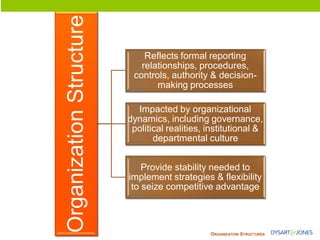
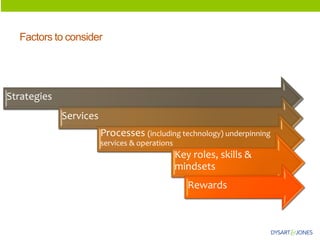
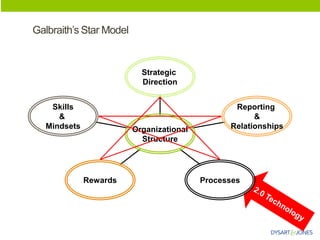
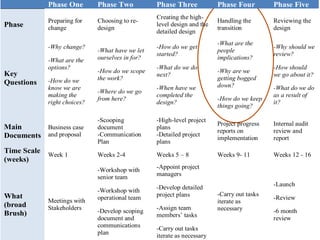
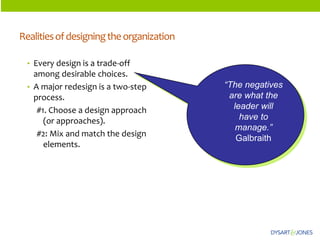
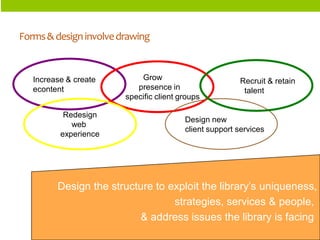
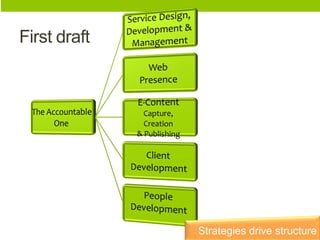
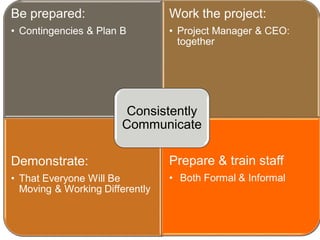
The document discusses organizational structure and principles for designing an effective structure. It provides examples of structures that focus on continuous improvement, breaking down barriers, and closer relationships with customers. The key factors to consider in structure design are strategies, services, processes, roles, skills, and rewards. Changing an organization's structure is a complex process that requires clear communication and training to help staff understand and transition to the new structure.