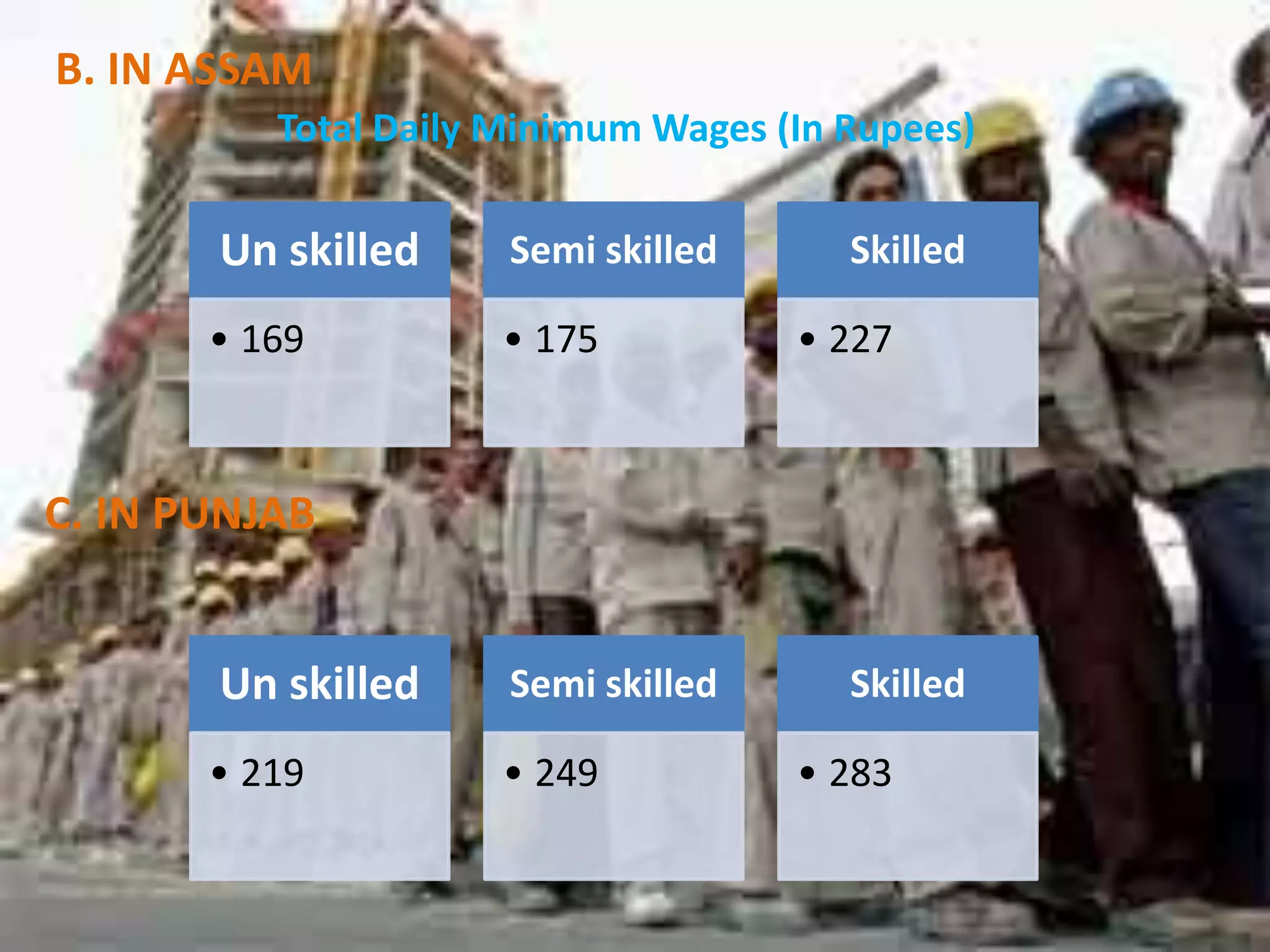
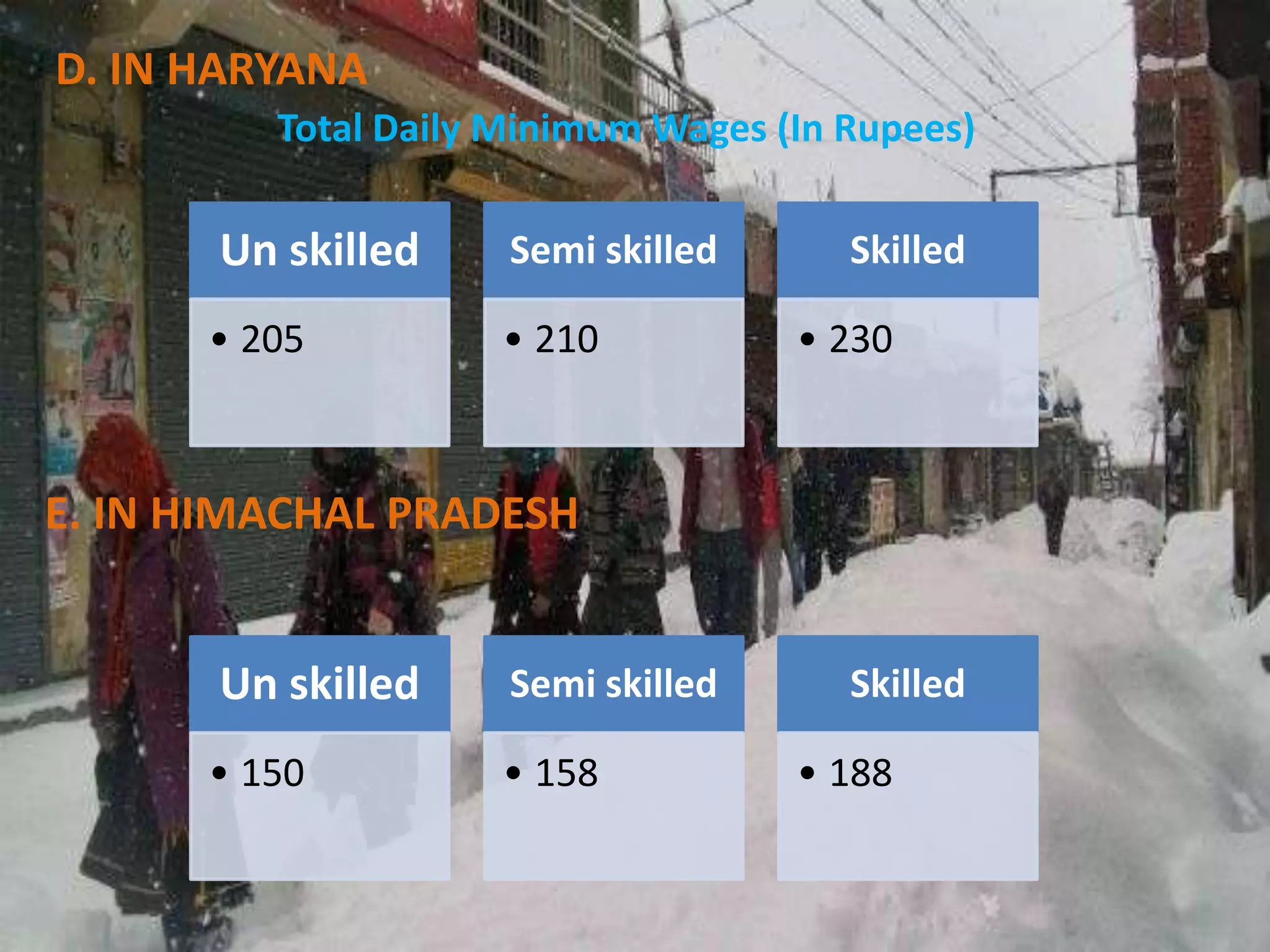
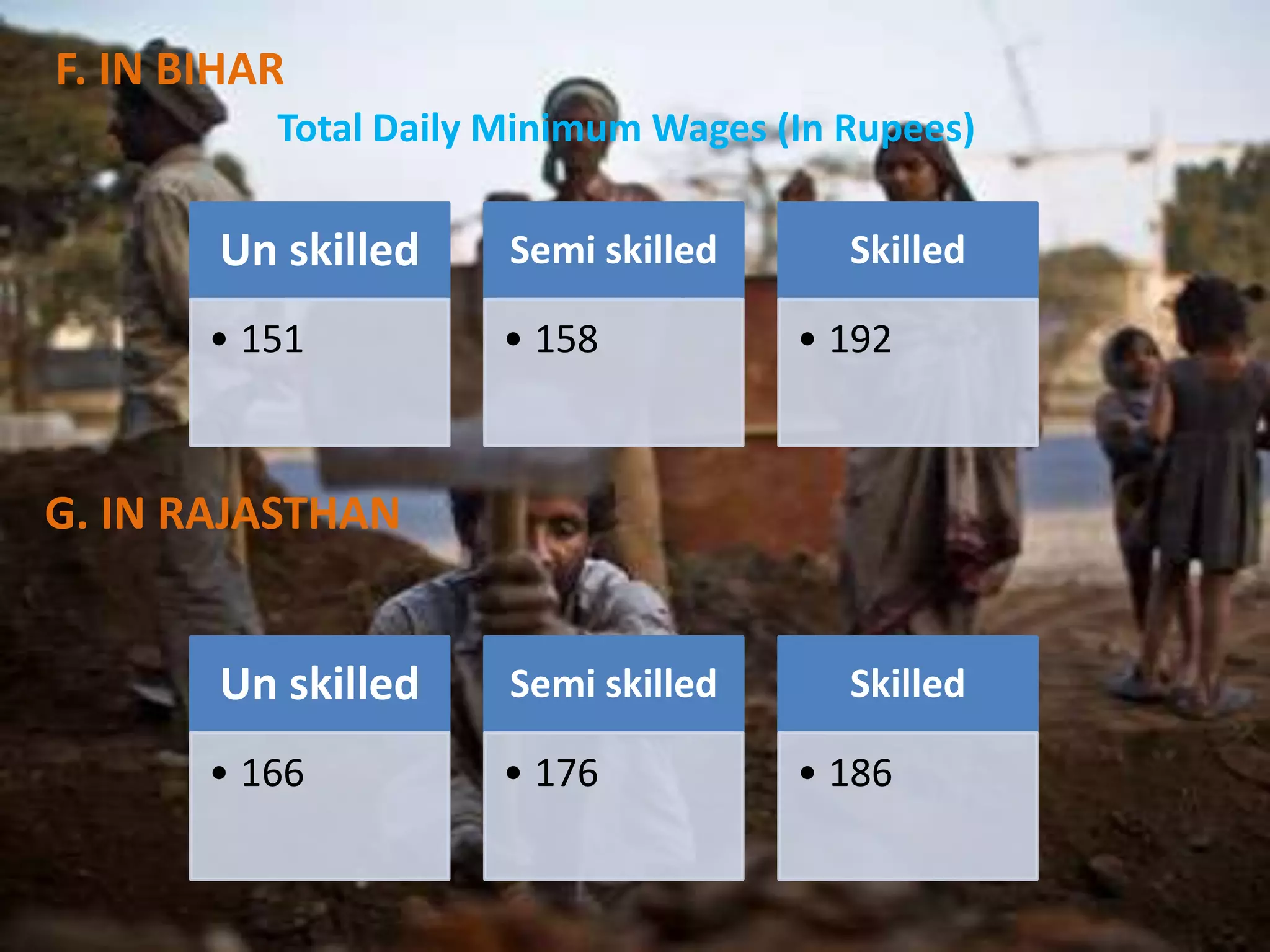
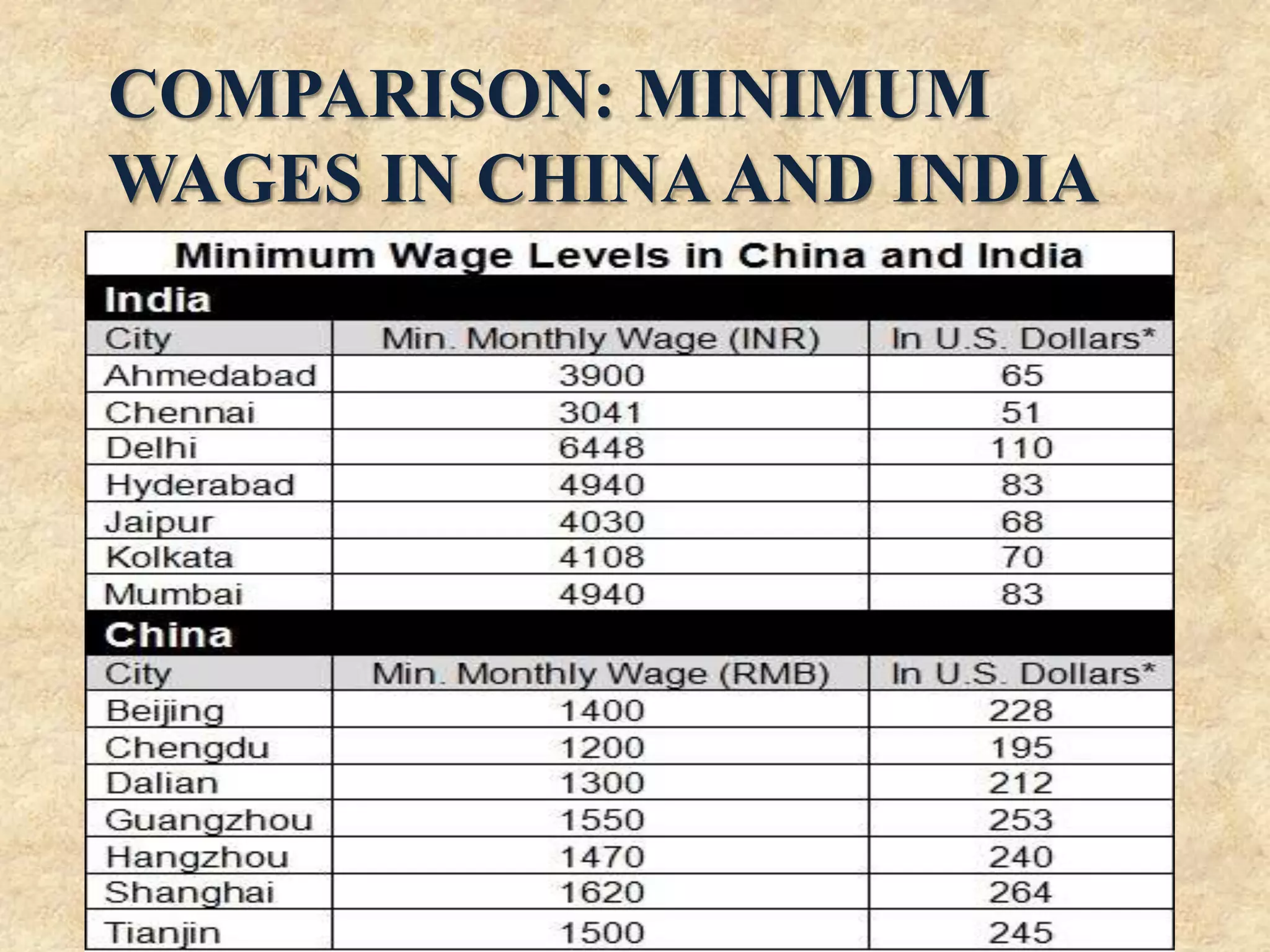
