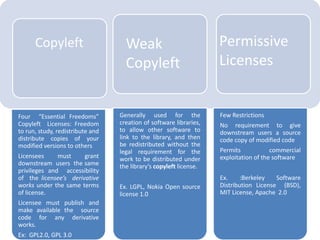
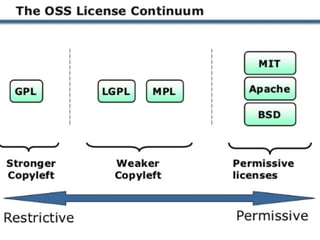
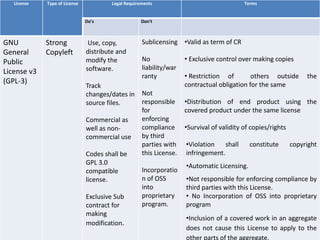
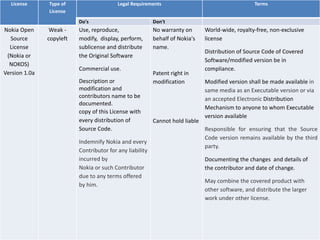
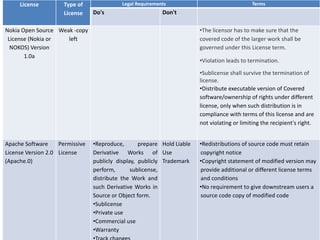
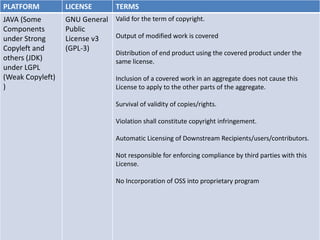
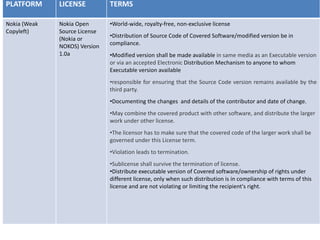
The document provides an overview of open source software (OSS) and its licensing, highlighting the essential differences between OSS and commercial software. It categorizes licenses into copyleft and non-copyleft, outlining their terms and conditions, and discusses relevant legal cases regarding compliance issues. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of understanding license terms for proper software usage and modification to avoid breach of contractual obligations.