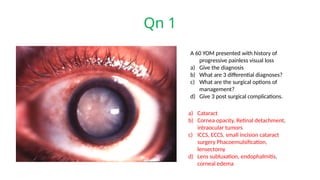
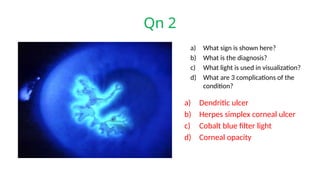
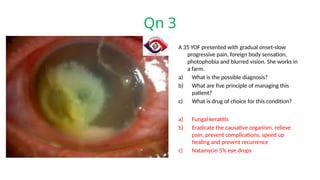
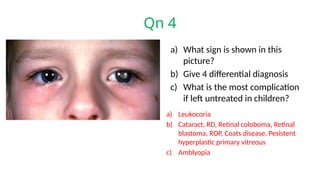
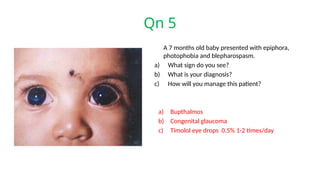
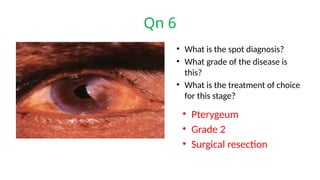
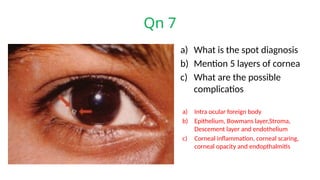
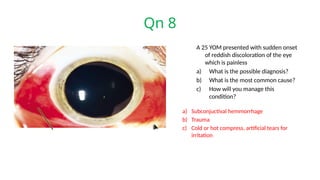
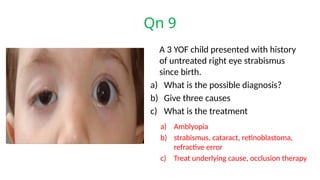
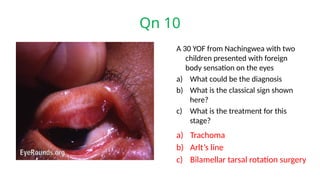
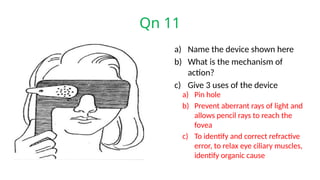
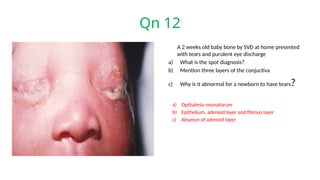
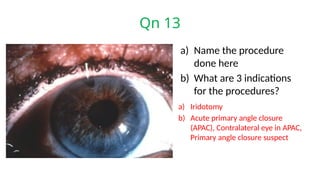
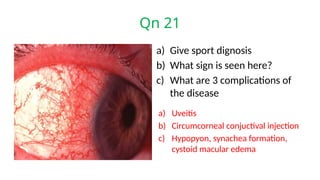
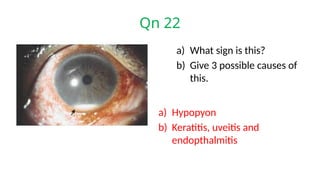
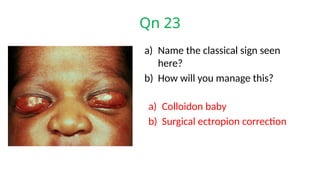
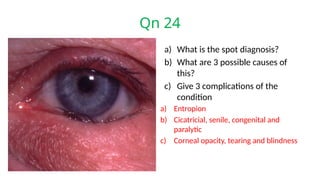
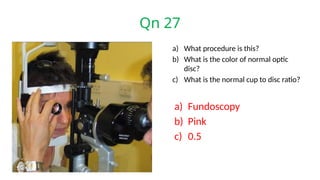
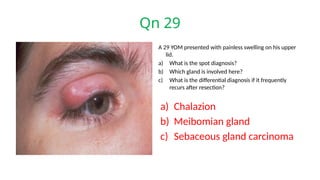
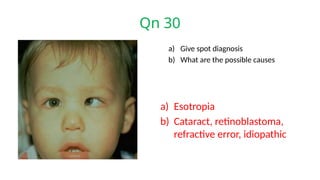
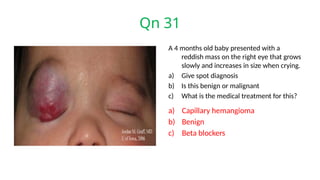
The document presents a series of ophthalmology case questions and answers, covering various conditions, their diagnoses, management options, and potential complications. Key conditions discussed include cataracts, corneal ulcers, amblyopia, and fungal keratitis, along with their respective treatments and surgical options. The format includes a mix of patient presentations, diagnostic inquiries, and clinical management strategies, aimed at medical training in ophthalmology.