Embed presentation
Download to read offline


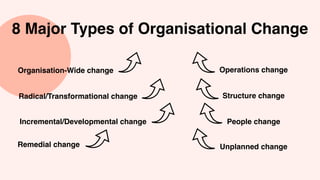


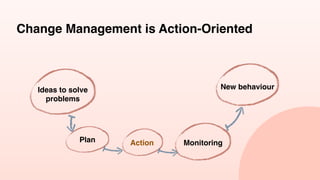


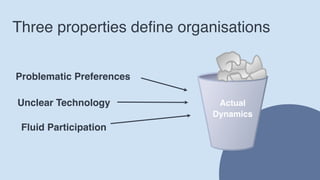
The document discusses the necessity of organizational change to adapt to environmental contingencies and maintain alignment. It outlines eight types of organizational change and emphasizes the importance of change management, which is often action-oriented despite a high failure rate of 70%. Additionally, it highlights the common pitfalls in managing change, particularly the neglect of the human element and an over-reliance on performance metrics.









