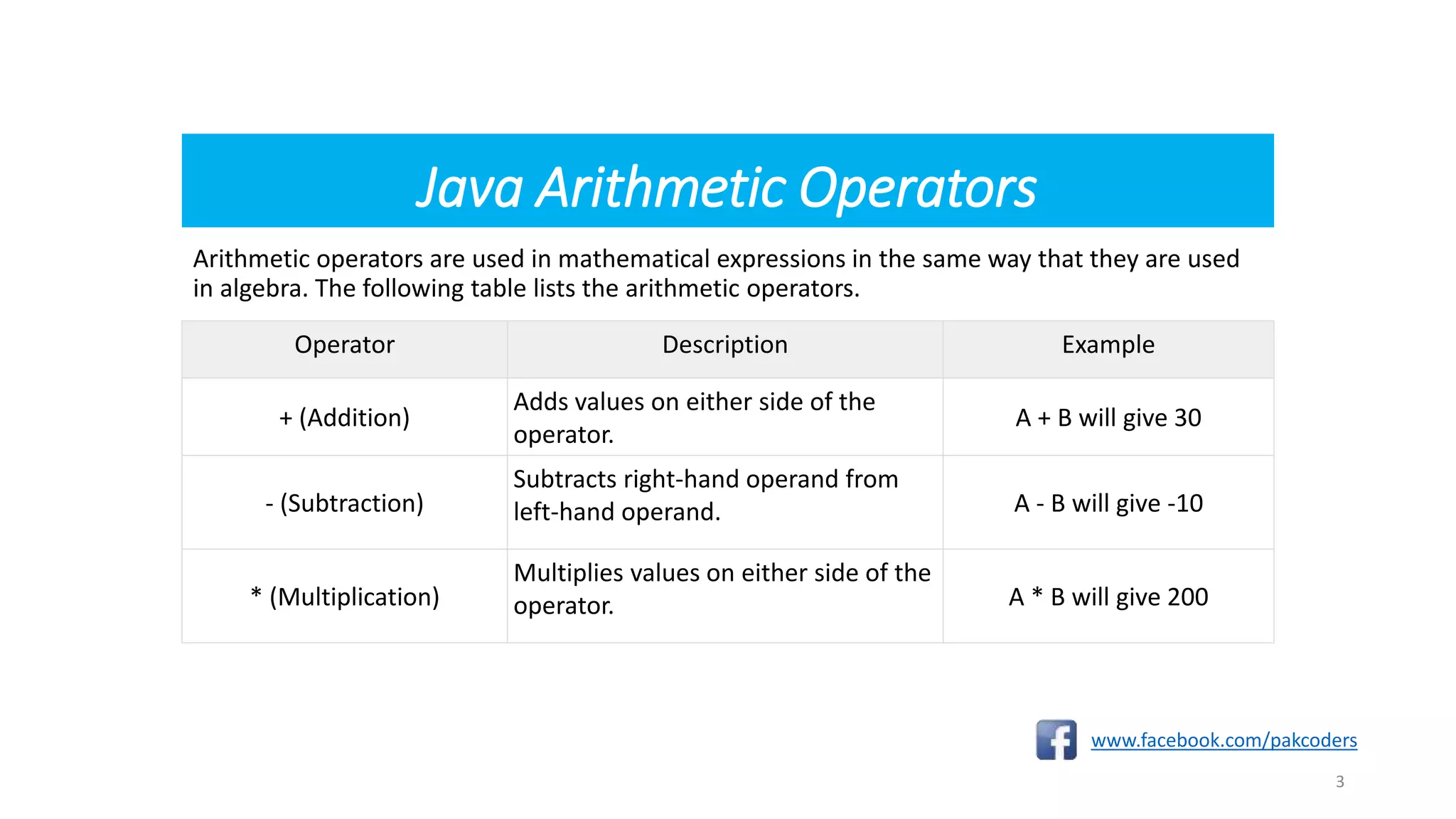
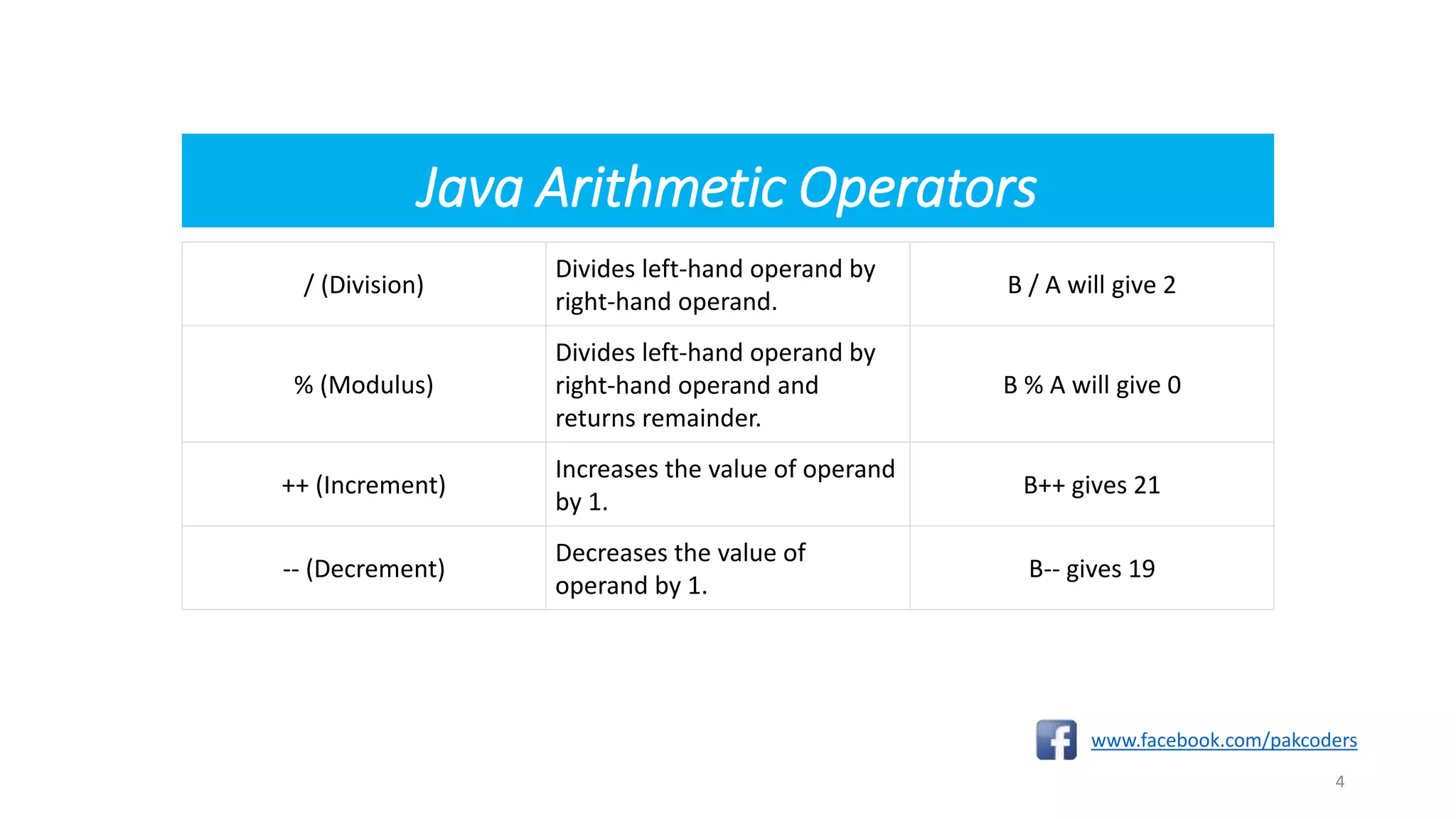
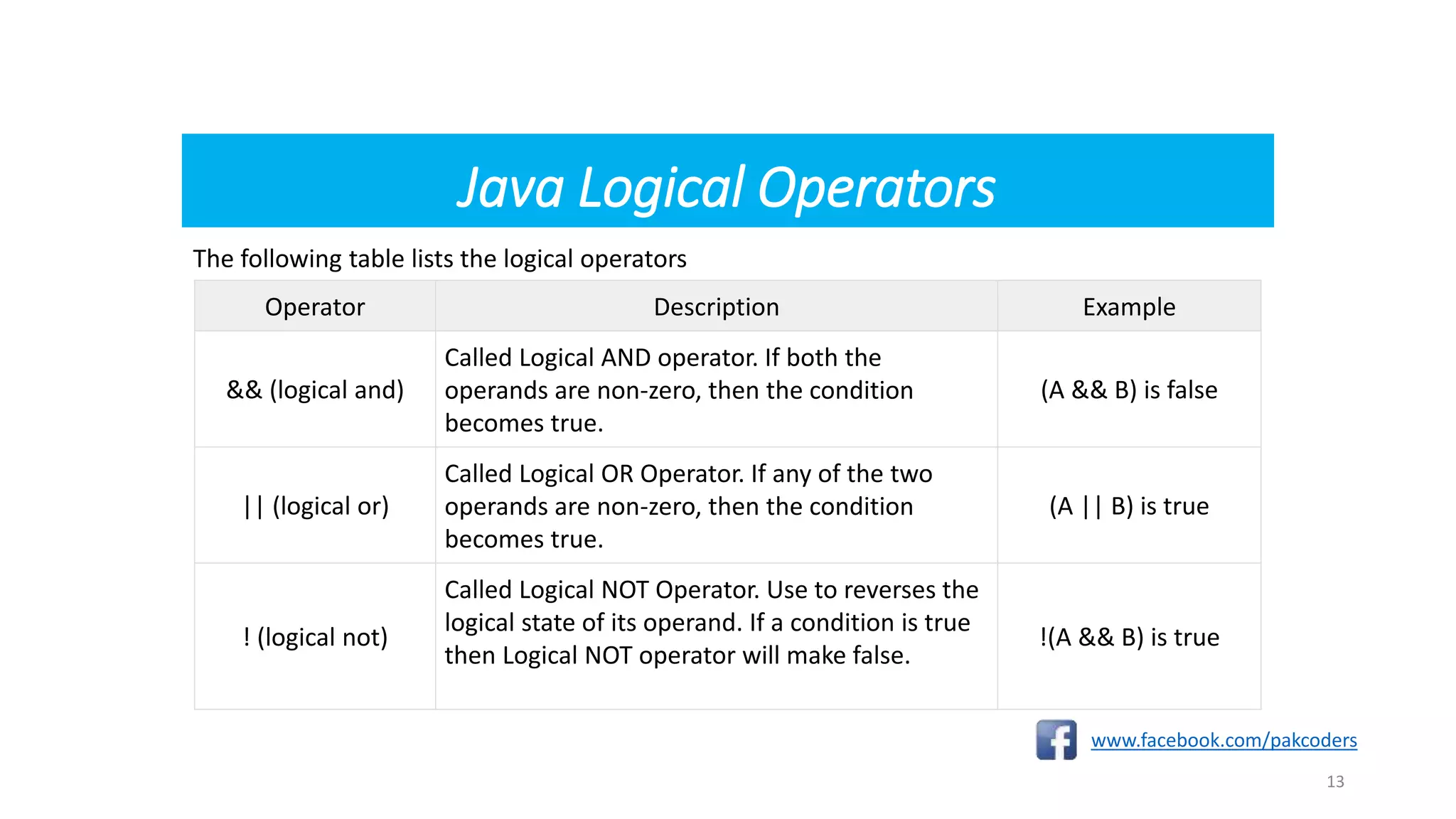
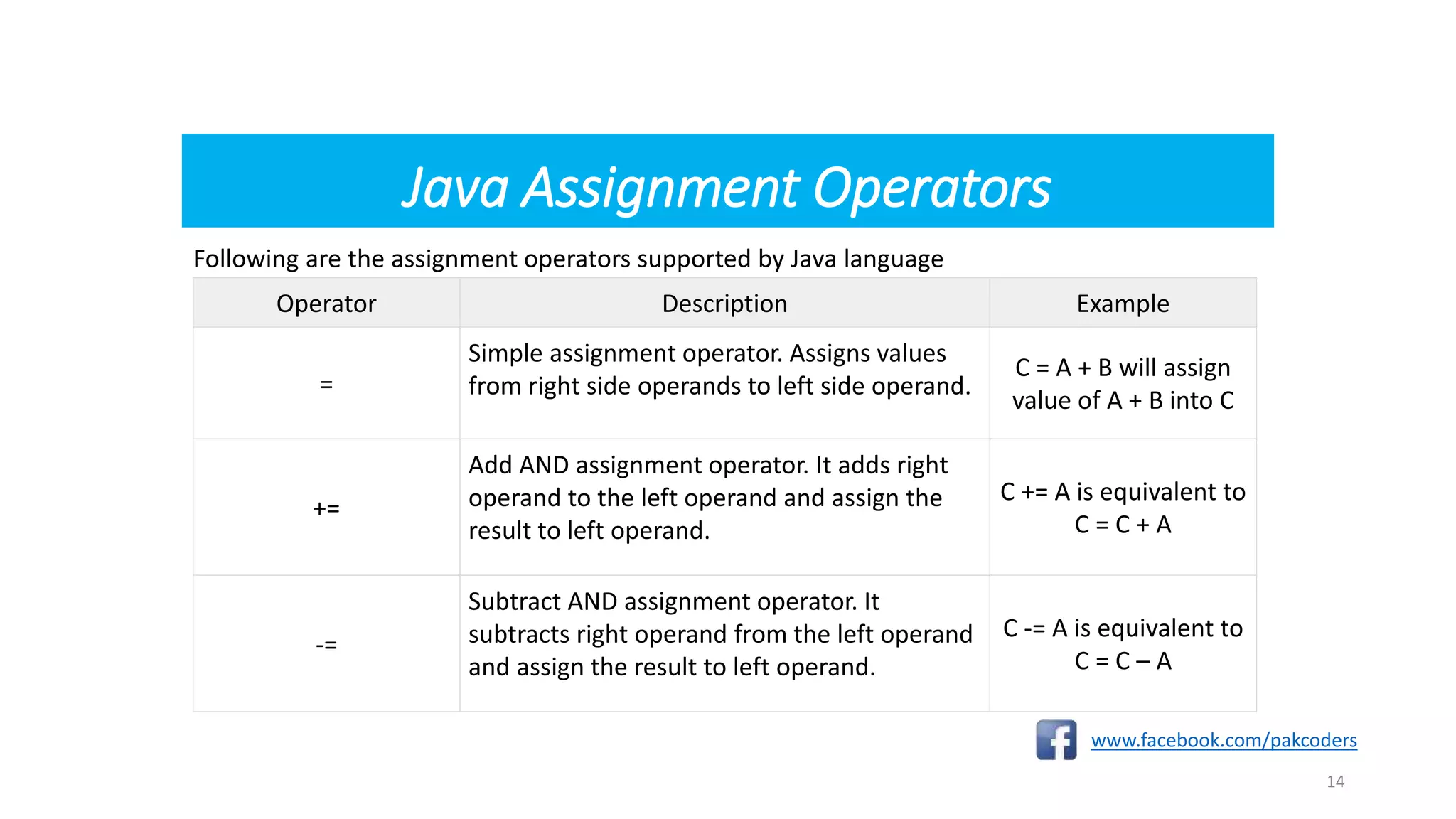
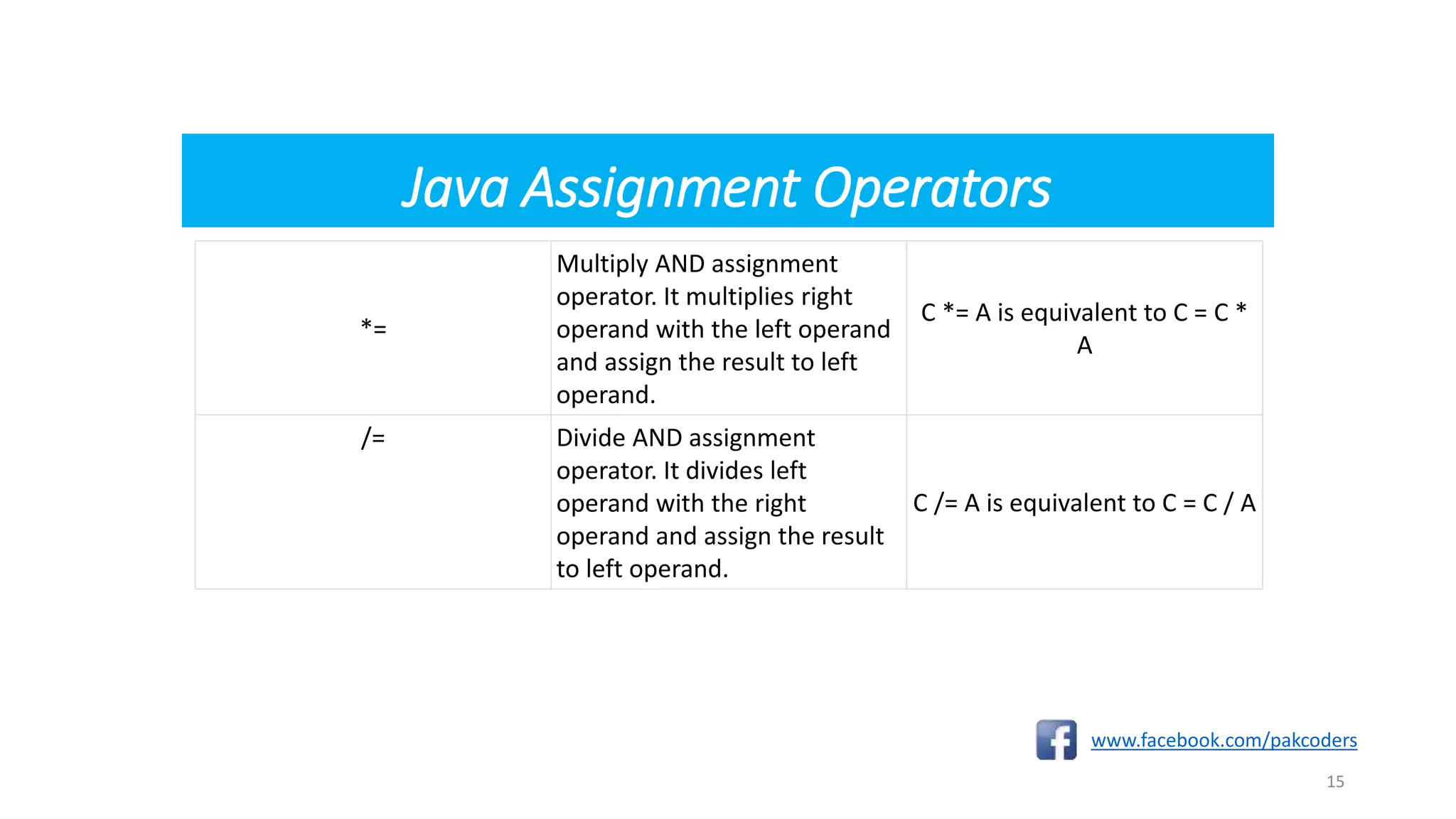
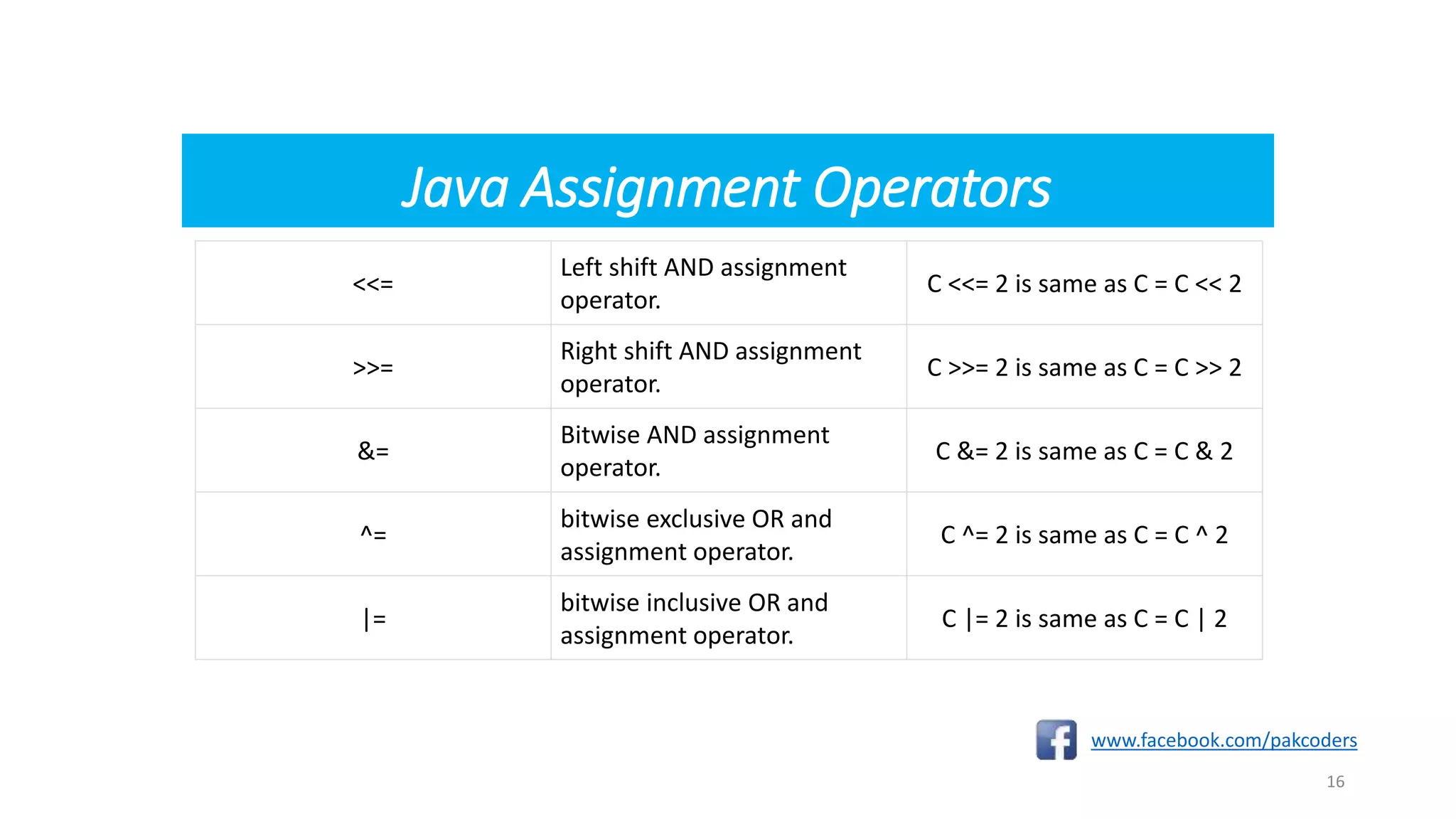
