Oral cancer-.pptx oncology and GI disorders
- 1. ORAL CANCER
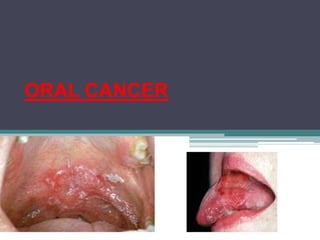
- 2. • Oral cancer is cancer that develops in the tissues of the mouth or throat. • Oral cancer, which includes cancers of the lips, tongue, cheeks, floor of the mouth, hard and soft palate, sinuses, and pharynx (throat), can be life threatening if not diagnosed and treated early.
- 3. Epidemiology • Men have twice the risk of developing oral cancer as women, and men who are over age 50 face the greatest risk.
- 4. Types of oral cancer PREMALIGNANT • Leukoplakia :Leukoplakia appears as thick, white patches on the inside surfaces of your mouth MALIGNANT • Squamous cell carcinoma: most common type of mouth cancer .Malignant growth arising from tiny, flat, squamous cells that lines mucous membrane. Mostly affects lower lip, tongue • Basal cell carcinoma : 2nd most common inoral cancer. Occurs on lips. Caused by excessive exposure to sunlight
- 5. Less common types of mouth cancer include: Oral malignant melanoma – where the cancer starts in cells called melanocytes, which help give skin its color Adenocarcinomas – cancers that develop inside the salivary glands
- 6. Risk factors for the development of oral cancer • Smoking • Smokeless tobacco users • Excessive consumption of alcohol • Family history of cancer. • Excessive sun exposure • Human papillomavirus (HPV). • Weakened immune system • Poor nutrition
- 7. Pathophysiology of oral cancer ETIOLOGY AND PRECIPITATINGFACTORS MUTATION OF PRO ONCOGENE CHANGES IN CELLULAR STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION ABNORMAL PROLIFERATION FORMATION OF MASS TUMOR INVADE SURROUNDING TISSUES/LYMPHNODES
- 8. Symptoms of Oral Cancer • Many oral cancers produce few or no symptoms in the early stages • Swellings/thickenings, lumps or bumps, rough spots/crusts/or eroded areas on the lips, gums, or other areas inside the mouth • The most common and frequent symptom is persistent painless sore or mass that does not heal with in 2 weeks.
- 9. Symptoms of Oral Cancer • Lesions in oral cancer is painless, indurated(hardened)ulcer with raised edges • Erythroplakia,leukoplakia • In advanced stages Bleeding in the mouth Numbness, pain/tenderness in any area of the face, mouth, or neck
- 10. Symptoms of Oral Cancer A soreness or feeling that something is caught in the back of the throat Difficulty chewing or swallowing, speaking, or moving the jaw or tongue Hoarseness, chronic sore throat, or change in voice, coughing of bloodtinged sputum Ear pain Changes in position of teethor ill fitting dentures Dramatic weight loss
- 11. STAGING OF ORAL CANCER Stage 0 Stage 0 is also called carcinoma in situ, and this is the very beginning of the scale. It describes abnormal cells in the lining of the lips or oral cavity, which have the potential to become cancer. Stage I Stage I describes a very early stage of cancer. The tumor is not more than 2 centimeters, and the cancer has not reached the lymph nodes.
- 12. Stage II Stage II describes a tumor that is larger than 2 centimeters but not more than 4 centimeters. Stage II cancer has not reached the lymph nodes. Stage III Stage III mouth cancer describes cancer that either is larger than 4 centimeters or has spread to a lymph node in the neck.
- 13. Stage IV Stage IV is the most advanced stage of mouth cancer. It may be any size, but it has spread to: Nearby tissue, such as the jaw or other parts of the oral cavity One large lymph node (more than 3 centimeters in size) and on the same side of the neck as the tumor, multiple lymph nodes of any size on the same side of the neck as the tumor, or one lymph node of any size on the side of the neck opposite the tumor Distant parts of the body beyond the mouth, such as the lungs
- 14. Staging of oral cancer – TNM CLASSIFICATION Tumor (T) • Using the TNM system, the "T" plus a letter or number (0 to 4) is used to describe the size and location of the tumor. .
- 15. TX Primary tumor cannot be assessed T0 No evidence of primary tumour Tis Carcinoma in situ T1 Tumour 2 cm or less in greatest dimension T2 Tumor more than 2 cm but not more than 4 cm in greatest dimension T3 Tumour more than 4 cm in greatest dimension T4a (lip) Tumour invades through cortical bone, inferior alveolar nerve, floor of mouth, or skin (chin or nose) T4a (oral cavity) Tumor invades through cortical bone, into deep/extrinsic muscle of tongue (genioglossus, hyoglossus, palatoglossus, and styloglossus), maxillary sinus, or skin of face T4b (lip and oral cavity) Tumor invades masticator space, pterygoid plates, or skull base; or encases internal carotidartery
- 16. Node (N) • The “N” in the TNM staging system stands for lymph nodes. • When cancer has spread through a lymph node and into the tissues directly surrounding it, it is called Extra Nodal Extension (ENE).
