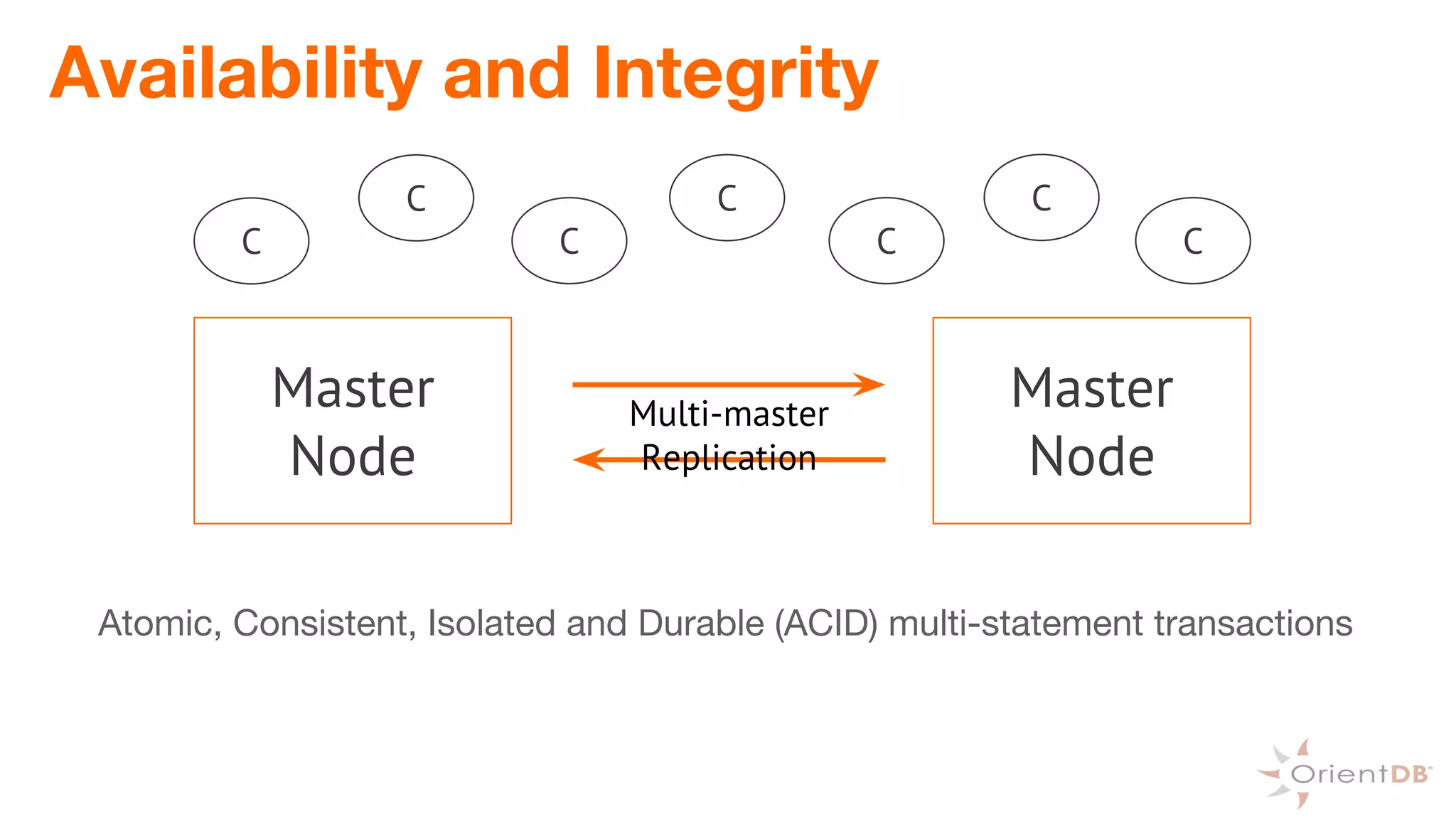
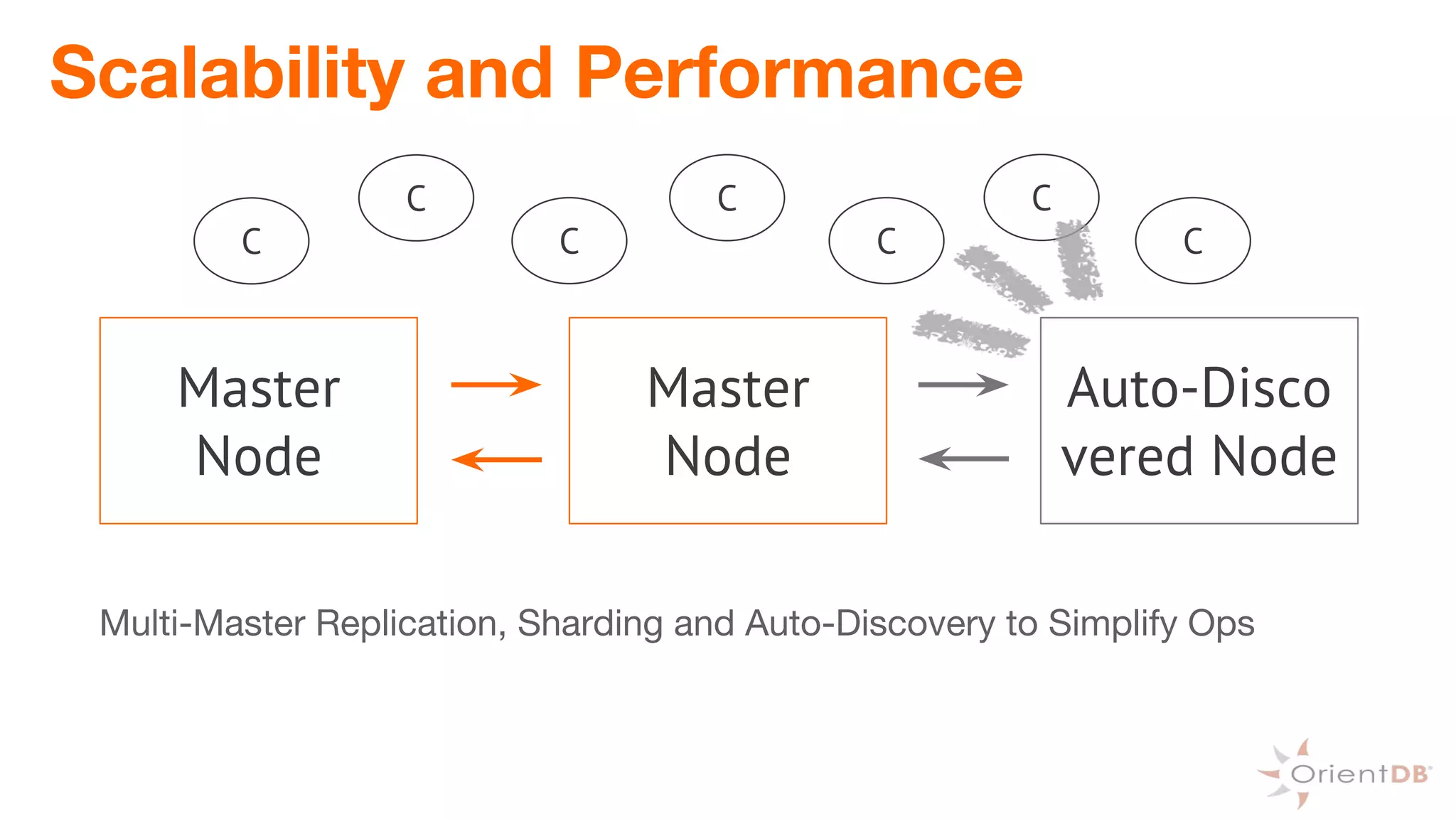
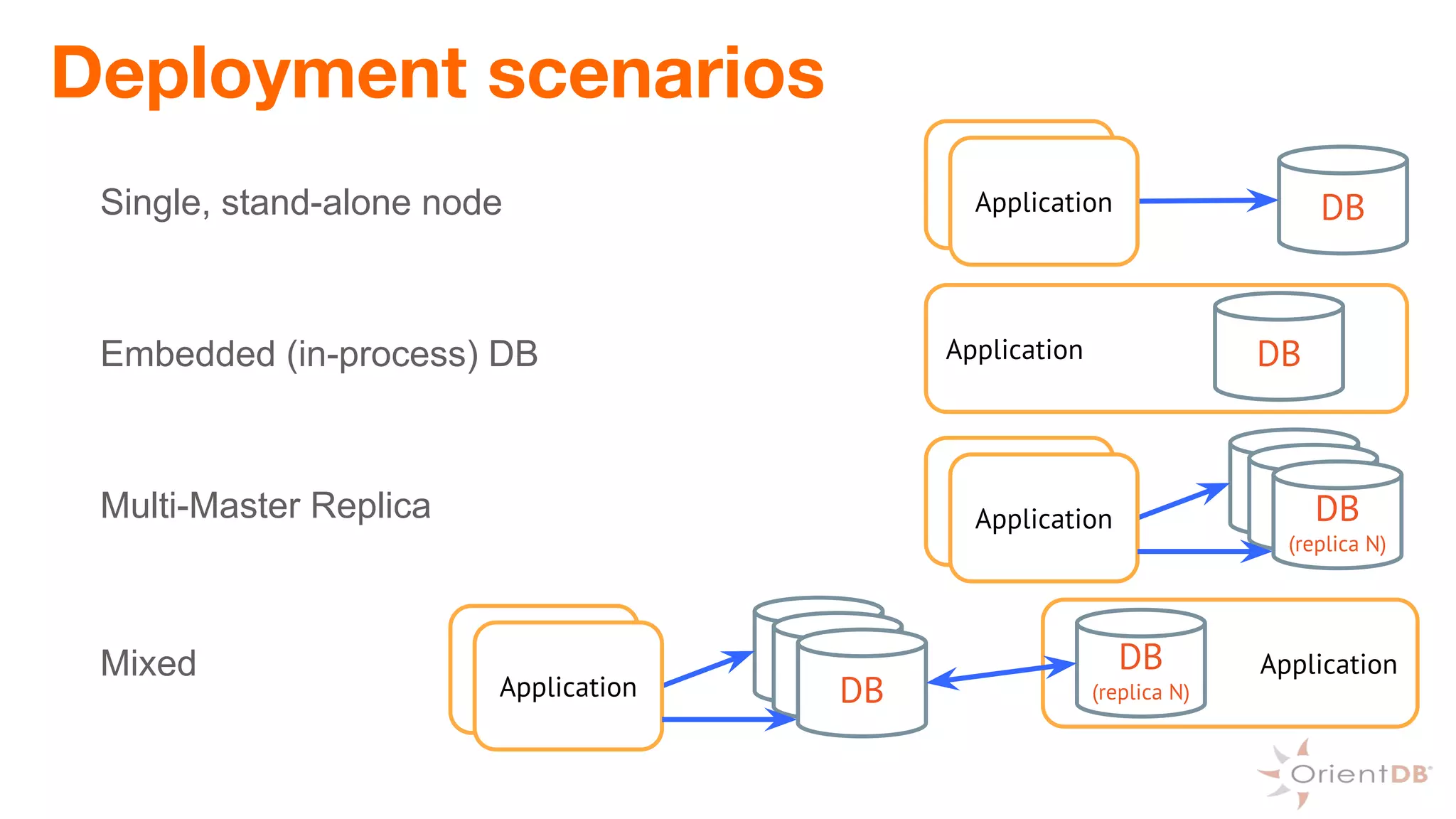
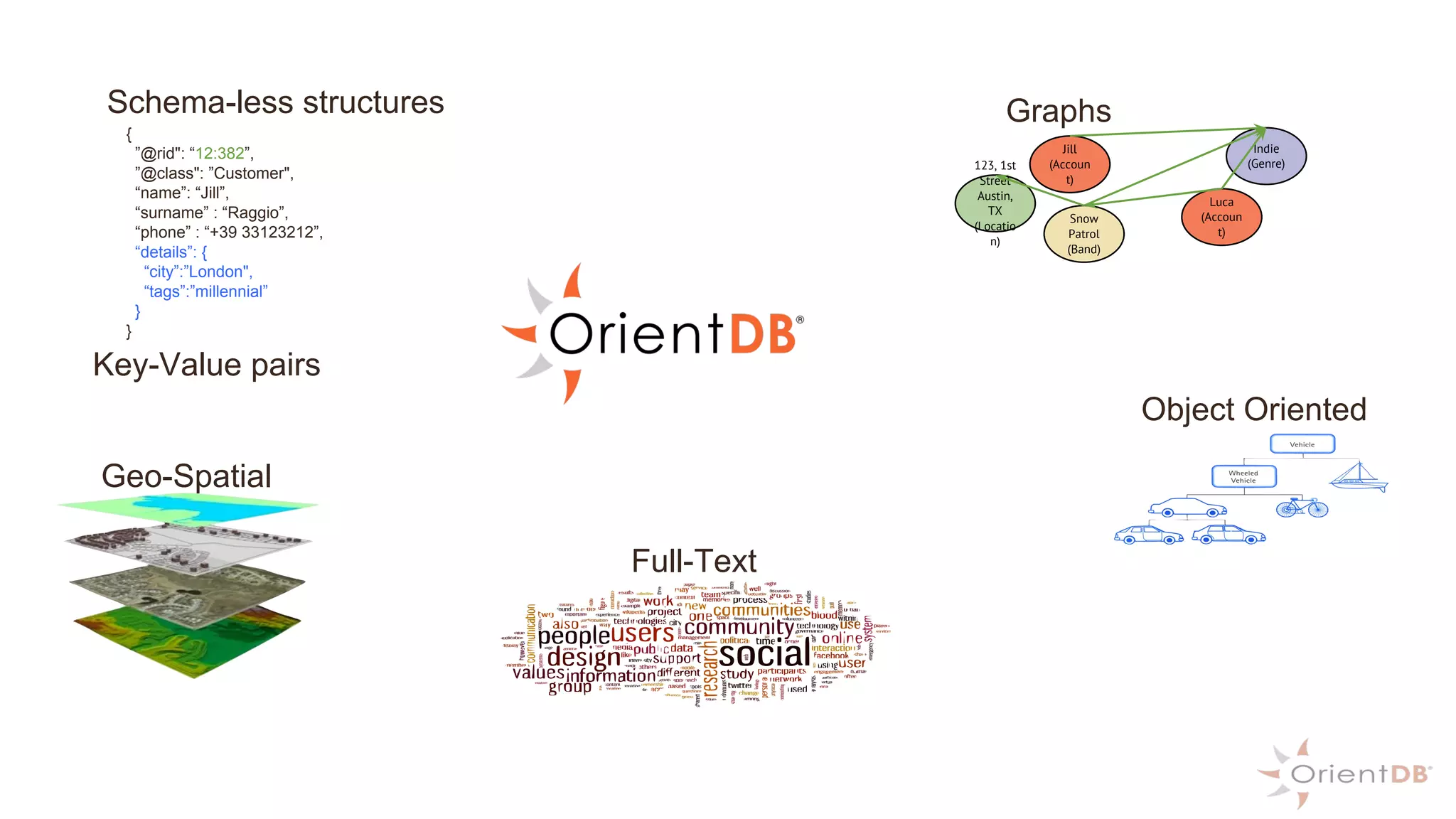
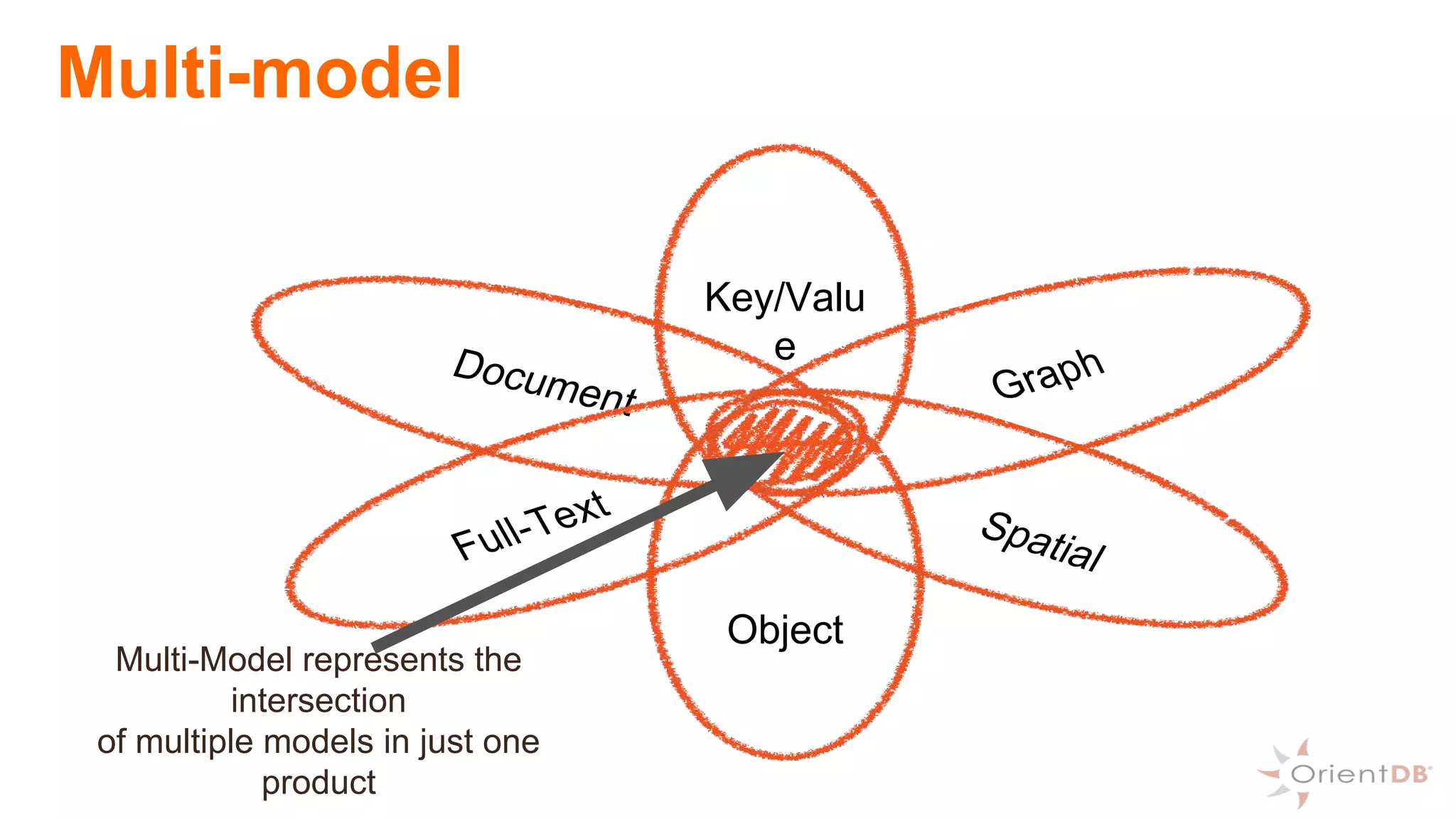
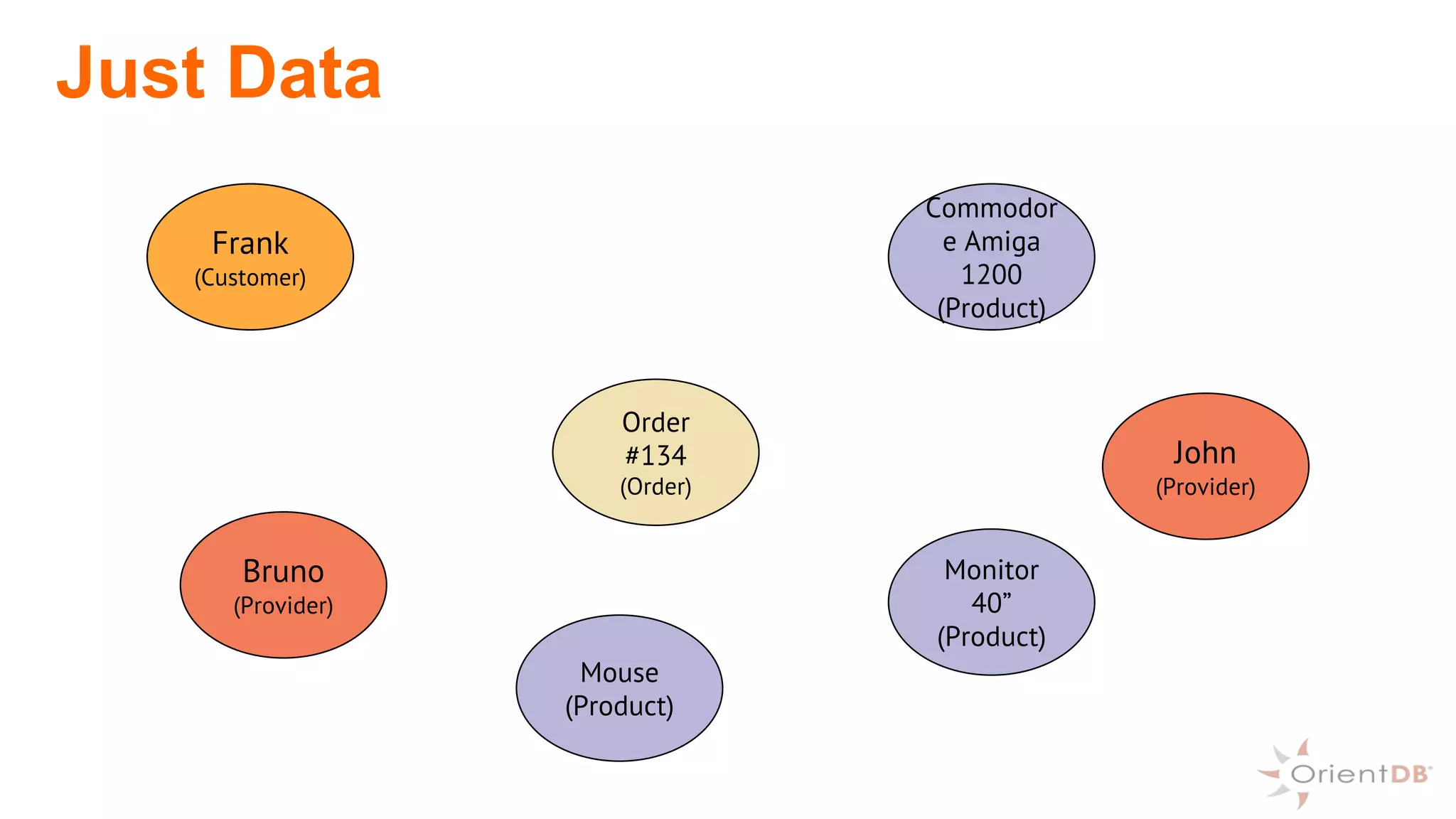
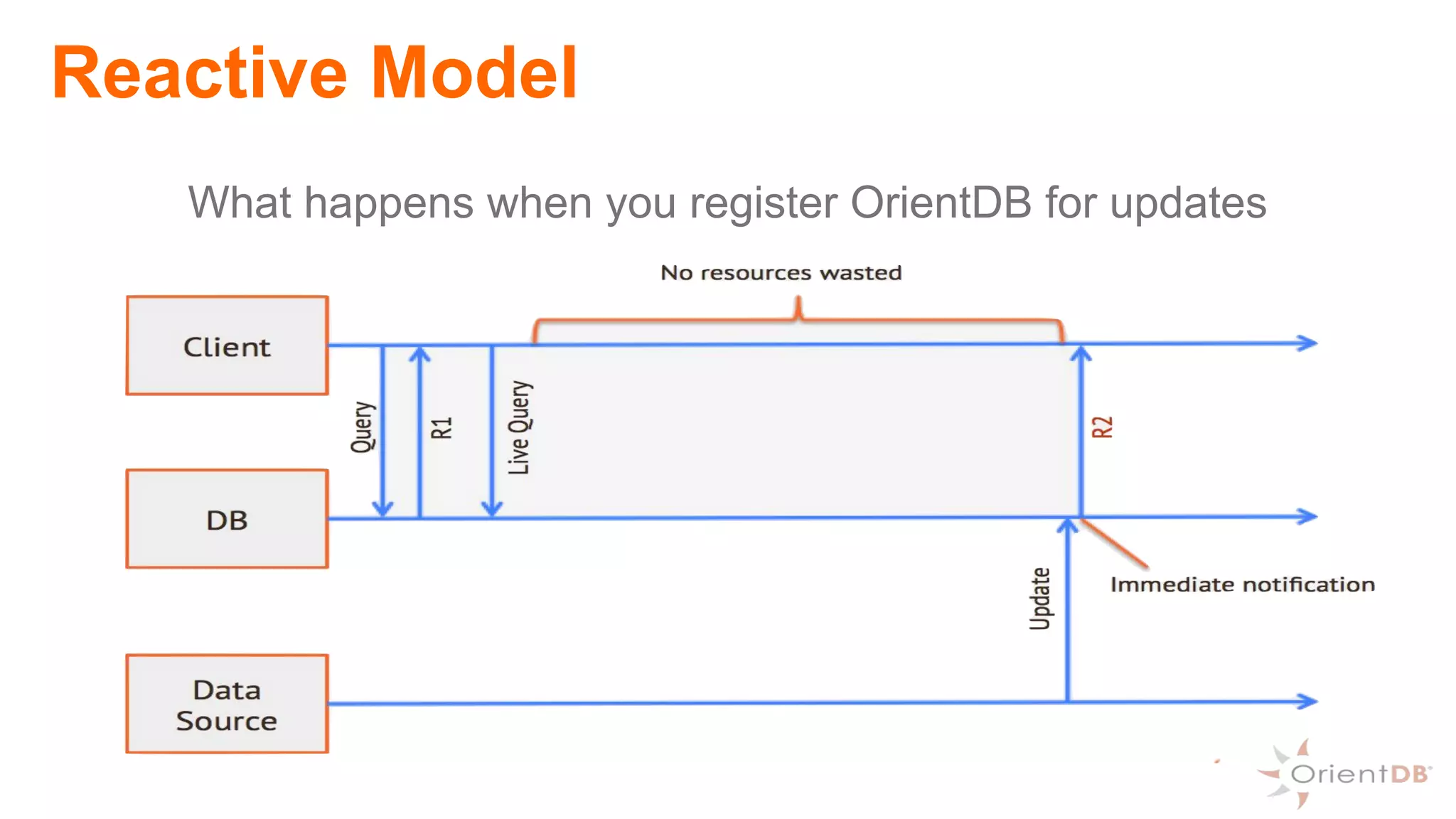