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the Java programming language, specifically detailing various types of operators including arithmetic, relational, logical, assignment, and miscellaneous operators. It illustrates each operator with examples and outputs of sample Java code. Additionally, it explains how operators work within expressions and their syntax in Java programming.
![Example
www.facebook.com/pakcoders
5
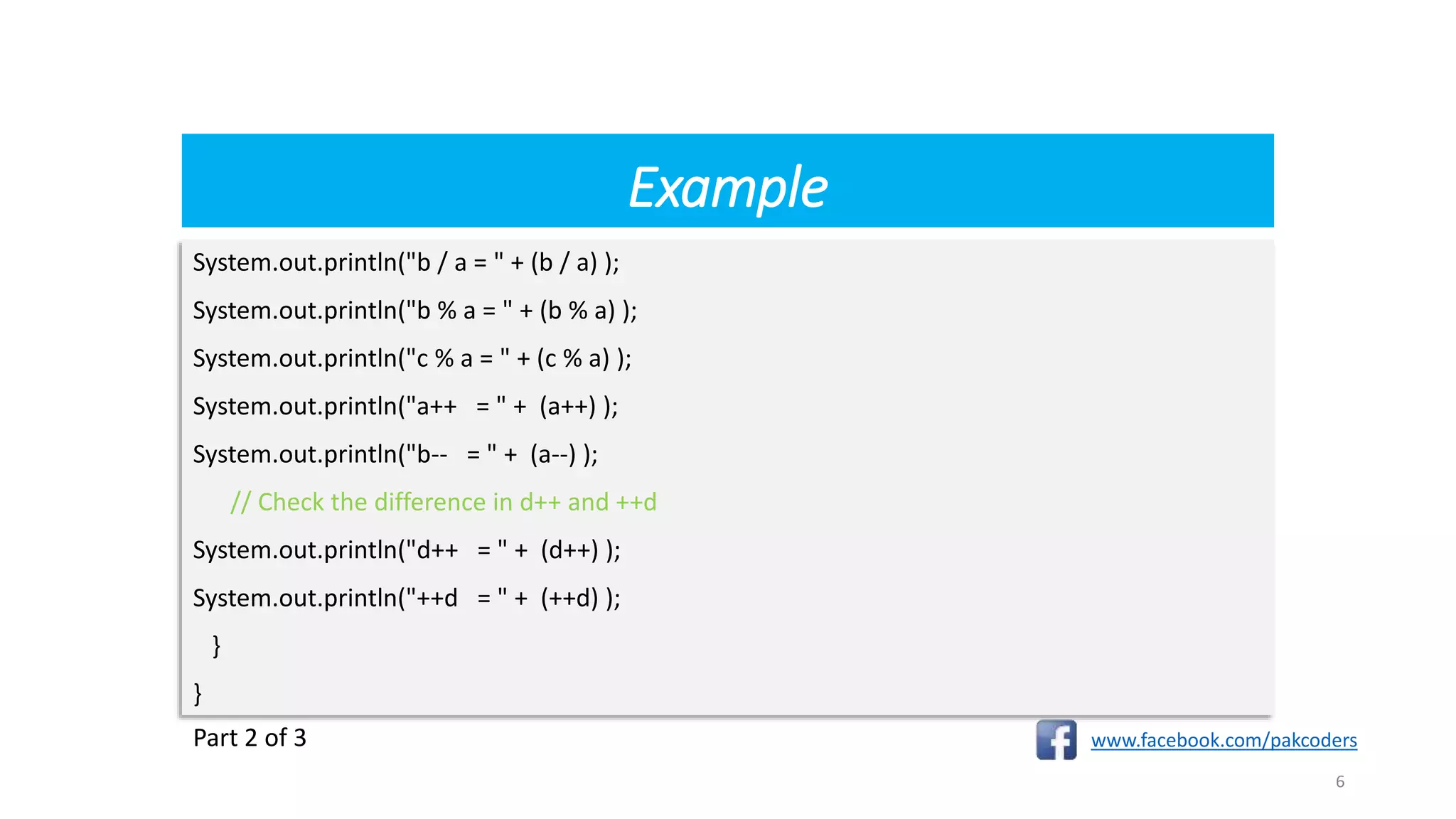
class Test{