- 17. N X Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed N0 No regional lymph node metastasis N1 Metastasis in a single ipsilateral lymph node, 3 cm or less in greatest dimension N2 a Metastasis in a single ipsilateral lymph node, more than 3 cm but not more than 6 cm in greatest dimension N2b Metastasis in multiple ipsilaterallymph nodes, none more than 6 cm in greatest dimension N2 c Metastasis in bilateral or contralateral lymph nodes, none more than 6 cm in greatest dimension N3 Metastasis in a lymph node more than 6 cm in greatest dimension
- 18. M0 No distant metastasis M1 Distant metastasis M - Distant metastasis
- 19. Stage 0 Tis N0 M0 Stage I T1 N0 M0 Stage II T2 N0 M0 Stage III T1, T2 N1 M0 T3 N0, N1 M0 Stage IVA T1, T2, T3 N2 M0 T4a N0, N1, N2 M0 Stage IVB Any T N3 M0 T4b Any N M0 Stage IVC Any T Any N M1 STAGING
- 20. SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS Many oral cancers produce few or no symptoms in the early stages Later, the most frequent symptom is a “ painless sore or mass that will not heal. A lip or mouth sore that doesn't heal A white or reddish patch on the inside of your mouth Loose teeth A growth or lump inside your mouth Mouth pain Ear pain Difficult or painful swallowing
- 21. Voice changes Lump or mass in the neck Weight loss Persistent bad breath It can go unnoticed it can be painless lymphadenopathy
- 22. Diagnosis of oral cancer • History collection • Physical examination • X-ray • Toluidine blue test • Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan • Computerized tomography (CT) scan • Positron emission tomography (PET) scan • Biopsy Remove a small sample of affected tissue to check for the presence of cancerous cells.
- 23. PUNCH BIOPSY • A punch biopsy may be used if the suspected affected area of tissue is in an easily accessible place, such as your tongue or the inside of your mouth. The area is first injected with a local anesthetic to numb it. The doctor will then cut away a small section of affected tissue and remove it with tweezers. The procedure is not painful, but can feel a little uncomfortable.
- 24. FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION (FNA) • A fine needle aspiration (FNA) is a type of biopsy used if it is suspected that a swelling in neck is the result of mouth cancer.
- 25. PAN ENDOSCOPY • A pan endoscopy is a procedure used to obtain a biopsy when the suspected tissue is at the back of throat or inside nasal cavities.
- 26. Management of oral cancer • Early-stage (I and II) oral carcinoma can be treated with surgery or radiation. • In advanced stage (III and IV) oral squamous cell carcinoma, a combination of surgery and radiation therapy
- 27. SURGERY • Surgery is often the first treatment used for these cancers. It's most commonly used for early stage cancers, those that are small and haven't spread. • After cancer is removed, reconstructive surgery can be done to help restore the appearance and function of the areas affected by the cancer or cancer treatment.
- 28. Tumor resection • In a tumor resection, the entire tumor and a margin (edge) of normal-looking tissue around it is removed (resected). • The margin of normal tissue is taken out to reduce the chance of any cancer cells being left behind. • The main (primary) tumor is removed using a method based on its size and location. For example, if a tumor is in the front of the mouth, it might be relatively easy to remove it through the mouth.
- 29. Mandibulotomy .In case of larger tumor (especially when it has grown into the oropharynx) may need to be removed through an incision (cut) in the neck or by cutting the jaw bone with a special saw to get to the tumor.
- 30. Mandibulectomy (mandibular resection) Removes all ( total Mandibulectomy) or part of the jaw bone (partial thickness mandibular resection or marginal mandibulectomy). • This operation may be needed if the tumor has grown into the jaw bone.
- 31. Mohs (micrographically oriented histographic surgery) Mohs surgery, is a precise surgical technique in which the complete excision of skin cancer is checked by microscopic margin control. It offers the highest cure rates while maximizing preservation of healthy tissue. Some cancers of the lip may be removed by Mohs surgery. The tumor is removed in very thin slices. Each slice islooked at right away under the microscope to see if there are cancer cells. Slices are removed and examined until no cancer cells are seen.
