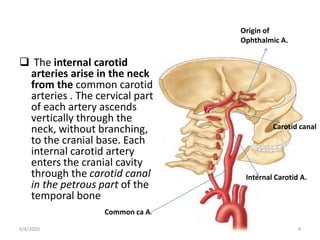
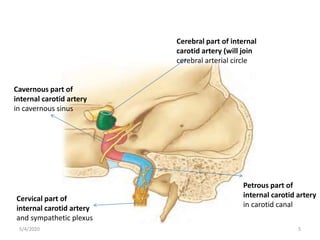
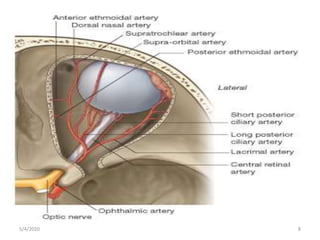
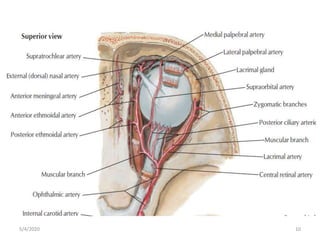
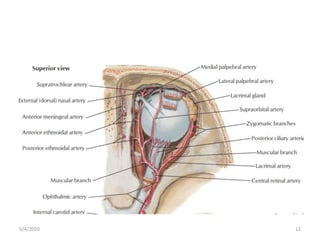
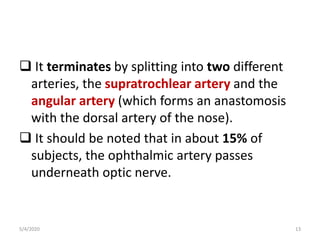
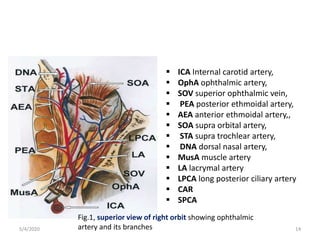
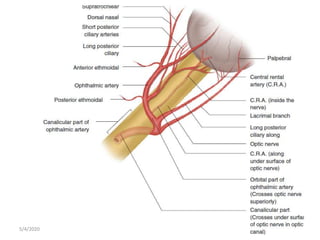
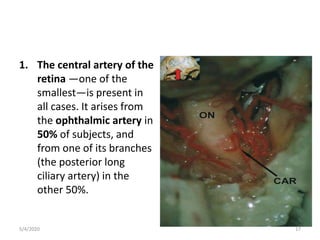
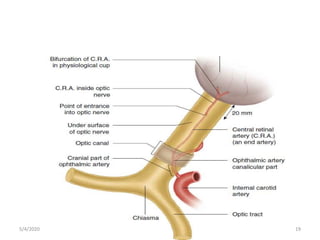
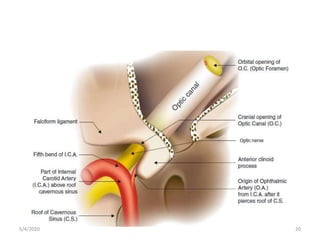
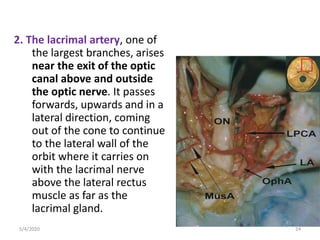
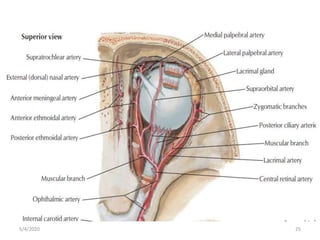
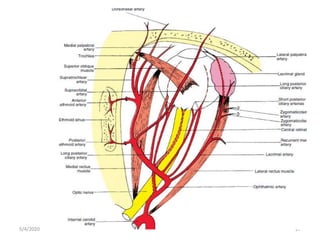
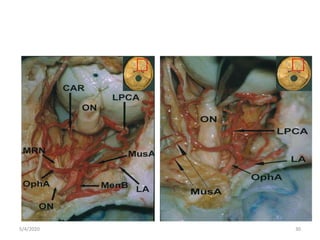
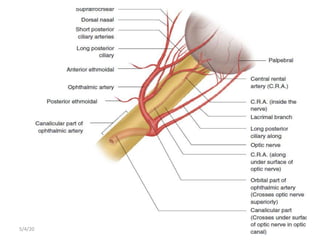
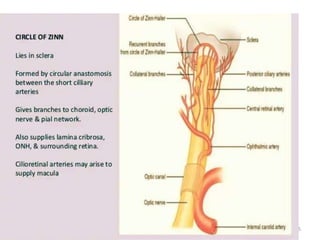
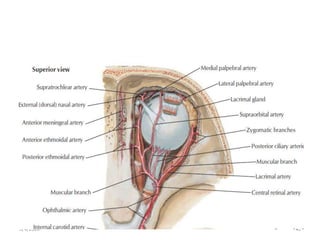
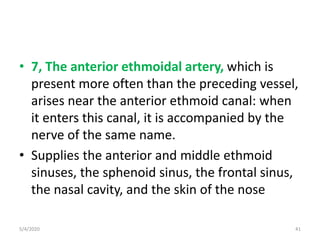
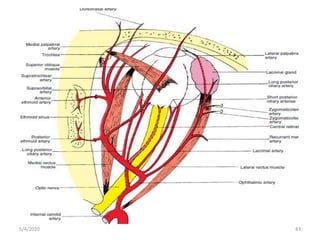
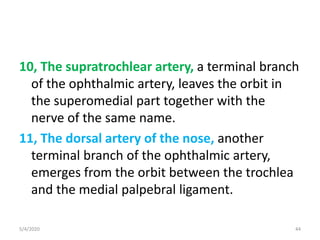
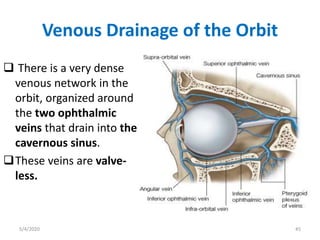
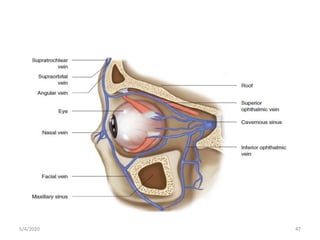
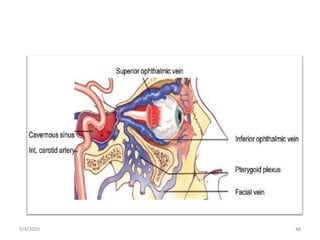
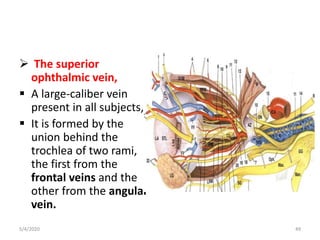
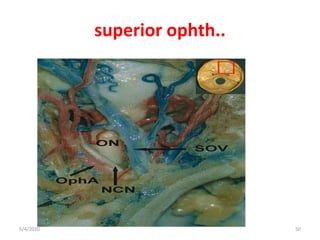
