This document provides an overview of Oracle's Application Development Framework (ADF). It discusses how ADF is Oracle's strategic solution for developing enterprise applications, as Oracle itself uses ADF extensively. The document outlines key aspects of ADF like its origins, how it provides a productive framework through declarative development as long as best practices are followed. It also notes that developing full ADF applications requires skills in areas like SQL, Java and HTML/CSS. The document demonstrates features through examples and emphasizes that getting started with ADF requires learning its capabilities and limitations.












![31
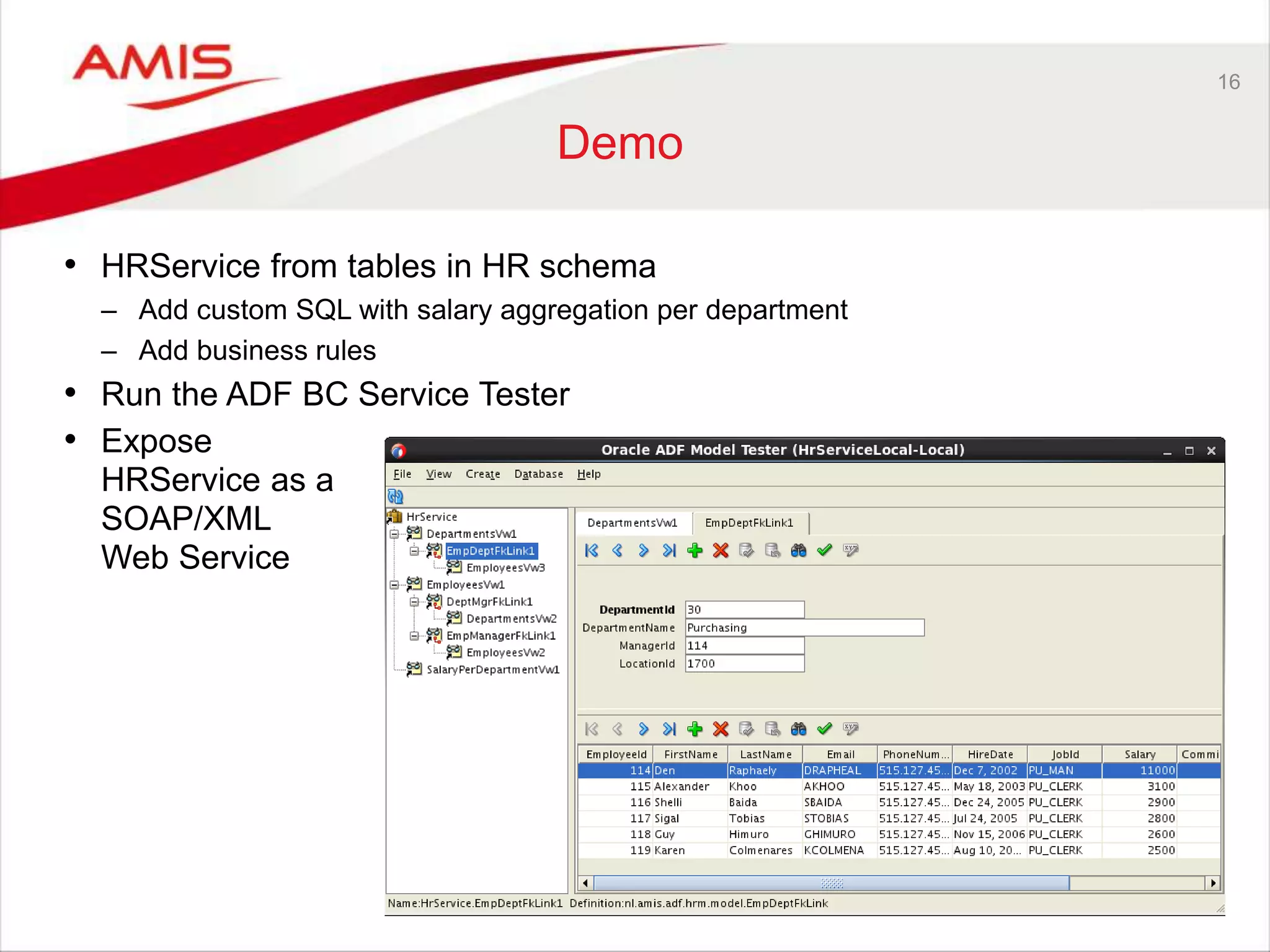
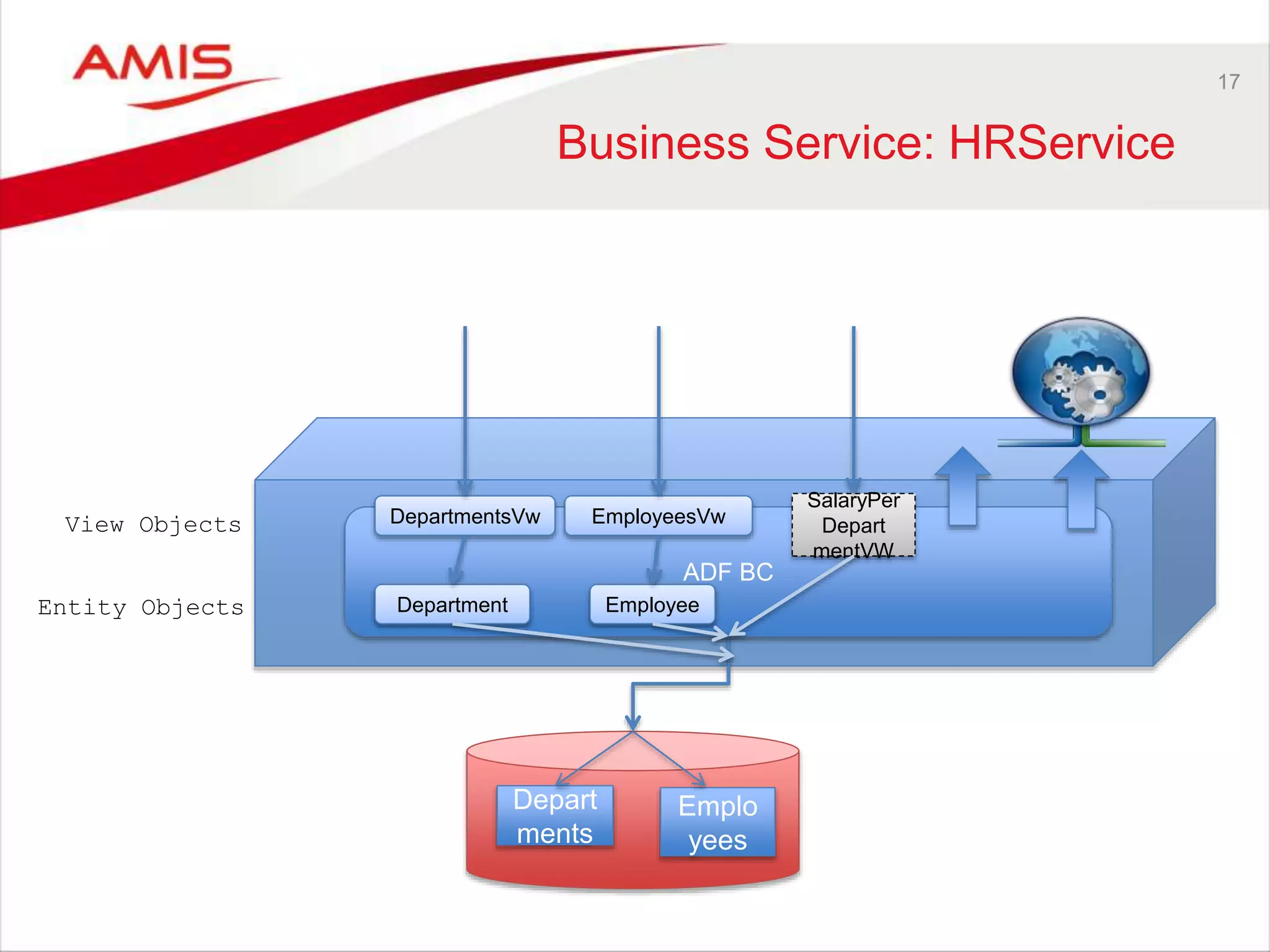
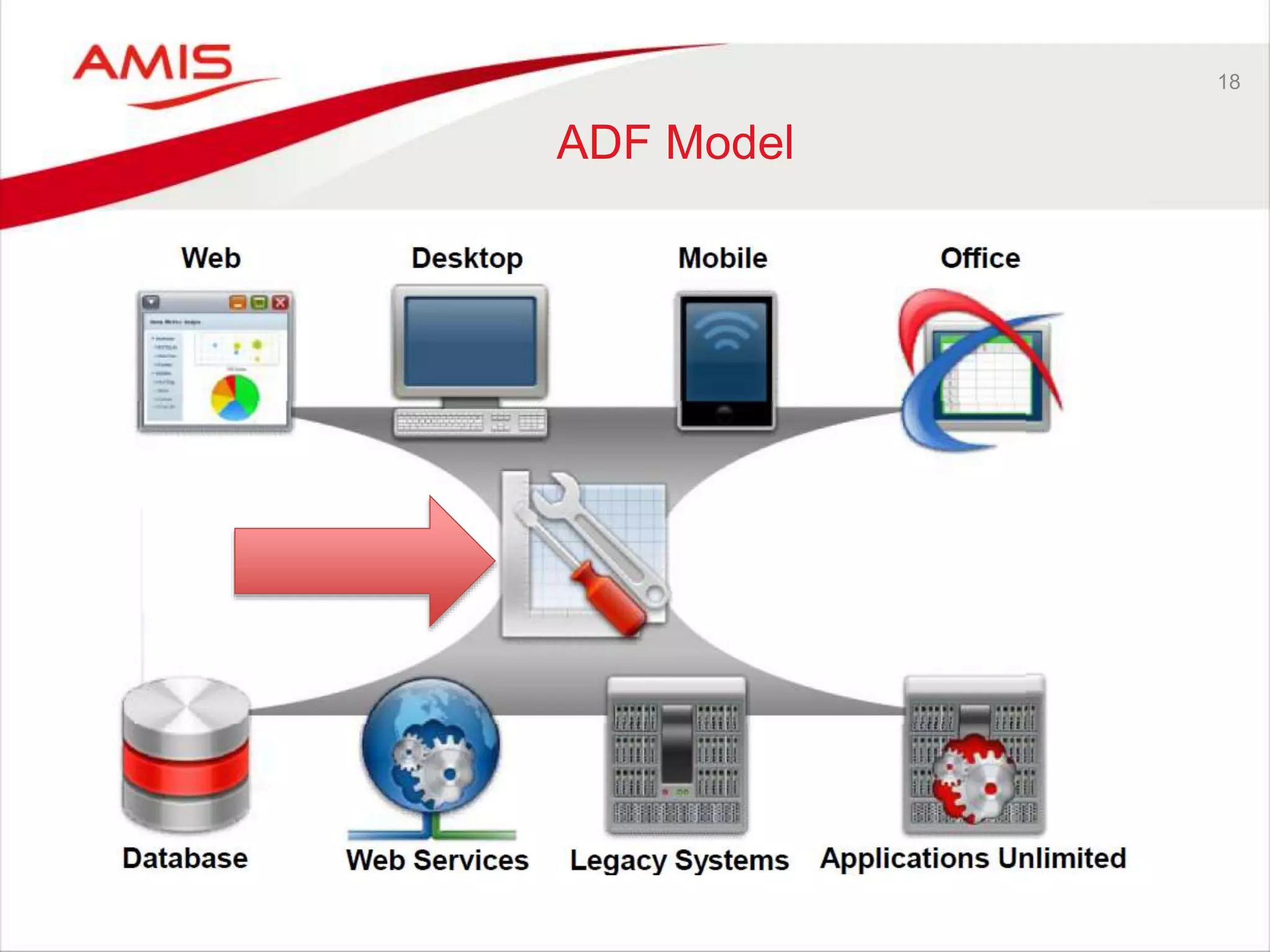
Summary
• Oracle’s strategic application development solution
– Taken the place Oracle Forms used to occupy
• Enterprise scale development of enterprise applications
– As Oracle itself puts into practice
• High productivity through rich
framework and declarative development
– As long as you work with the framework (and accept its limitations)
• Developing end to end ADF applications requires many skills
– Specialization is probably a good strategy
• The imminent 12.1.3 release continues a long history of evolution
– No major upheaval – new features, ease of development, more tablet and more UX
• ADF Essentials makes free ADF development and deployment possible
– ADF Essentials on [Glassfish | JBoss | Tomcat] against [MySQL | Oracle XE]
ADF](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/adfinactionougfjune2014-140606020733-phpapp02/75/ADF-in-Action-getting-re-acquainted-with-Oracle-s-premier-application-development-framework-OUGF-2014-Harmony-31-2048.jpg)
