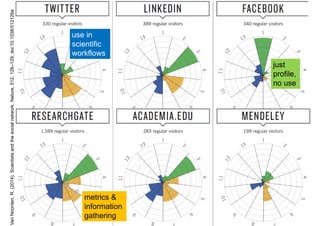
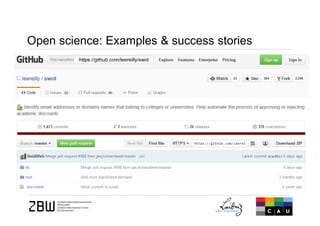
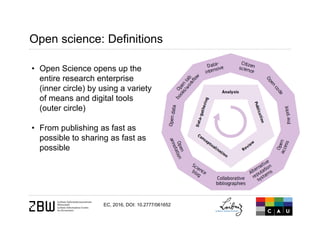
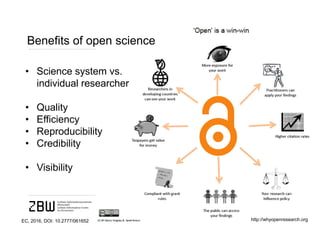
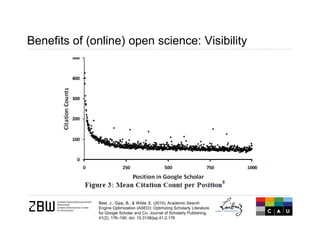
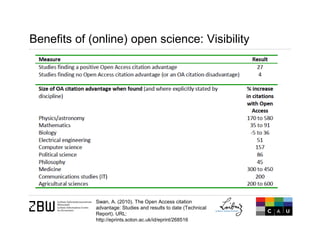
The document discusses open science and the role of social media in scholarly communication, highlighting how digital technologies are transforming the way science and innovation operate. It emphasizes the benefits of open science, such as increased visibility and collaboration, while also addressing potential risks and criticisms associated with open publishing, particularly in regard to peer review and academic legitimacy. Additionally, it introduces altmetrics as a means to measure the impact of scientific work beyond traditional citation metrics.













![Risks (?) of open science
• Blogging is a waste of precious time that could be spent on “legitimate”
publishing
• Because it’s a form of self-publishing that lacks peer review, blogging
isn’t usually viewed as a legitimate form of scholarship
• Dismissal of my work because it’s online [and] criticisms that my work
isn’t good enough to be published anywhere else.
• Sometimes blogging is even seen as disseminating one’s ideas too
freely. In a competitive academic field, research ideas could be
“scooped” from a blog, while established journals may not want to
publish work that’s available in some form online.
http://blogs.lse.ac.uk/impactofsocialsciences/2011/11/3
0/should-you-enter-the-academic-blogosphere/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sofia2017petersfinal-170304110735/85/Open-Science-Altmetrics-23-320.jpg)

![Doom of metrics: Academia fights back
San Francisco Declaration of Research Assessment
(http://am.ascb.org/dora)
• “The declaration intends to halt the practice of correlating the
journal impact factor to the merits of a specific scientist's
contributions. [:] this practice creates biases and inaccuracies
when appraising scientific research. [:] the impact factor is not
to be used as a substitute ‘measure of the quality of individual
research articles, or in hiring, promotion, or funding decisions’”
Altmetrics Manifesto (http://altmetrics.org/manifesto)
• “Altmetrics expand our view of what impact looks like, but also of
what’s making the impact. [:] Unlike citation metrics, altmetrics
will track impact outside the academy, impact of influential but
uncited work, and impact from sources that aren’t peer-reviewed.
[:] The speed of altmetrics presents the opportunity to create
real-time recommendation and collaborative filtering systems”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sofia2017petersfinal-170304110735/85/Open-Science-Altmetrics-25-320.jpg)