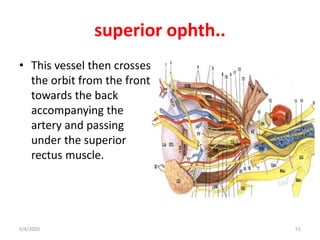
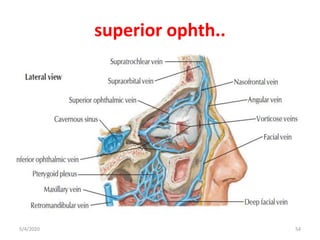
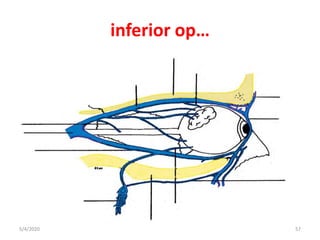
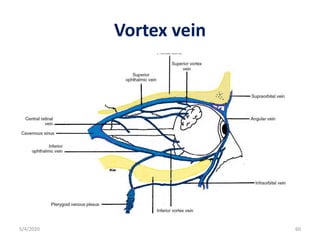
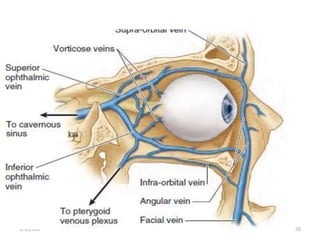
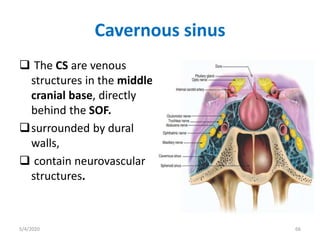
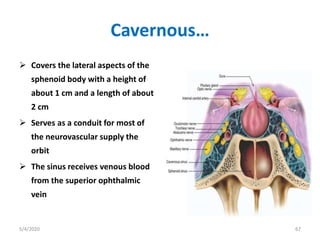
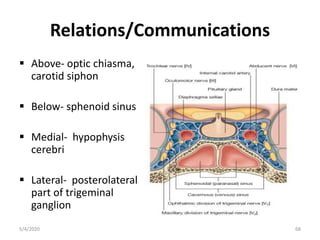
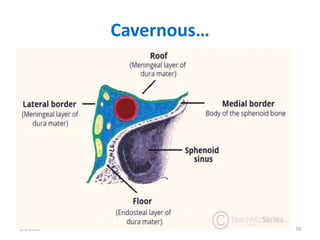
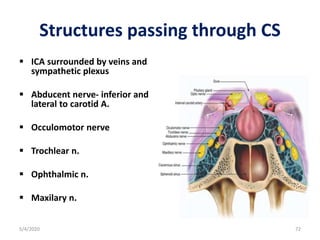
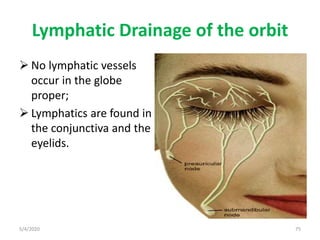
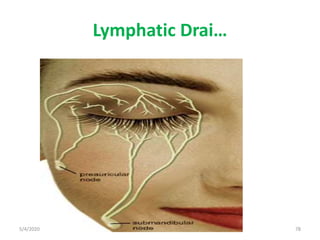
This document summarizes a seminar on the vascular supply and drainage of the orbit. It describes the key arteries supplying the orbit, including the ophthalmic artery and its branches, which provide blood to the eye muscles, lacrimal gland, retina and other orbital structures. It also discusses the venous drainage pathways, with the two ophthalmic veins and angular vein draining into the cavernous sinus and facial veins respectively. Clinical implications of diseases affecting these arterial and venous structures are presented.