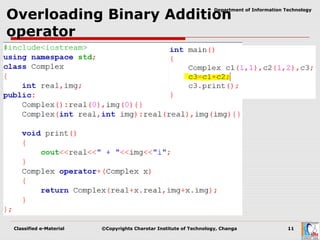
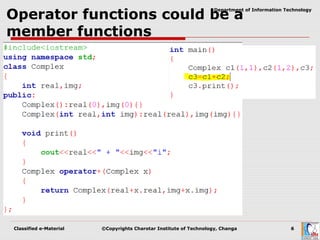
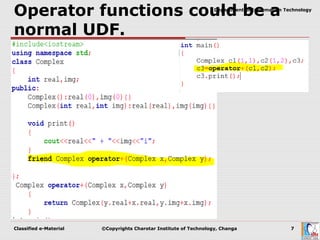
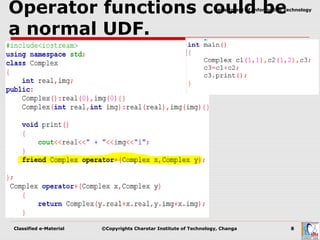
Operator overloading allows user-defined types to have special meanings applied to operators like + and *. It is a form of polymorphism that allows operators to work on custom data types like user-defined objects in the same way they work on built-in types. To overload an operator, a programmer defines operator functions that specify the behavior for that operator when used on a class. These functions can be member functions or non-member functions. Certain operators cannot be overloaded and rules govern the number of arguments for operator functions.





![Classified e-Material ©Copyrights Charotar Institute of Technology, Changa 9
Department of Information Technology
Rules for operator overloading
Only existing operators is overloaded. Can
not create new operators.
Overloaded operator must have at least one
operands.
Basic meaning of operator could not be
changed.
Some operators can not be overloaded like
dot(.), ::, ?:, sizeof, etc.
We can not use friend function to overload
some operators like =, (), [], ->.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/operatoroverloading-180403061900/85/Operator-overloading-9-320.jpg)