Public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 25;
int d = 25;
System.out.println("a + b = " + (a + b) );
System.out.println("a - b = " + (a - b) );
System.out.println("a * b = " + (a * b) );
Part 1 of 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operators-190924171513/75/Operators-In-Java-Part-8-5-2048.jpg)

![Example
www.facebook.com/pakcoders
10
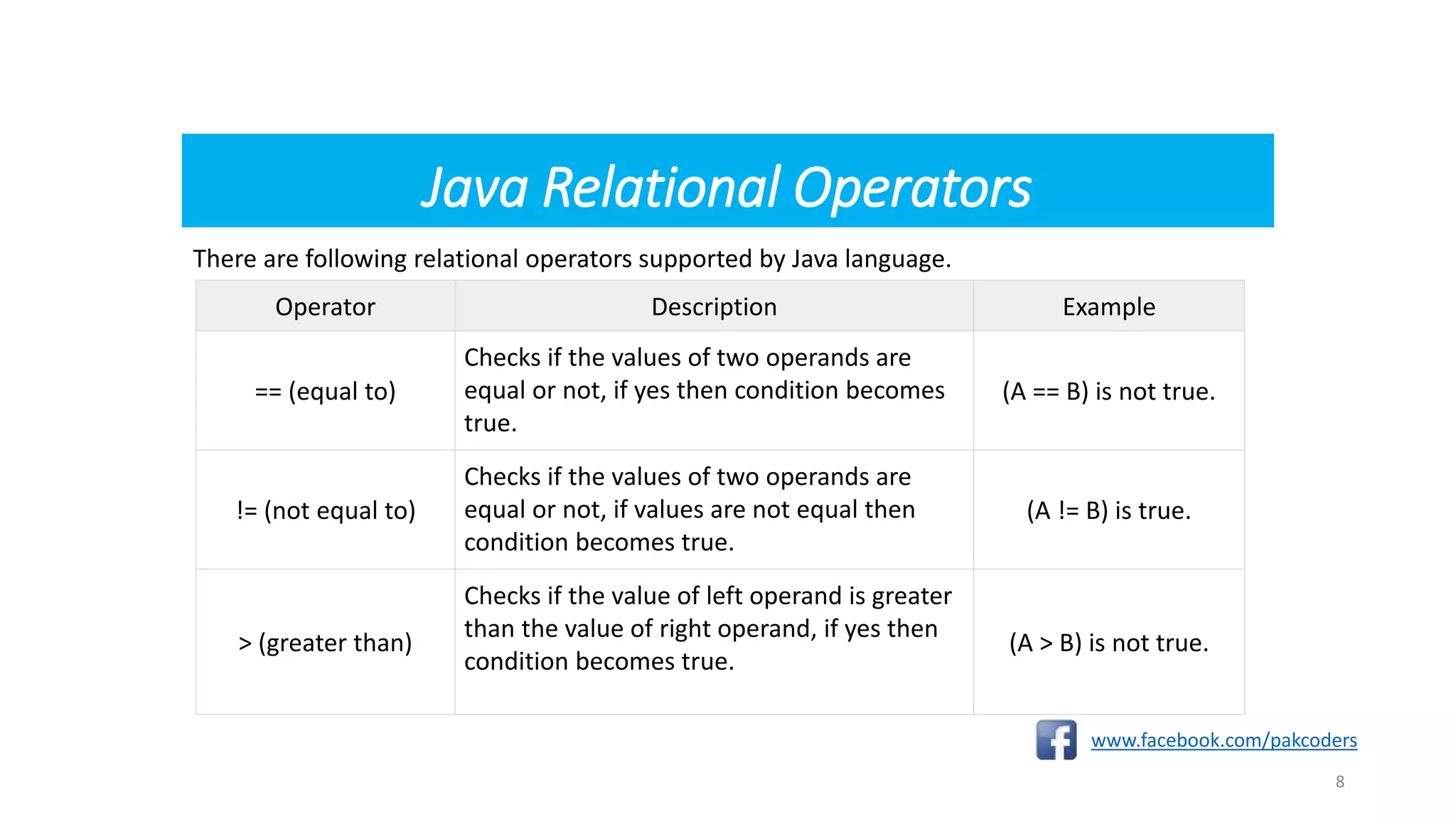
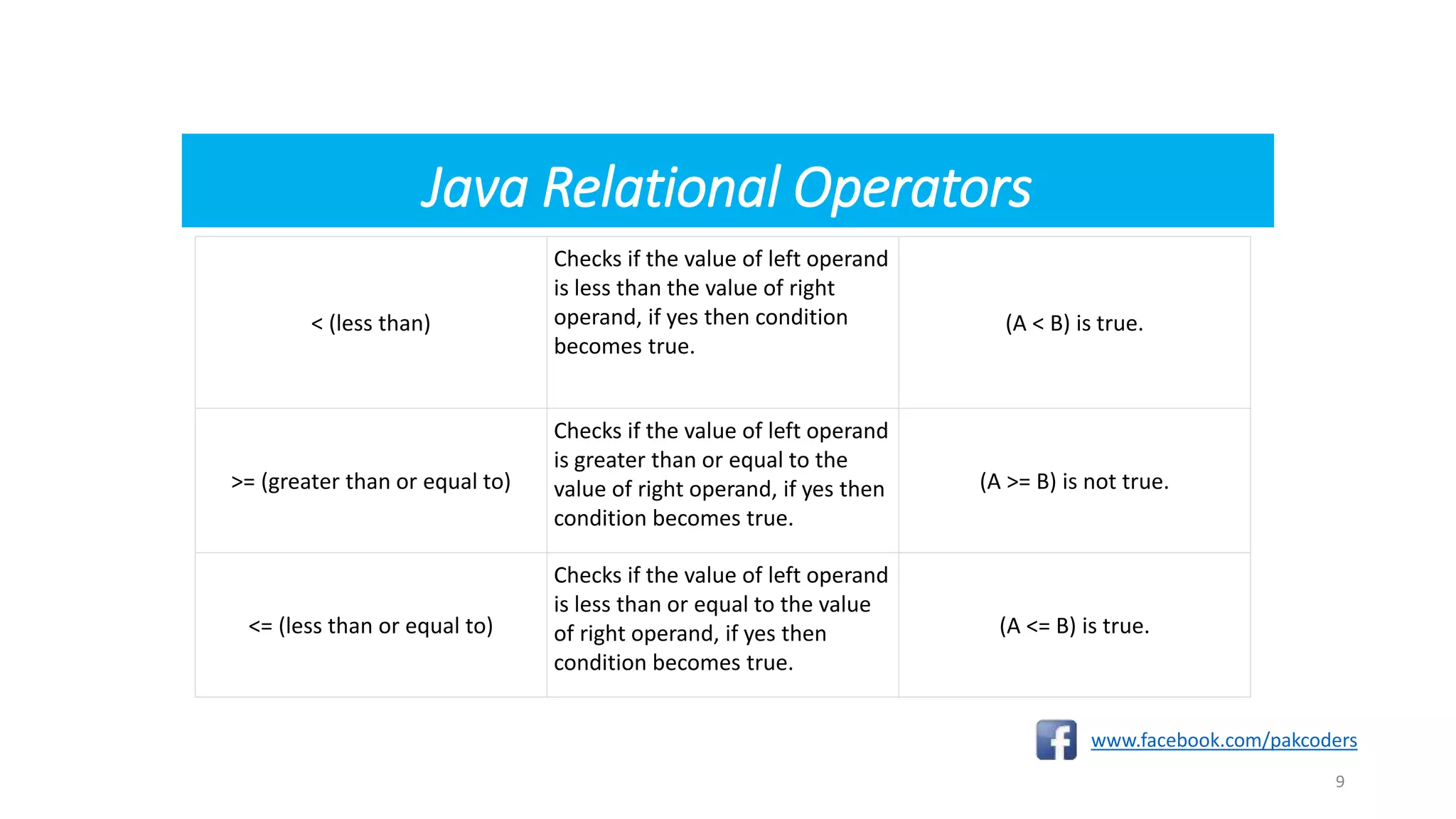
class Test{
Public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
