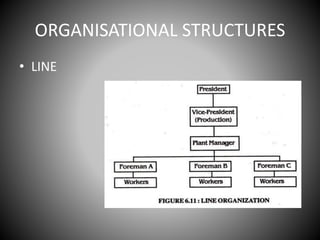
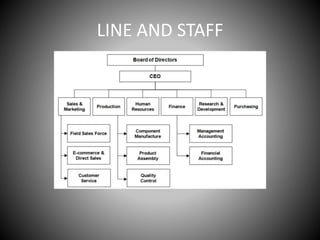
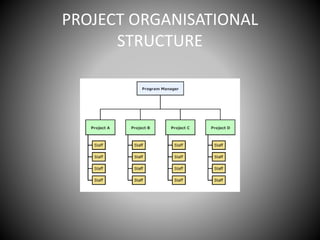
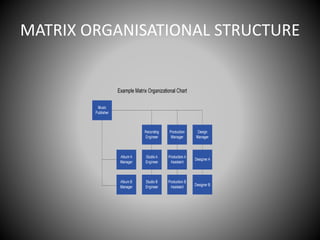
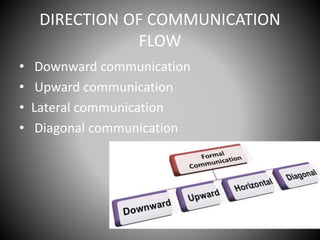
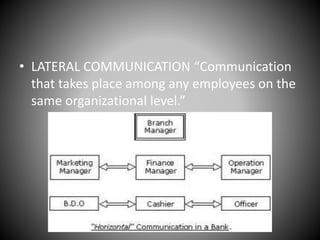
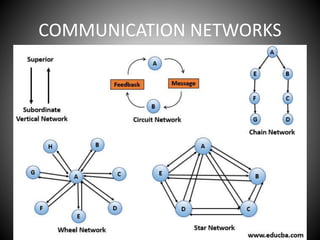
This document provides an overview of organizational communication. It defines key terms like organization, communication, and organizational communication. It discusses the nature of organizations including concepts like division of labor. It also covers organizational design, structures, communication networks and flows. The document outlines different barriers to communication like physical, cultural, language, organizational and perceptual barriers. It provides examples and ways to overcome each type of barrier.