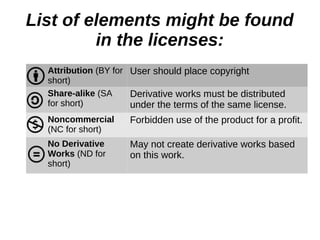
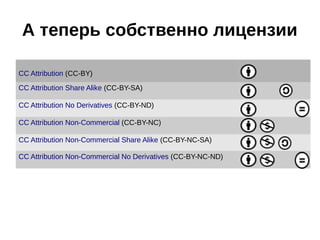
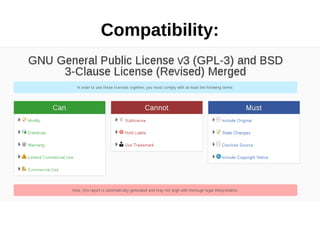
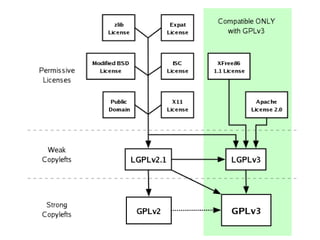
The document provides an overview of licenses related to intellectual property, including distinctions between permissive licenses, copyleft, and various types of licenses such as GPL, LGPL, and Creative Commons. It emphasizes the importance of licenses in protecting copyright, allowing modifications, and ensuring the distribution of software, along with the rights and obligations they entail. Additionally, it outlines the rights granted to users, including the ability to use, modify, and share software within the constraints of each specific license.