System.out.println("a == b = " + (a == b) );
System.out.println("a != b = " + (a != b) );
System.out.println("a > b = " + (a > b) );
System.out.println("a < b = " + (a < b) );
System.out.println("b >= a = " + (b >= a) );
Part 1 of 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operators-190924171513/75/Operators-In-Java-Part-8-10-2048.jpg)


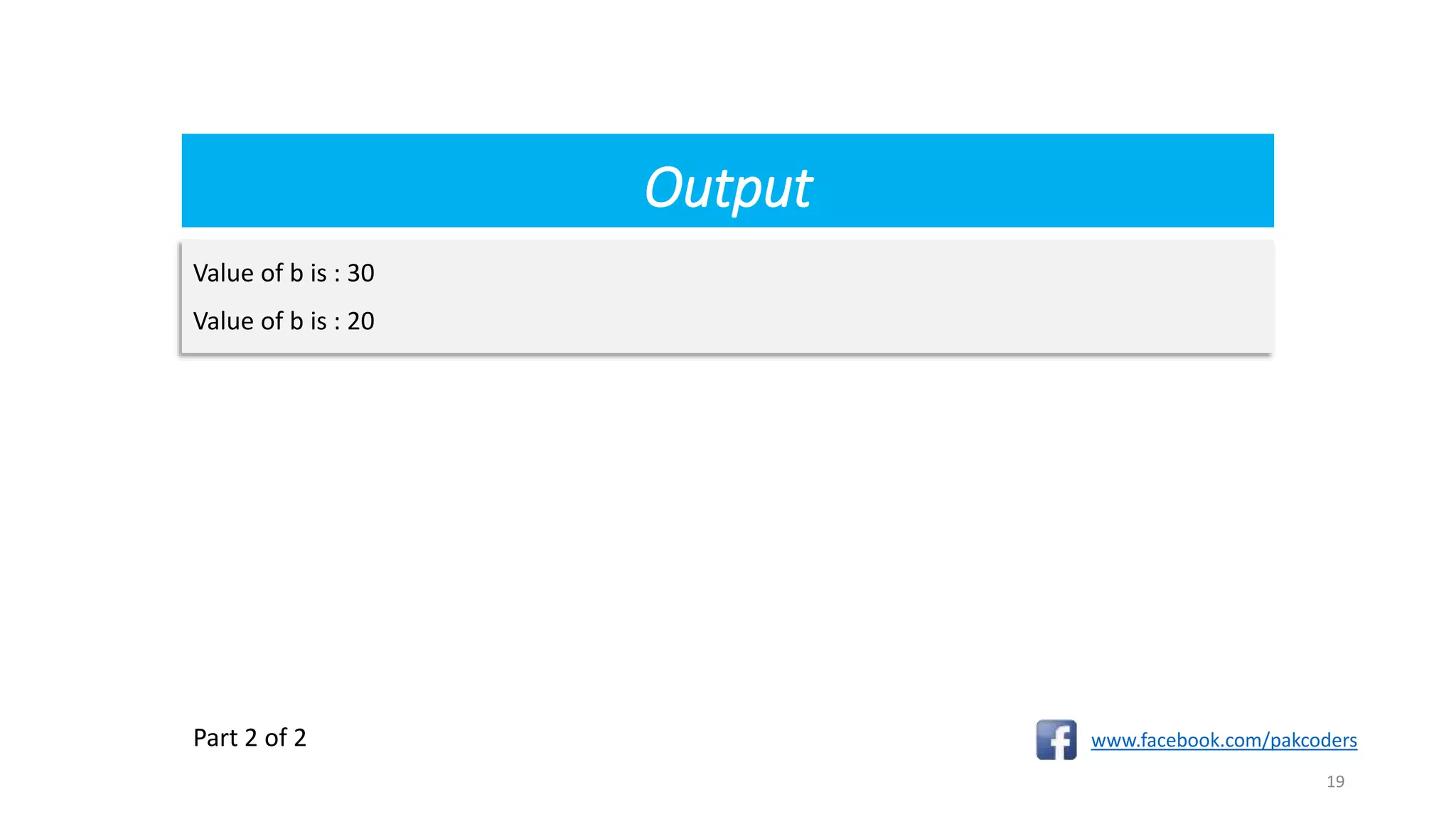
![Example
www.facebook.com/pakcoders
18
class Test{
Public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = (a == 1) ? 20 : 30;
System.out.println( "Value of b is : " + b );
b = (a == 10) ? 20 : 30;
System.out.println( "Value of b is : " + b );
Part 1 of 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operators-190924171513/75/Operators-In-Java-Part-8-18-2048.jpg)