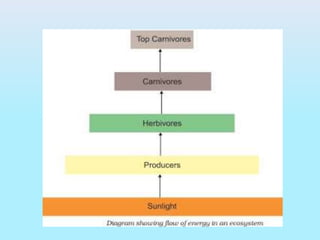
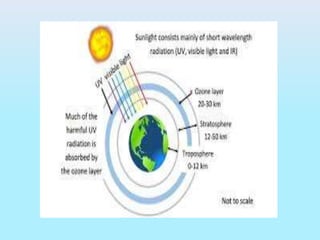
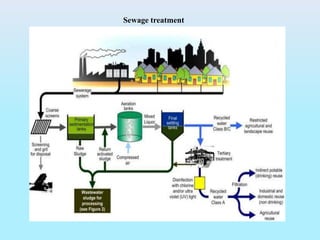
The document provides an overview of ecosystems, explaining their components, types, and the relationships between organisms through food chains and food webs. It covers the distinction between biotic and abiotic factors, describes trophic levels, and discusses energy flow, highlighting the 10% energy transfer rule. Additionally, it addresses environmental concerns like ozone layer depletion and garbage management strategies.