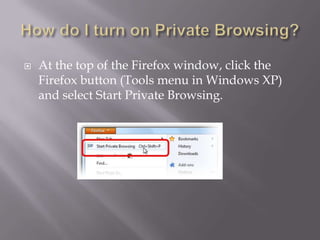
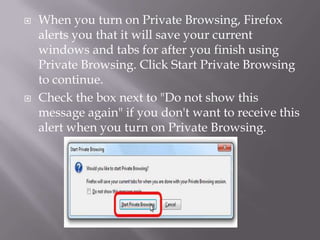
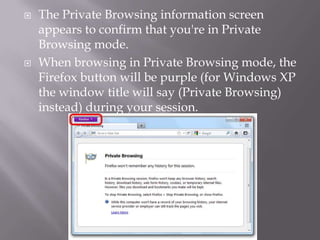
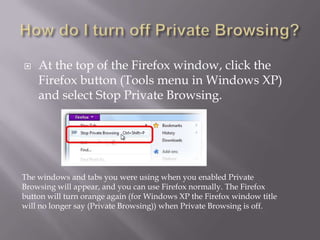
This document discusses computer privacy and security. It defines privacy as the right to control personal information online. It then discusses phishing scams, which try to steal user credentials by posing as trustworthy entities. The document provides examples of phishing scams and outlines best practices for social media privacy and security, including using private browsing which doesn't save browsing history or passwords.