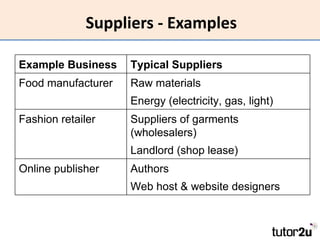
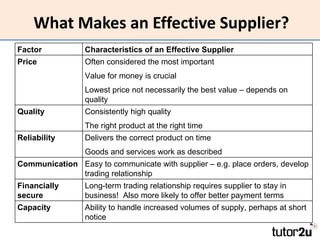
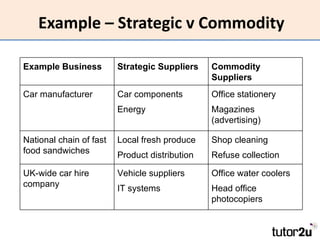
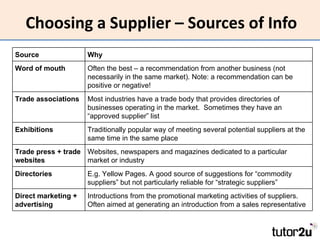
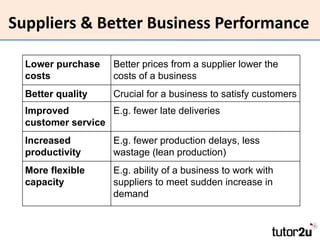
The document discusses suppliers and how to work effectively with them. It defines a supplier as a business or individual that provides goods and services to another business. It notes that suppliers determine costs and quality and can be a source of financing. Effective suppliers provide competitive pricing, high quality, reliability, good communication and financial stability. The document emphasizes choosing suppliers carefully based on strategic importance and provides tips for contracting with suppliers to improve business performance through lower costs, better quality and service, increased productivity and flexibility.