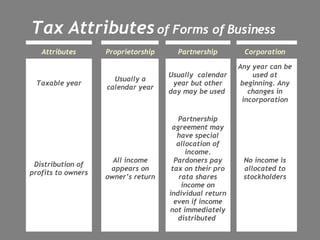
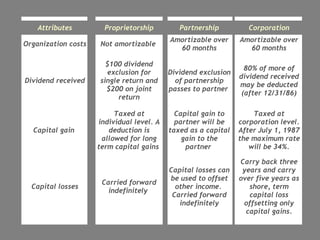
This document discusses organizational plans and forming a business entity. It outlines key aspects of an organizational plan including setting priorities, tasks, responsibilities, and goals. It then discusses different forms of business structure like proprietorship, partnership, and corporation. For each, it outlines factors such as costs, continuity, control, and tax implications. It also discusses building a management team, job descriptions, and the role and selection of a board of directors.