ORAL CANCER PPT.pptx
- 2. INTRODUCTION • Oral cancer is one of the most prevalent diseases worldwide, accounting for 30-40% of the head and neck cancer. It is fairly common and very curable if found and treated at an early stage. Most develop in the squamous cells found in the mouth, tongue and lips.
- 4. DEFINITION • Oral Cancer: It also known as mouth cancer, is cancer of the lining of the lips, mouth or upper throat. It belongs to a larger group of cancers called head and neck cancers.
- 5. EPIDEMIOLOGY • According to World Health Organization, oral cavity cancer is amongst the most prevalent cancers worldwide and incidence rates are higher in men than women. • In India, incidence of oral cancer for males and females was highest. For males, it was 64.8% and for females it was 37.2% at 70 yrs of age. • The highest magnitude was observed in west and northeast regions (58.45%) at 60 years of age.
- 6. ETIOLOGY AND RISK FACTORS 1) GENERAL • Gender: Oral cancer is twice as common in men as in women. • Age: The average age at diagnosis for oral cancer is 62, and two- thirds of individuals with this disease are over age 55, although it may occur in younger people, as well. • Ultraviolet light: Cancers of the lip are more common among people who work outdoors and visit tanning beds, and among those with prolonged exposure to sunlight.
- 7. CONTD… • Poor nutrition: Studies have found a link between diets low in fruits and vegetables and an increased oral cancer risk. 2) GENETICS • Genetic syndromes: Some inherited genetic mutations, which cause different syndromes in the body, carry a high risk of oral cancer. These include: Fanconi anemia is a blood condition caused by inherited abnormalities in several genes. Patients may experience symptoms at an early age and may develop anemia or aplastic anemia.
- 8. CONTD… • Dyskeratosis congenita is a genetically linked syndrome that may also cause aplastic anemia, and carries a high risk of oral cancer, beginning at an early age. 3) LIFESTYLE • Tobacco use: About 80 percent of patients with oral cancers use tobacco in the form of cigarettes, chewing tobacco or snuff. The risk of developing oral cancer depends on the duration and frequency of tobacco use.
- 9. CONTD… • Alcohol: About 70 percent of people diagnosed with oral cancer are heavy drinkers. This risk is higher for people who use both alcohol and tobacco. • Betel quid: Many people in Southeast Asia and other parts of the world chew betel quid. Chewing gutka, a combination of betel quid and tobacco, is also common. Both of these substances are associated with an increased oral cancer risk.
- 10. OTHER CONDITIONS: • Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection • Immune system suppression • Lichen planus • Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD): This condition may develop after a stem-cell transplant, in which bone marrow is replaced following cancer occurrence or treatment.
- 11. CLASSIFICATION OF ORAL CANCER • The TNM classification system stages different types of cancer based on certain standard criteria: • T describes the size of the original (primary) tumor. N indicates whether or not the cancer has reached nearby lymph nodes. M measures whether the cancer has spread (metastasized) to other areas of the body.
- 12. CONTD… T — Primary tumour TX Primary tumour cannot be assessed T0 No evidence of primary tumour Tis Carcinoma in situ T1 Tumour 2 cm or less in greatest dimension T2 Tumour more than 2 cm but not more than 4 cm in greatest dimension T3 Tumour more than 4 cm in greatest dimension T4a (lip) Tumour invades through cortical bone, inferior alveolar nerve, floor of mouth, or skin (chin or nose)
- 13. T4a (oral cavity) Tumour invades through cortical bone, into deep/extrinsic muscle of tongue (genioglossus, hyoglossus, palatoglossus, and styloglossus), maxillary sinus, or skin of face T4b (lip and oral cavity) Tumour invades masticator space, pterygoid plates, or skull base; or encases internal carotid artery N - Regional Lymph Nodes NX Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed N0 No regional lymph node metastasis N1 Metastasis in a single ipsilateral lymph node, 3 cm or less in greatest dimension N2 Metastasis as specified in N2a, 2b, 2c below N2a Metastasis in a single ipsilateral lymph node, more than 3 cm but not more than 6 cm in greatest dimension
- 14. N2b Metastasis in multiple ipsilateral lymph nodes, none more than 6 cm in greatest dimension N2c Metastasis in bilateral or contralateral lymph nodes, none more than 6 cm in greatest dimension N3 Metastasis in a lymph node more than 6 cm in greatest dimension M - Distant metastasis M0 No distant metastasis M1 Distant metastasis
- 15. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Due to the etiological factors Mutation inactivates tumor suppressor gene Cells proliferate Mutation inactivates DNA repair gene Mutation of proto-oncogene creates an oncogene Mutation inactivates several more tumor suppressor genes Cancer
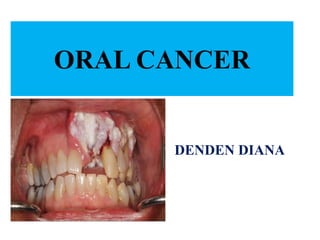
- 16. CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS: • A sore on the lip or in the mouth that doesn't heal • Pain in the mouth that doesn’t go away • A lump or thickening in the lips, mouth, or cheek • A white or red patch on the gums, tongue, tonsil, or lining of the mouth • A sore throat • Trouble chewing or swallowing • Trouble moving the jaw or tongue • Persistent halitosis
- 17. CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS: • Numbness of the tongue, lip, or other area of the mouth • Swelling or pain in the jaw • Dentures that start to fit poorly or become uncomfortable • Loosening of the teeth or pain around the teeth • Voice changes • A lump or mass in the neck or back of the throat • Weight loss • Pain in the ear
- 18. DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATIONS: • A complete medical history, asking about the patient’s signs and symptoms of oral cancer and risk factors. • Feel for any lumps on the neck, lips, gums, and cheeks. • Examine the area behind the nose, the larynx (voice box), and the lymph nodes of the neck.
- 19. DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATIONS: • E n d o s c o p y : A n endoscopy allows to see inside the mouth and throat. Typically, is inserted through the nose to examine the head and n e c k a r e a s .
- 20. BIOPSY: • During a fine needle aspiration biopsy, cells are removed using a thin needle inserted directly into the suspicious area.
- 21. ORAL BRUSH BIOPSY: During routine dental examinations, some dentists are using a newer, simple technique to detect oral cancer in which the dentist uses a small brush to gather cell samples of a suspicious a r e a .
- 22. X-RAY: • An x-ray is a way to create a picture of the structures inside of the body, using a small amount of radiation to look for abnormal findings in the mouth or n e c k .
- 23. Barium swallow/modified barium swallow. : The first is . During an x-ray exam, the patient is asked to swallow liquid barium to look for any changes in the structure of the oral cavity and throat and see whether the liquid passes e a s i l y t o t h e s t o m a c h . or videofluoroscopy, may be used to evaluate difficulties with swallowing.
- 24. Computed tomography (CT or CAT) scan: • A special dye called a contrast medium is given before the scan to provide better detail on the image. This dye can be injected into a patient’s vein or given as a pill or liquid to swallow.
- 25. MRI : An MRI uses magnetic fields, not x- rays, to produce detailed images of the body, especially images of soft tissue, such as the tonsils and the base of the tongue. MRI can be used to measure the tumor’s size. A special dye called a contrast medium is given before the scan to create a clearer picture.