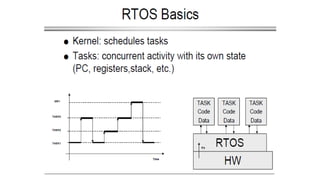
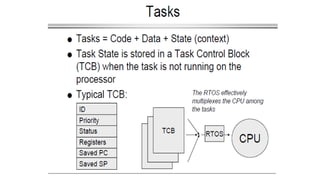
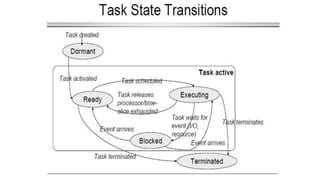
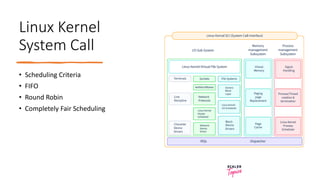
This document discusses criteria for CPU scheduling and optimization in operating systems. It covers metrics like CPU utilization, throughput, turnaround time, and waiting time. The key goals of optimization are to maximize CPU usage and throughput while minimizing times. Real-time requirements can be soft or hard, with hard deadlines requiring failure prevention. Real-time kernels provide benefits like abstraction of timing, modularity, and improved efficiency. Linux uses scheduling algorithms like FIFO, round robin, and completely fair scheduling to optimize these metrics.