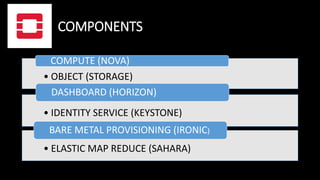
OpenStack is a free and open-source cloud computing platform primarily deployed as infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) to manage pools of data center resources. Initiated in 2010 through a collaboration between NASA and Rackspace, OpenStack has evolved to provide a comprehensive cloud environment with components for computing, storage, and management. Its flexible architecture allows integration with various technologies, making it suitable for public and private cloud implementations.