This document provides an overview of OrientDB, a multi-model database that combines features of document, graph, and other databases. It discusses data modeling and schema, querying and traversing graph data, full-text and spatial search, deployment scenarios, and APIs. Examples show creating classes and properties, inserting and querying graph data, and live reactive queries in OrientDB.
















![Multi-field search
CREATE CLASS City EXTENDS V
CREATE PROPERTY City.name STRING
CREATE PROPERTY City.description STRING
CREATE PROPERTY City.size INTEGER
CREATE INDEX City.name_description_size
ON City(name, description,size) FULLTEXT ENGINE LUCENE METADATA {...}
SELECT FROM City
WHERE
SEARCH_CLASS ("name:cas* AND description:piemonte AND size:[20000 TO 40000]" = true](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatameetupto20170405-170405185655/75/OrientDB-The-2nd-generation-of-multi-model-NoSQL-36-2048.jpg)
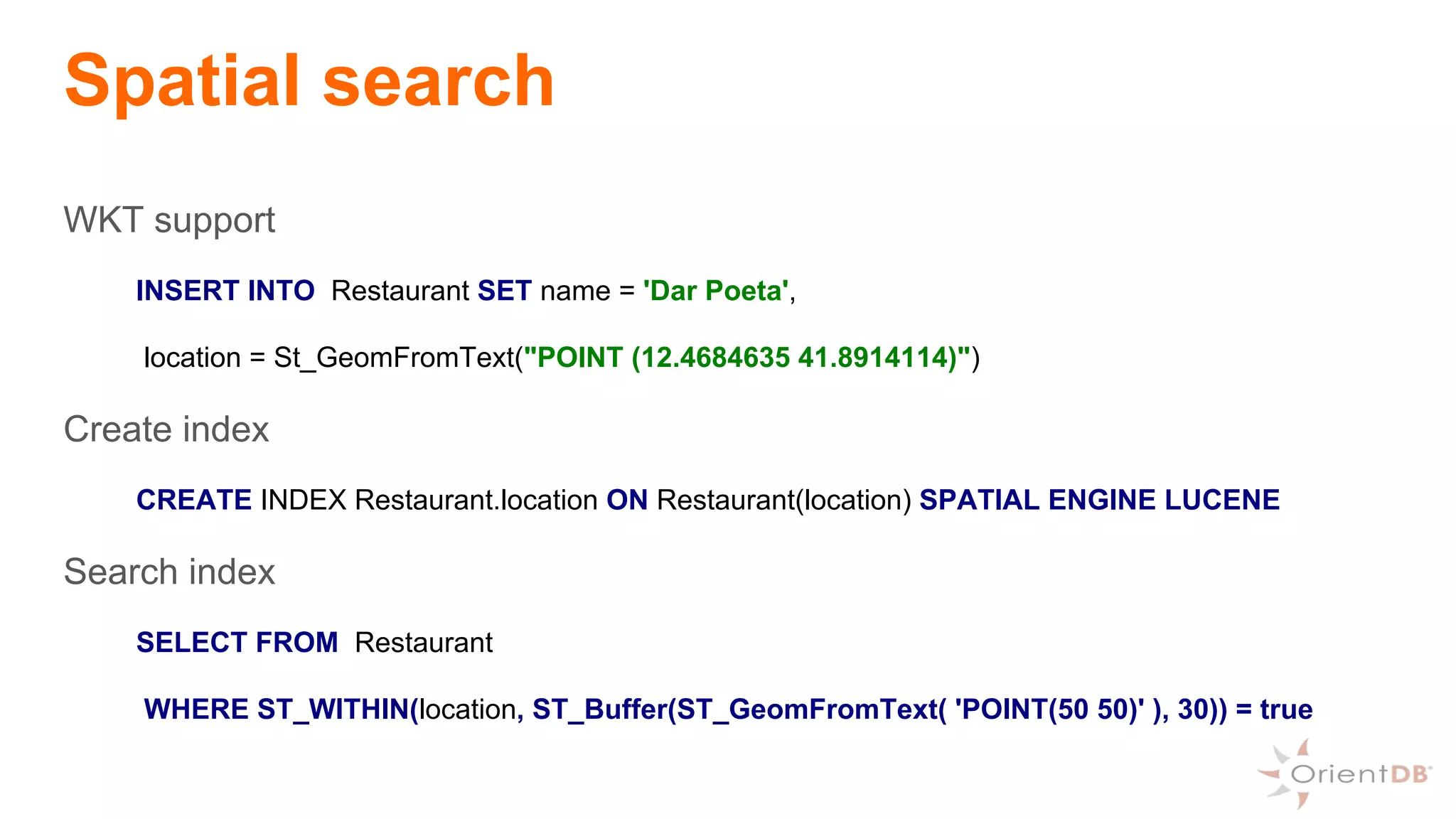
![Spatial search
Add location
CREATE class Restaurant
CREATE PROPERTY Restaurant.name STRING
CREATE PROPERTY Restaurant.location EMBEDDED OPoint
Insert
INSERT INTO Restaurant SET name = 'Dar Poeta',
location = {"@class": "OPoint","coordinates" : [12.4684635,41.8914114]}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatameetupto20170405-170405185655/75/OrientDB-The-2nd-generation-of-multi-model-NoSQL-38-2048.jpg)

![Java
orientDB = new OrientDB("remote:localhost", "root", "root", OrientDBConfig.defaultConfig());
pool = new ODatabasePool(orientDB, "demodb", "admin", "admin");
db = pool.acquire();
OResultSet result = db.query(
"SELECT from ArchaeologicalSites where search_fields(['Name'],'foro') = true");
result.vertexStream() .forEach(v-> System.out.println("v = " + v.toJSON()));
db.close();
pool.close();
orientDB.close();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdatameetupto20170405-170405185655/75/OrientDB-The-2nd-generation-of-multi-model-NoSQL-41-2048.jpg)