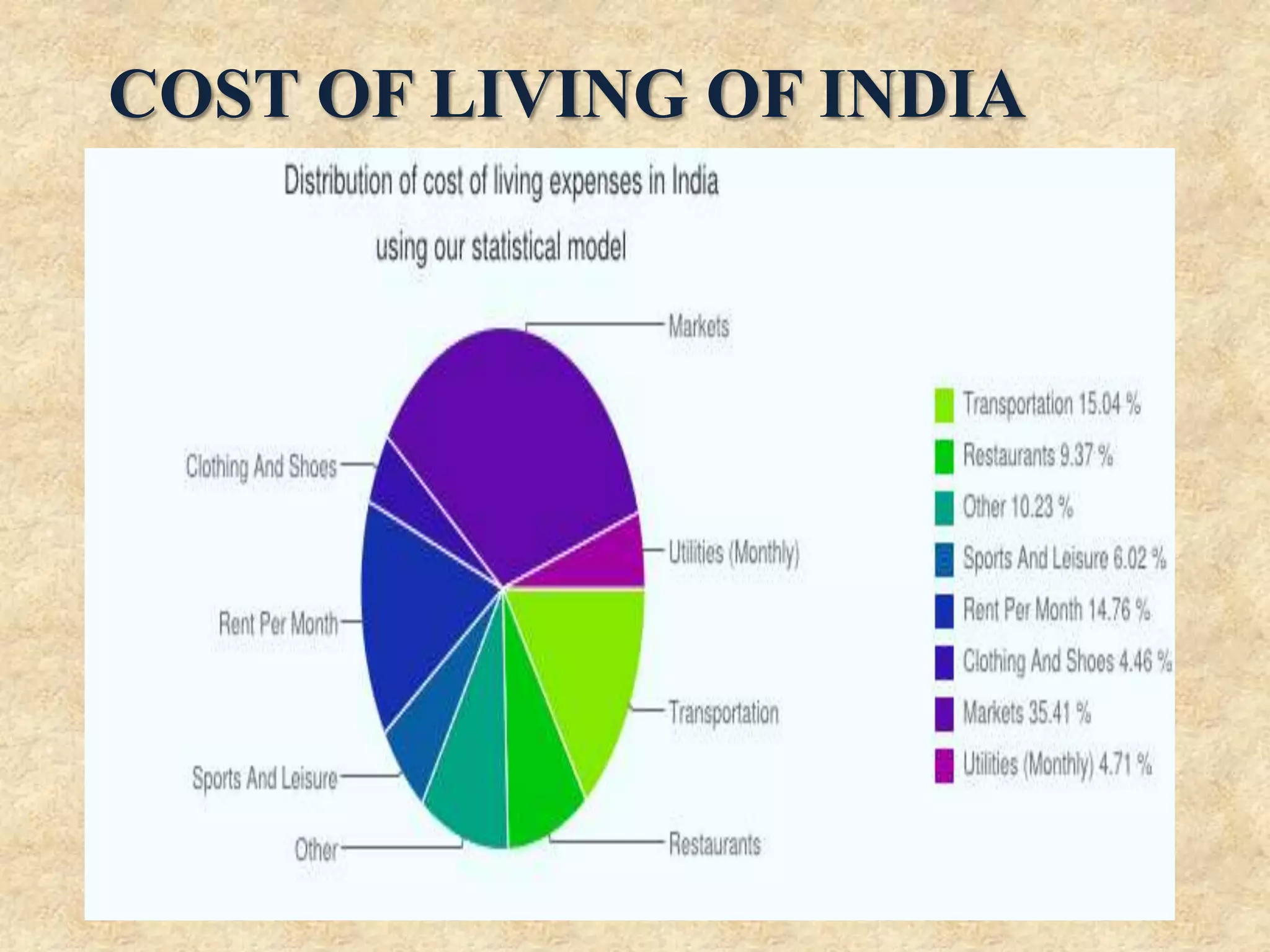
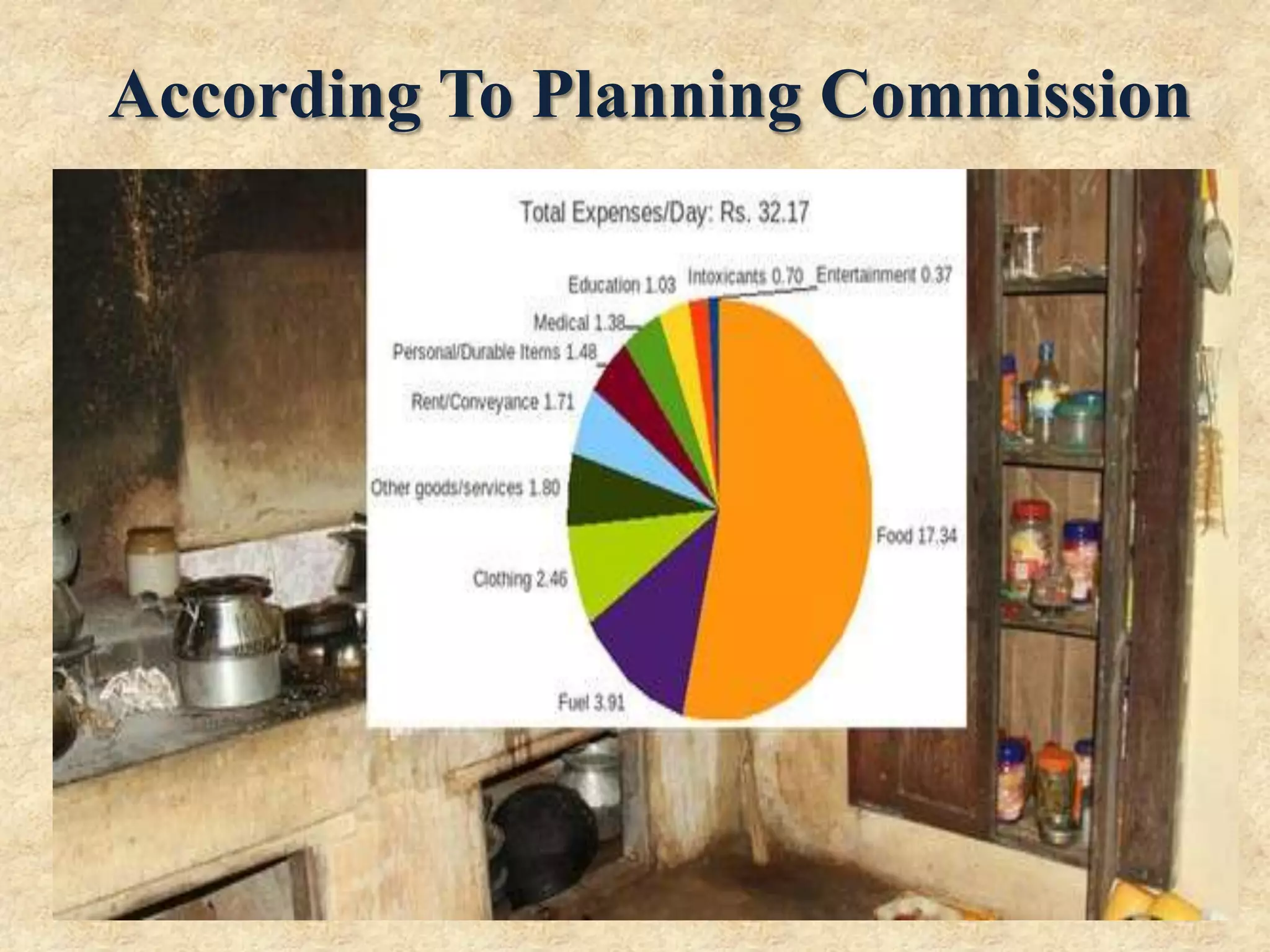
The document discusses the Minimum Wages Act of 1948 in India. It was created based on Article 43 of the Indian Constitution, which guarantees all workers a living wage. The Act aims to prevent the exploitation of workers, especially in industries where laborers are not organized. It allows the appropriate government to prescribe minimum wage rates for certain employments. Key features include fixing minimum wage rates, working hours, overtime pay, record keeping, inspections, and penalties for violations. The document also provides current minimum wage rates across various Indian states and compares rates in India and China.