- 32. Glossectomy (removal of the tongue) Glossectomy may be needed to treat cancer of the tongue. partial glossectomy -For smaller cancers, only part of the tongue (less then 1/3) may need to be removed. Total glossectomy-For larger cancers, the entire tongue may need to be removed
- 33. Maxillectomy • If cancer has grown into the hard palate all (maxillectomy) or part of the involved bone (partial maxillectomy )is removed.
- 34. Laryngectomy (removal of the voice box) Very rarely, surgery to remove large tumors of the tongue or oropharynx may require removing voice box (larynx). When the voice box is removed, the windpipe (trachea) is attached to a hole (stoma) made in the skin in the front of the neck. This is called tracheostomy or trach (trake).
- 35. Neck dissection • Cancers of the oral cavity and oropharynx often spread to the lymph nodes in the neck. Removingthese lymph nodes (and other nearby tissues) is calleda neck dissection or lymph node dissection and is done at the same time as the surgery to remove the main tumor.
- 37. There are several types of neck dissection procedures • In a partial or selective neck dissection only a fewlymph nodes are removed. • For a modified radical neck dissection, most lymph nodes on one side of the neck between the jaw bone and collarbone are removed, as well as some muscle and nerve tissue. • In a radical neck dissection, nearly all nodes on one side, as well as even more muscles, nerves, andveins are removed.
- 38. RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY Operations may be needed to help restore the structure of areas affected by more extensive surgeries to remove the cancer. SPLIT THICKNESS Split-thickness skin grafts are composed of full- thickness epidermis and partial-thickness dermis, and they most commonly range in thickness between 0.015 inches and 0.20 inches
- 39. SKIN GRAFT A cutaneous flap A skin flap consists of skin and subcutaneous tissue that survives based on its own blood supply. A myocutaneous flap A skin flap consists of subcutaneous tissue, muscle and skin. A microvascular free flap Microvascular free-tissue transfer to the head and neck has become an accepted method of reconstruction owing to increased success rates. The large number of arteries and veins in the neck make free-flap revascularization easier than in other recipient sites of the body
- 41. chemotherapy • 5 flurouracil • Methotrexate • Cisplastin • Carboplatin • Paclitaxel • bleomycin
- 42. Radiation therapy • Combination of interstitial implants and external beam radiation
- 43. BRACHYTHERAPY Brachytherapy is a type of internal radiation therapy in which seeds, ribbons, or capsules that contain a radiation source are placed in your body, in or near the tumor.
- 44. Pre operative nursing management GENERAL PREOPERATIVEASSESSMENT • Obtain surgical consent • Obtain a thorough medical history and perform a physical examination. • Specific diagnostics ▫ Laboratory tests ▫ Preoperative cardiac assessment ▫ Preoperative pulmonary assessment ▫ Preoperative nutritional statusassessment ▫ Pre anesthetic consent
- 45. Pre operative nursing diagnosis • Chronic pain related to tumor invasion to surrounding tissues • Imbalanced nutritional status less than body requirement related to dysphagia • Impaired oral mucous membrane related to cancer of oral cavity
- 46. 1)Maintain adequate nutrition NG tube feeding Enteral feeding Parenteral feeding 2)Promote verbalcommunication Use of paper and pen Use of pictures Use of gestures 3)Pain management Analgesics to reducepain Comfortable position Use topical anesthetics, either painted or sprayed onto the painful areas or swished over the mucosa’s surface. Two topical anesthetics used are dyclonine and benzocaine. Systemic analgesics include aspirin, acetaminophen, propoxyphene, and codeine. 4)Promote oral hygiene
- 47. Pre operative teaching • Informed about the type of surgery, type of unit,health care team • Airway maintenance after surgery. Emphasis about need for stoma care, humidification,suctioning Provide communication training- teach alternative forms of communication and use of laryngeal communication devices Educate regarding enteralnutrition Preventing constipation In case of emergency alerting healthcare personnel Get access to information resources and support groups
- 48. Nursing Diagnosis • Chronic pain related tosurgery • Risk for ineffective airway clearance relatedto surgery • Imbalanced nutritional status less than body requirement related to oral surgery • Impaired oral mucous membrane related to surgery of oral cavity • Impaired verbal communication related to excision of tongue or larynx • Ineffective coping related to hospitalization • Ineffective health maintenance related to hospitalisation • Disturbed body image related to surgical excision • Risk for bleeding related to surgery • Risk for infection related to surgical incision/low immune status
- 49. Post operative nursing management Pain management- ▫ pain assessment and medication administration. ▫ Comfortable position ▫ Promote drainage of secretions Ensure airway patency o Assess airway patency and respiratory status every hour until stable o Propped up position with supporting arms o Deep breathing and coughing exercises as tolerable every 2 to 4 hours Control of postoperative bleeding Prophylactic antibiotic administration
