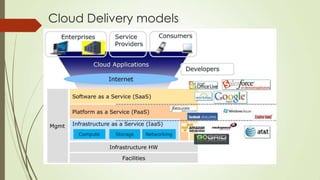
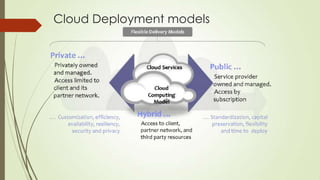
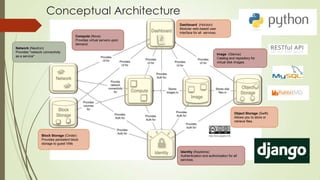
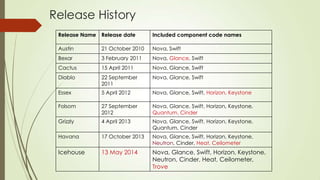
OpenStack is an open source software platform for building private and public clouds. It allows companies to build their own clouds that provide infrastructure as a service. The software controls large pools of compute, storage, and networking resources throughout a datacenter, all managed through APIs. DevStack is a tool that developers use to quickly deploy OpenStack locally for testing their code changes before they are reviewed. It builds a complete OpenStack development environment on a single node.












![localrc Sample
[[local|localrc]]
FIXED_RANGE=10.254.1.0/24
NETWORK_GATEWAY=10.254.1.1
LOGDAYS=1
LOGFILE=$DEST/logs/stack.sh.log
SCREEN_LOGDIR=$DEST/logs/screen
ADMIN_PASSWORD=quiet
DATABASE_PASSWORD=$ADMIN_PASSWORD
RABBIT_PASSWORD=$ADMIN_PASSWORD
SERVICE_PASSWORD=$ADMIN_PASSWORD
SERVICE_TOKEN=a682f596-76f3-11e3-b3b2-e716f9080d50](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/openstackcommunity-openstackintroduction-140401141007-phpapp02/85/GDL-OpenStack-Community-Openstack-Introduction-17-320.jpg)


