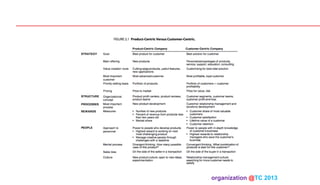
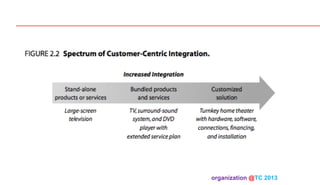
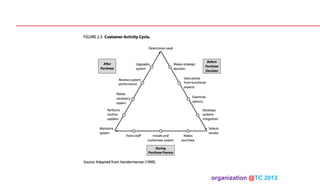
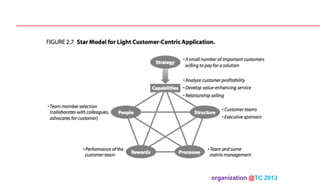
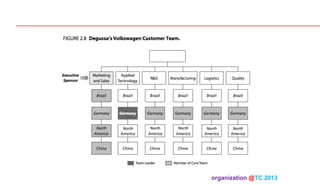
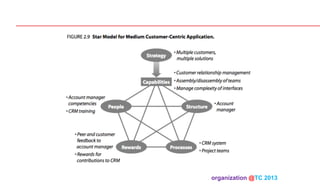
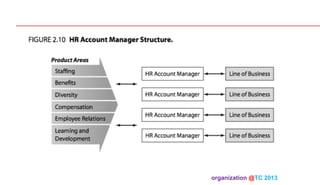
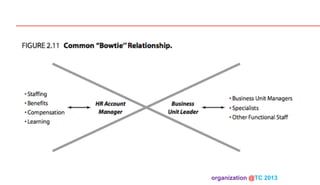
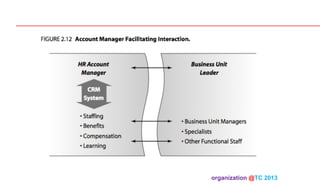
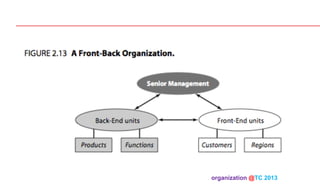
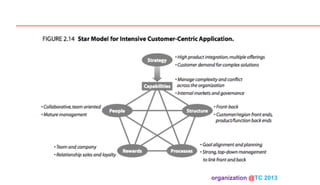
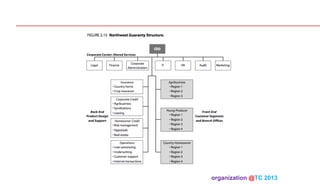
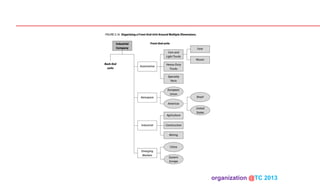
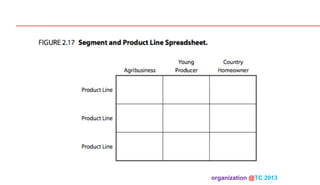
The document discusses designing organizations around the customer. It explains that customer-centric organizations focus their strategy, structure, processes, rewards, and people on serving customers. The document also discusses different levels of customer centricity that organizations can adopt, from customer-centric light to more intensive approaches. It emphasizes that customer-centric organizations understand customer profitability and segmentation to best meet customer needs.