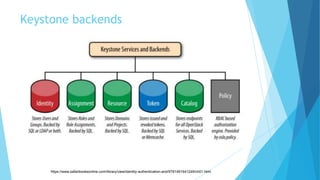
Keystone is the identity service for OpenStack. It handles authentication, authorization, and managing service catalogs and endpoints. Keystone provides a user directory and authentication mechanism for other OpenStack services to use. It supports user management, project/tenant isolation, role-based access control and token validation. Keystone uses pluggable backends like SQL, LDAP or Memcached to store user and credential data.









![Token formats - PKI/PKIZ
● PKI - Public Key Infrastructure
● PKI and PKIZ tokens are nearly identical (and in fact share the same
payload), but PKIZ tokens add compression to the mix
● Payload
● JSON response that would normally be produced as a result of online
token validation
● Format
● CMS (Cryptographic Message Syntax) + [zlib] + base64
● Pros
● Does not go back to keystone for validation
● Cons
● Complex to setup
● E.g
● MIIKtgYJKoZIhvcNAQcCoIIKpzCCCqMCAQExCTAHBgUrDgMCGjCCCY8GCSqGSIb3DQEHAaCCCYAEggl8eyJhY2Nlc3MiOiB7InRva2VuIj
oMFQxNTo1MjowNi43MzMxOTgiLCAiZXhwaXJlcyI6ICIyMDEzLTA1LTMxVDE1OjUyOjA2WiIsICJpZCI6ICJwbGFjZWhvbGRlciIsICJ0ZW
5bCwgImVuYWJsZWQiOiB0cnVlLCAiaWQiOiAiYzJjNTliNGQzZDI4NGQ4ZmEwOWYxNjljYjE4MDBlMDYiLCAibmFtZSI6ICJkZW1vIn19L
Cb2ludHMiOiBbeyJhZG1pblVSTCI6ICJodHRwOi8vMTkyLjE2OC4yNy4xMDA6OD
http://docs.openstack.org/admin-guide/keystone_certificates_for_pki.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c3220366-6ec7-4ae1-9fab-1b43caf9a6c9-160822184134/85/OpenStack-Keystone-11-320.jpg)






