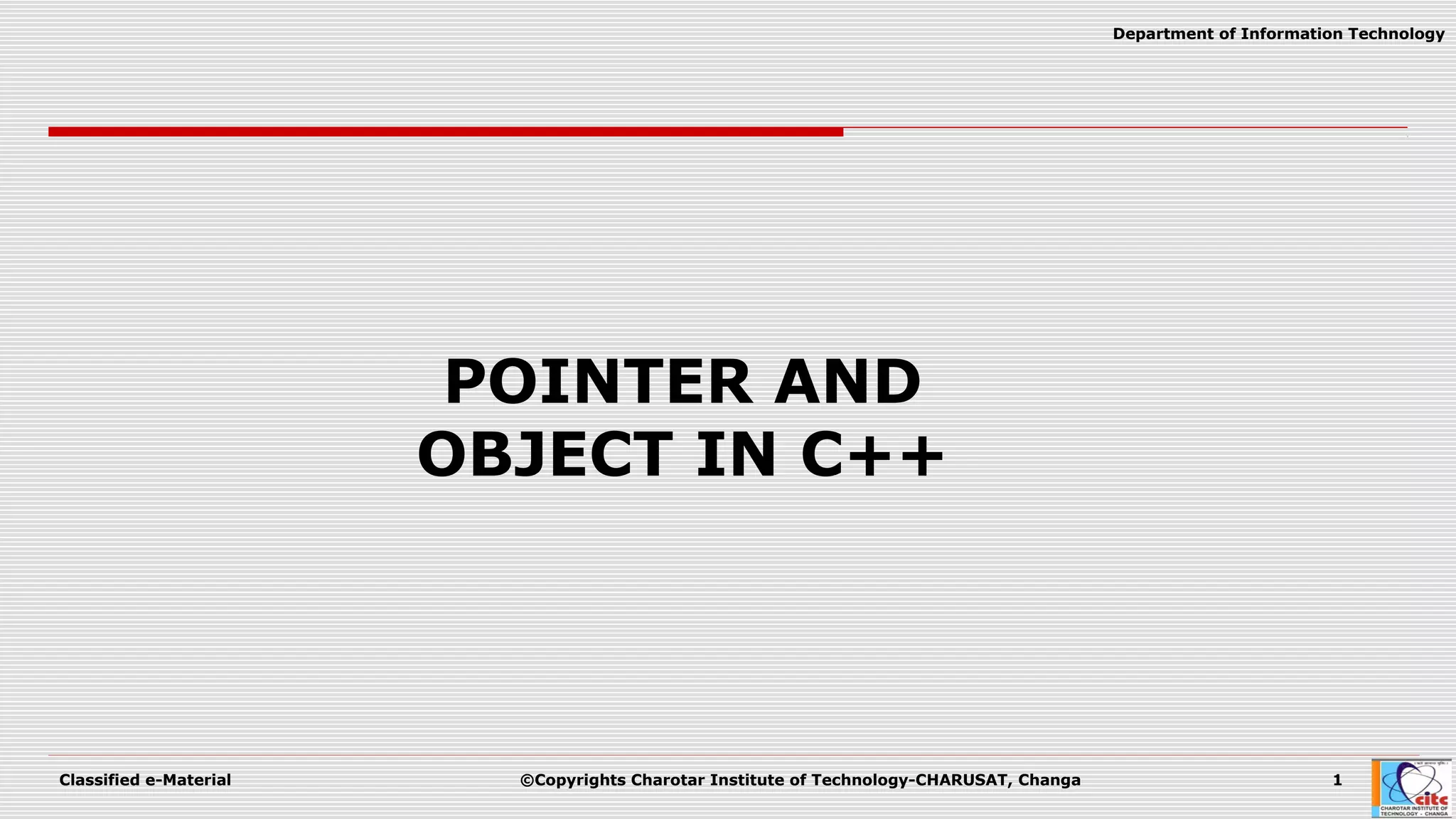
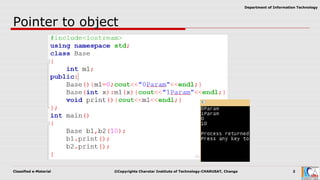
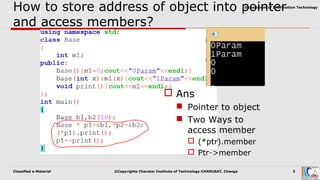
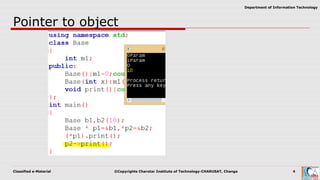
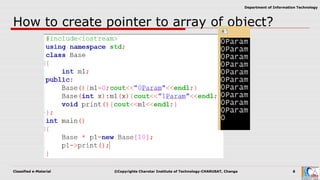
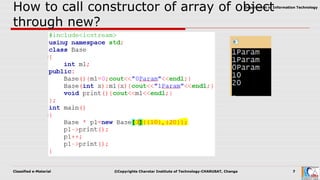
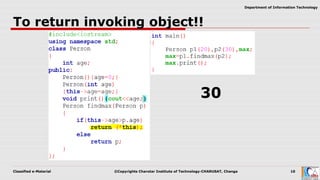
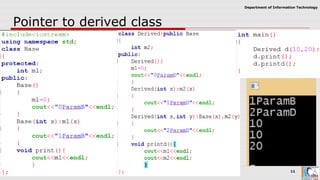
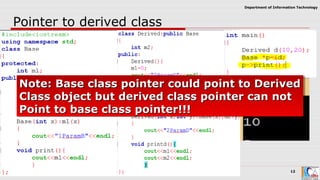
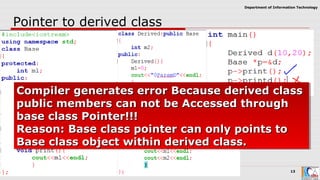
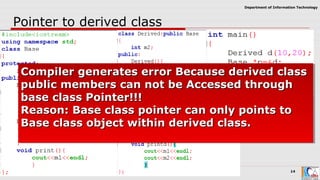
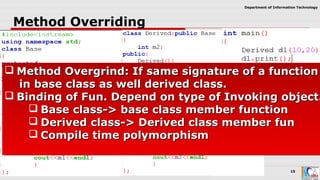
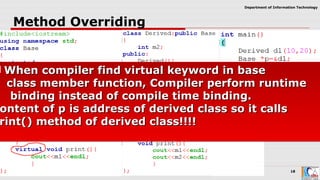
This document discusses pointers and objects in C++. It covers storing the address of an object in a pointer, accessing members through pointers, pointers to derived classes, and method overriding. It explains that pointers to base classes can point to derived class objects, but pointers to derived classes cannot point to base class objects. Method overriding and virtual functions allow calling derived class methods through base class pointers at runtime.