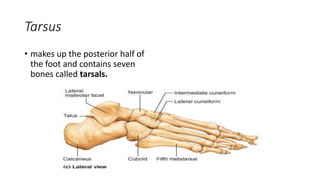
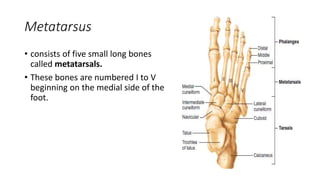
The appendicular skeleton includes the pectoral girdle, upper limbs, pelvic girdle, and lower limbs. The pectoral girdle consists of the clavicles and scapulae. The upper limbs are divided into the arm, forearm, and hand. The arm contains the humerus, while the forearm contains the radius and ulna. The hand includes carpal bones, metacarpal bones, and phalanges. The pelvic girdle attaches the lower limbs and supports pelvic organs, consisting of paired hip bones and the sacrum fused from three bones in adults. The lower limbs are divided into the thigh, leg, and foot. The thigh