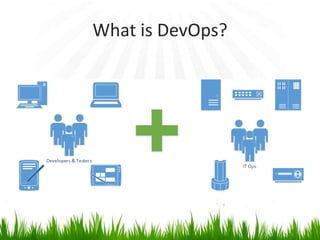
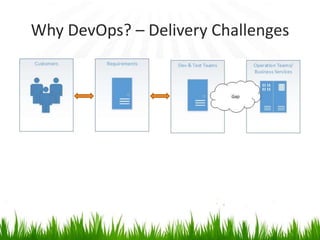
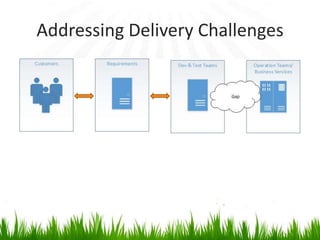
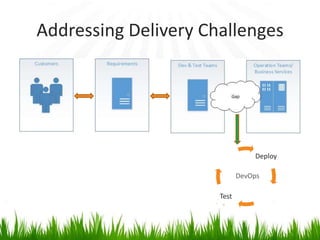
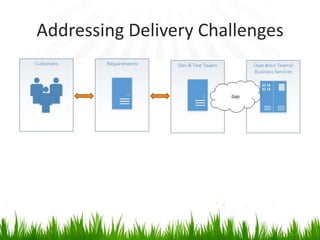
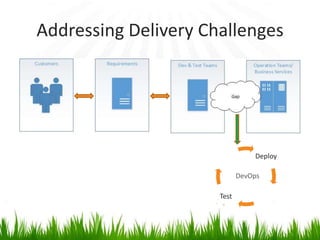
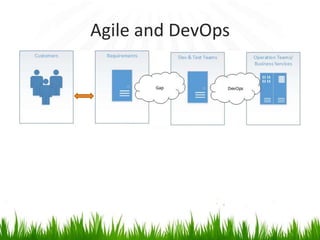
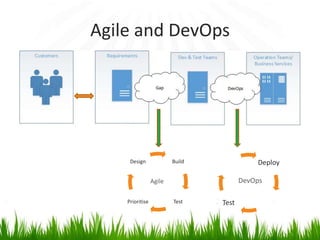
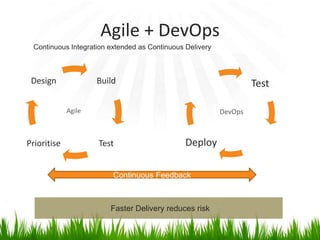
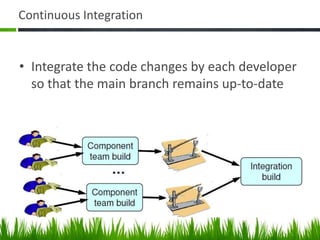
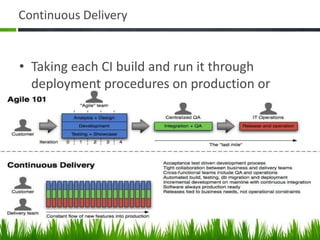
The document provides an overview of DevOps, emphasizing its role in enhancing collaboration between development and operations teams to improve product delivery, quality, and reduce costs. It outlines the principles of DevOps, the challenges faced in delivery, and the distinctions between DevOps and traditional release management. Additionally, it discusses factors driving the adoption of DevOps and when it is appropriate to implement this methodology.