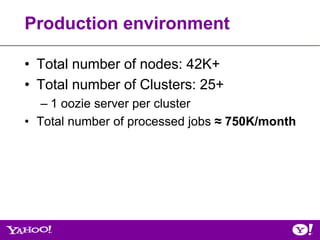
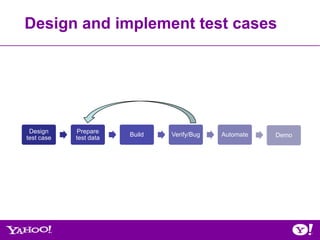
The document outlines the Oozie QE qualification process, detailing its purpose as a scalable and secure workflow scheduling system for Hadoop. It describes qualification stages, including developing test plans, executing tests, and supporting production deployments, while also highlighting challenges and future tasks. Key aspects include various types of testing, such as functional, stress, and integration tests, along with lessons learned and ongoing work to improve test coverage and system compatibility.



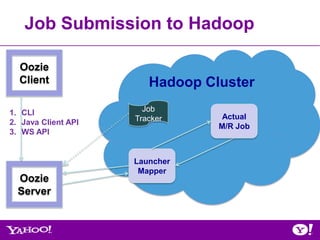




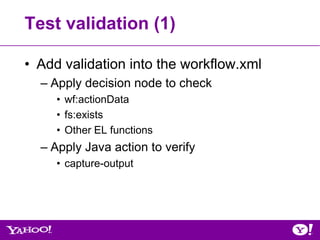


















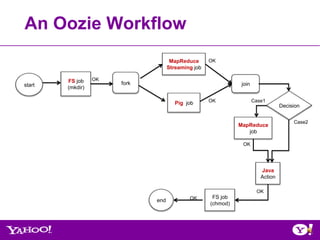
![Oozie ‘Wordcount’ Workflow Example
• Non-Oozie (single map-reduce job)
From Gateway,
[yourid@gwgd2211 ~]$ hadoop jar hadoop-examples.jar wordcount
-Dmapred.job.queue.name=queue_name inputDir outputDir
• Oozie
MapReduce OK
Start
wordcount
End Workflow.xml
ERROR
Kill](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oozie-qa-hug-071812-120719173602-phpapp01/85/July-2012-HUG-Overview-of-Oozie-Qualification-Process-37-320.jpg)
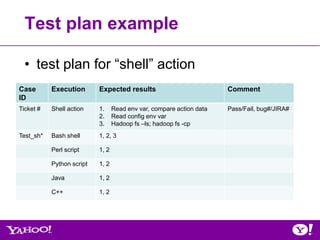
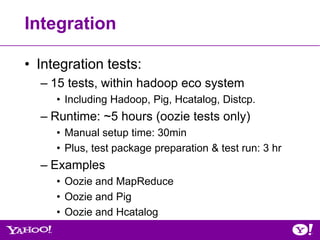
![Example: shell-action workflow.xml
<shell xmlns="uri:oozie:shell-action:0.1">
<!– skip lines -->
Shell action <exec>${SCRIPT}</exec>
<argument>-classpath</argument>
<argument>./${SCRIPTFILE}:$CLASSPATH</argument>
<argument>script</argument>
<file>${SCRIPTFILE}#${SCRIPTFILE}</file>
<capture-output/>
wf:actionData
</shell>
matches?
false
<decision name="decision1">
true <switch><case to="end">${wf:actionData('shell-
sh')['PATH1'] == 'Reset'}</case>
<default to="fail" />
end </switch>
kill </decision>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oozie-qa-hug-071812-120719173602-phpapp01/85/July-2012-HUG-Overview-of-Oozie-Qualification-Process-38-320.jpg)