The document discusses the principles of object-oriented programming (OOP) using PHP, including key concepts like classes, objects, inheritance, and interfaces. It highlights the advantages of OOP such as code reusability and organization while also noting potential pitfalls like complexity and tightly coupled code. The presentation emphasizes best practices for designing classes and methods, including the single responsibility principle and the use of dependency injection.



![LonestarPHP
2015
4
Class
class Employee {
protected $name; // This is a member
protected $number;
// This is a Method
public function setData($data) {
$this->name = $data['name'];
$this->number = $data['number'];
}
public function viewData() {
echo <<<ENDTEXT
Name: {$this->name}
Number: {$this->number}
ENDTEXT;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopismorethancatsanddogs-150417103743-conversion-gate02/85/OOP-is-more-than-Cars-and-Dogs-4-320.jpg)









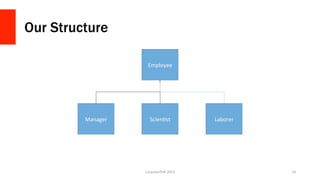
![The Employee Class
LonestarPHP
2015
15
abstract class Employee {
protected $name; // Employee Name
protected $number; // Employee Number
public function setData($data) {
$this->name = $data['name'];
$this->number = $data['number'];
}
public function viewData() {
echo <<<ENDTEXT
Name: {$this->name}
Number: {$this->number}
ENDTEXT;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopismorethancatsanddogs-150417103743-conversion-gate02/85/OOP-is-more-than-Cars-and-Dogs-15-320.jpg)
![The Manager Class
LonestarPHP
2015
16
class Manager extends Employee {
protected $title; // Employee Title
protected $dues; // Golf Dues
public function setData($data) {
parent::setData($data);
$this->title = $data['title'];
$this->dues = $data['dues'];
}
public function viewData() {
parent::viewData();
echo <<<ENDTEXT
Title: {$this->title}
Golf Dues: {$this->dues}
ENDTEXT;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopismorethancatsanddogs-150417103743-conversion-gate02/85/OOP-is-more-than-Cars-and-Dogs-16-320.jpg)
![The Scientist Class
LonestarPHP
2015
17
class Scientist extends Employee {
protected $pubs; // Number of Publications
public function setData($data) {
parent::setData($data);
$this->pubs = $data['pubs'];
}
public function viewData() {
parent::viewData();
echo <<<ENDTEXT
Publications: {$this->pubs}
ENDTEXT;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopismorethancatsanddogs-150417103743-conversion-gate02/85/OOP-is-more-than-Cars-and-Dogs-17-320.jpg)





![The Employee Class
LonestarPHP
2015
23
abstract class Employee {
protected $name; // Employee Name
protected $number; // Employee Number
public function setData($data) {
$this->name = $data['name'];
$this->number = $data['number'];
}
public function viewData() {
echo <<<ENDTEXT
Name: {$this->name}
Number: {$this->number}
ENDTEXT;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopismorethancatsanddogs-150417103743-conversion-gate02/85/OOP-is-more-than-Cars-and-Dogs-23-320.jpg)
![The Manager Class
LonestarPHP
2015
24
class Manager extends Employee {
protected $title; // Employee Title
protected $dues; // Golf Dues
public function setData($data) {
parent::setData($data);
$this->title = $data['title'];
$this->dues = $data['dues'];
}
public function viewData() {
parent::viewData();
echo <<<ENDTEXT
Title: {$this->title}
Golf Dues: {$this->dues}
ENDTEXT;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopismorethancatsanddogs-150417103743-conversion-gate02/85/OOP-is-more-than-Cars-and-Dogs-24-320.jpg)
![An Example
<?php!
// Cannot do this. This will throw the following error:!
// Fatal error: Cannot instantiate abstract class Employee!
$employee = new Employee(); !
// We can do this though!!
$manager = new Manager(); !
// Name is protected, so we can't do this. This throws:!
// Fatal error: Cannot access protected property Manager::$name!
$manager->name = 'Bob McManager’;!
// setData is public, so we can use that!
$manager->setData(['name' => 'Bob McManager’,'number' => 1]);!
// We can also view the data, since it's public!
$manager->viewData();
LonestarPHP
2015
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopismorethancatsanddogs-150417103743-conversion-gate02/85/OOP-is-more-than-Cars-and-Dogs-25-320.jpg)











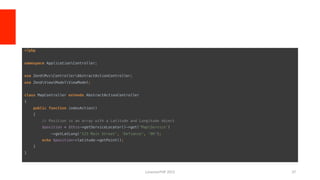









![An Example
/**
* Create a new invoice instance.
*
* @param LaravelCashierContractsBillable $billable
* @param object
* @return void
*/
public function __construct(BillableContract $billable, $invoice)
{
$this->billable = $billable;
$this->files = new Filesystem;
$this->stripeInvoice = $invoice;
}
/**
* Create an invoice download response.
*
* @param array $data
* @param string $storagePath
* @return SymfonyComponentHttpFoundationResponse
*/
public function download(array $data, $storagePath = null)
{
$filename = $this->getDownloadFilename($data['product']);
$document = $this->writeInvoice($data, $storagePath);
$response = new Response($this->files->get($document), 200, [
'Content-Description' => 'File Transfer',
'Content-Disposition' => 'attachment; filename="'.$filename.'"',
'Content-Transfer-Encoding' => 'binary',
'Content-Type' => 'application/pdf',
]);
$this->files->delete($document);
return $response;
}
LonestarPHP
2015
47
hFps://github.com/laravel/cashier/blob/master/src/Laravel/Cashier/Invoice.php](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopismorethancatsanddogs-150417103743-conversion-gate02/85/OOP-is-more-than-Cars-and-Dogs-47-320.jpg)