- 50. Post operative nursing management • Nutritional management NPO Usually 7 to 10 days after surgery-To allow mucosal suture line and surgical sites to heal by preventing stress or pressure during eating or swallowing and reduce risk of infection Nasogastric tube feedings Diet that’s high in protein and calories, small frequent diet and supplemented with vitamins and minerals. Avoid foods that are coarse, rough, acidic, orspicy. • Wound management Wound care 2 to 4 times per day as ordered by physician to keep incisions clean and help preventinfection. Care of drainage tubes
- 51. Post operative nursing management Tracheostomy care of tracheostomy suctioning prevention of infection Ensure graft viability normally pink and warm Blue color indicates venouscongestion White color indicates arterial congestion Assess for presenceof pulse Oral care Rinses/ gentlebrushing Oral suctioning Avoid vigorous brushing No oral care if intraoral resection until approved by physician
- 52. Intravenous (iv) solutions/medications ▫ IV is necessary to administer fluids until oral or NG intake is adequate ▫ IV will be used to administer antibiotics as needed and to provide access for administration of other medications including analgesics
- 53. Neck dissection Provide comfort care and airway management Skin flap will be assessed for adequate circulation. Avoid constrictive clothing around neck. Neck may have a sunken or depressed appearance on side of dissection. Promote positive self image. Patient may experience loss of sensation to posterior scalp, neck, and shoulder. Reinforce safety measures to protect skin from injury. Promote airway clearance Elevate head of bed 30 degree Encourage coughing deep breathing and use of incentive spirometry Monitor vitals every 4 hours
- 54. Assess the wound and proper care If hemorrhage apply direct pressure suction airway reassure patient Care of suture lines as ordered Maintain drainage output colour and consistency Maintain suction to drain Milk tubing every 1-2hrs for 24 hours then every 4 hours is needed Assess skin flap every shift drain patency or infection Monitor intake and output and record every shift
- 55. Prevent complication Monitor shoulder droop secondary to loss of nerve supply to trapezium muscle and inability to raise hand over head Reinforce need to do shoulder strengthening exercise three times per day Manage nutrition Monitor patients ability to inject food Weight daily at same time Consult with dietitian Provide patient and family support
- 56. To maintain physical mobility Diagonal neck stretch: Up Gently turn your head so you’re looking up and to the right. Place your right hand on your left cheek and jaw. Apply mild pressure to give yourself a deeper stretch
- 57. Repeat this in the other direction. Hold each stretch for 30 seconds, then relax. Take 1 full breath between each repetition. Repeat this 5 times on each side
- 58. Side neck stretch Sit or stand and point your right arm downward. Place your left hand on top of your head. Gently pull down your head toward your left shoulder, to stretch the muscles on the right side of your neck Repeat this in the other direction. Hold each stretch for 30 seconds, then relax. Take 1 full breath between each repetition. Repeat this 5 times on each side.
- 59. Pectoral stretch using doorway Stand in a doorway. Place your hands and forearms at shoulder level on the sides of the doorway Gently step forward until you feel a gentle stretch across your chest and in front of your shoulders. Keep your back straight, and your neck and shoulders relaxed. Hold for 30 seconds, then relax. Return to the starting position with your arms at your sides. Take 1 full breath between each repetition. Repeat this 5 times
- 60. Chin tuck Sit or stand with your back and head leaning against the wall. Tuck your chin in and try to flatten the back of your neck against the wall Hold this position for 5 seconds, then relax. Return to the starting position. Take 1 full breath between each repetition. Repeat this 10 times.
- 61. Arm circles Sit or stand with your arms at your sides. Have your palms facing forward and your thumbs pointing to the ceiling. Lift your arms up and circle them backward Return to the starting position. Take 1 full breath between each repetition. Repeat this 10 times.
- 62. Arm and shoulder retraction Sit or stand with your arms in front of you and your palms facing forward. Push your shoulders down and away from your ears. This stops you from shrugging. Move your arms out to the sides, while squeezing your shoulder blades together. Hold this position for 5 seconds, then relax.
- 63. Monitoring and managing potential complications Hemorrhage Chyle fistula Chyle fistula is defined as a leakage of lymphatic fluid from the lymphatic vessels, typically accumulating in the thoracic or abdominal cavities Nerve injury
- 64. promote Communication • Discuss patient's inability to speak until edema decreases. • Determine ability to read and write and discuss appropriate communication methods (i.e., writing materials, picture board). • Use call bells . Provide psychologicalsupport • Promote mental health • Improves self esteem
- 65. CONCLUSION Oral cancer is cancer that develops in the tissues of the mouth or throat. It belongs to a larger group of cancers called head and neck cancers. Most develop in the squamous cells found in your mouth, tongue, and lips.