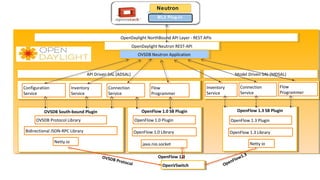
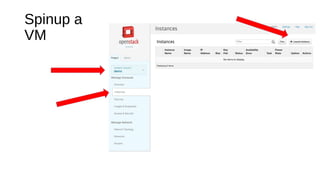
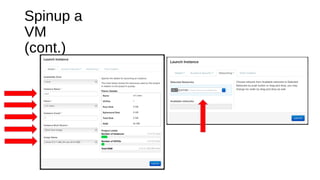
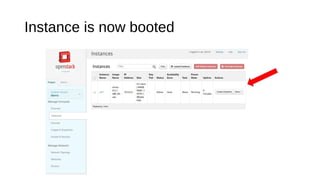
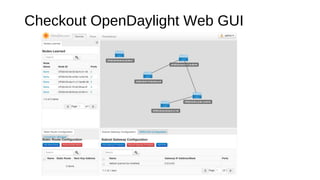
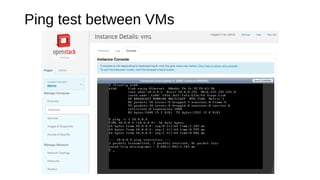
The document provides a detailed guide for setting up and using OpenDaylight with OpenStack, including hands-on experiences with virtualization on Fedora and building a multi-node environment. Key topics include configuration, using REST APIs, and specific practical steps for launching OpenDaylight and OpenStack instances. It also outlines requirements, logistics, and troubleshooting tips for the setup process.