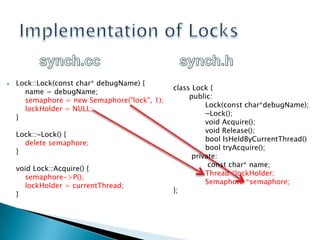
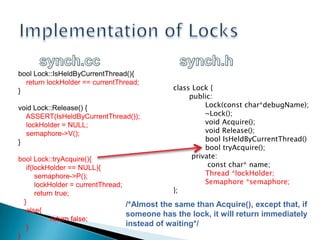
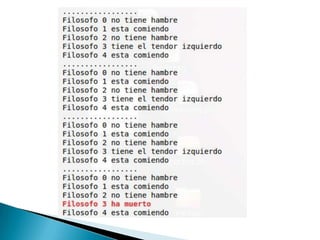
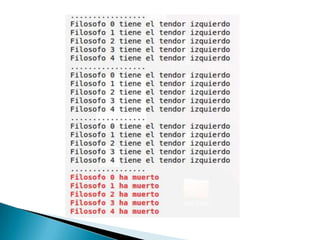
The document describes the implementation of locks and conditions variables in an operating system project. It includes code for a Lock class that uses a semaphore to synchronize access with its Acquire and Release methods. It also includes code for a Condition class that allows threads to wait on and signal conditions, managing a wait queue of semaphores. The document concludes by briefly explaining the dining philosophers problem in concurrent programming and some potential solutions like using tokens to establish turns.