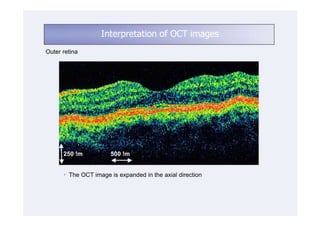
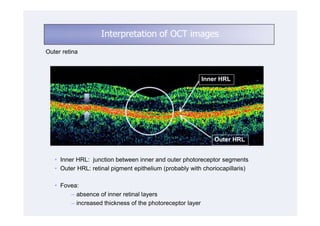
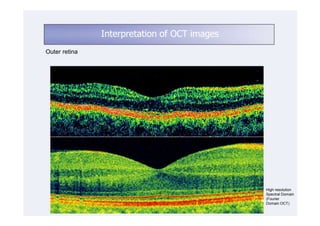
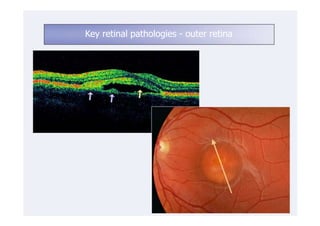
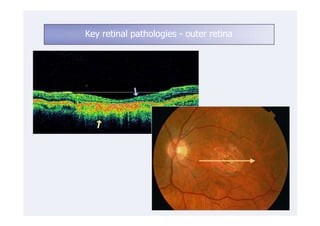
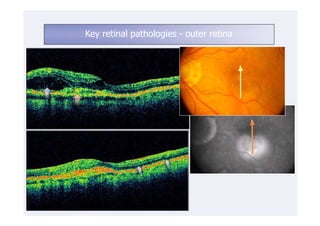
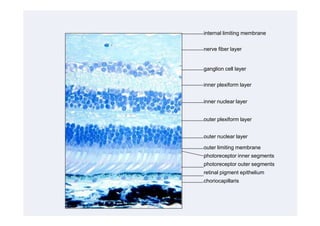
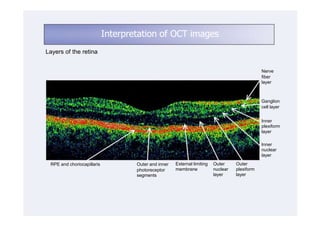
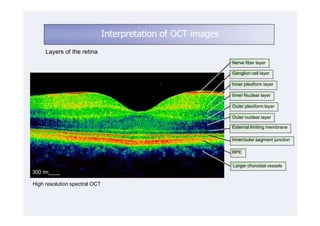
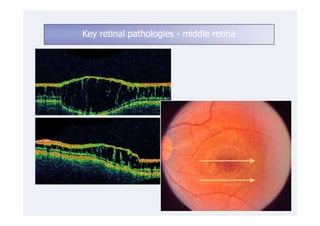
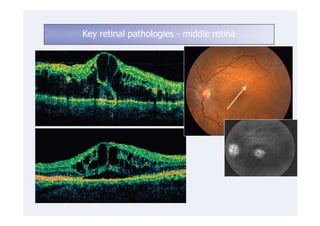
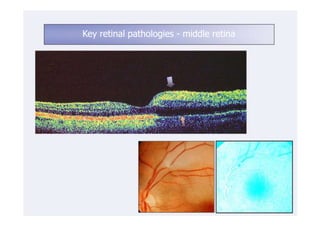
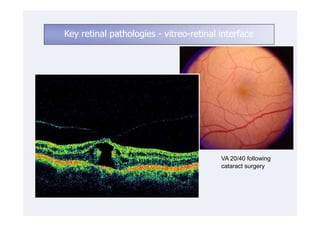
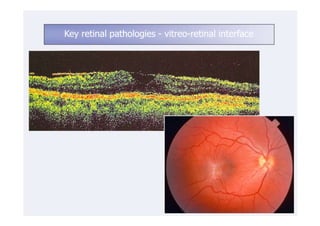
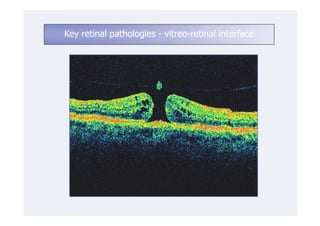
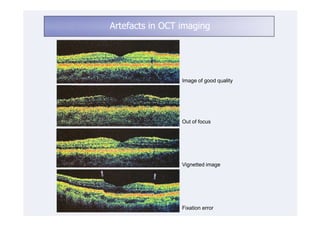
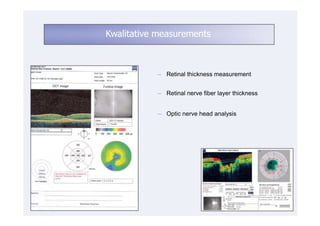
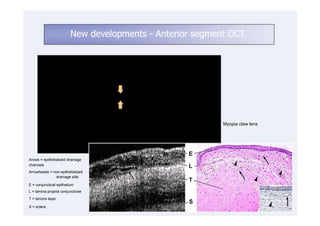
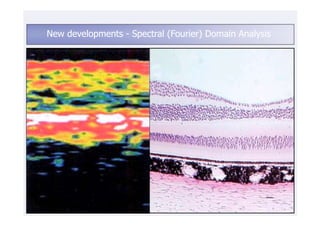
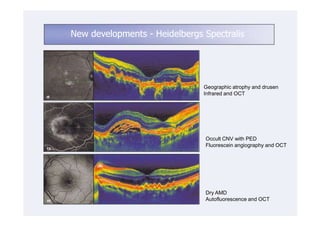
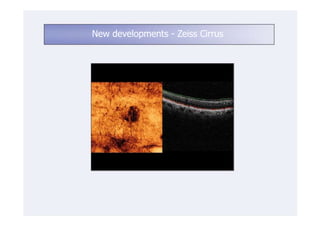
This document discusses the interpretation of optical coherence tomography (OCT) images of the retina. It begins by explaining how OCT images expand the retina in the axial direction and identifies key layers such as the inner and outer photoreceptor segments. It then examines pathologies affecting the outer, middle, and vitreo-retinal interface of the retina. New developments discussed include using anterior segment OCT to image the anterior chamber, and spectral domain techniques that provide higher resolution images to better visualize conditions like geographic atrophy. In closing, several OCT devices including Heidelberg Spectralis and Zeiss Cirrus are highlighted.