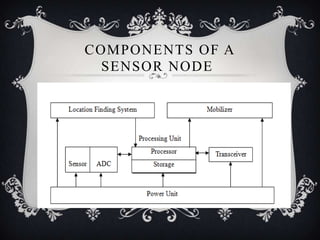
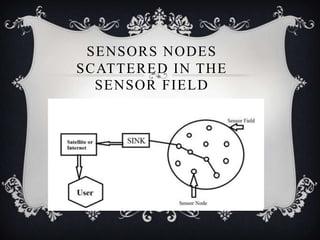
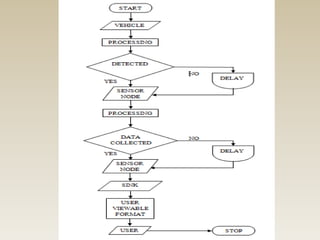
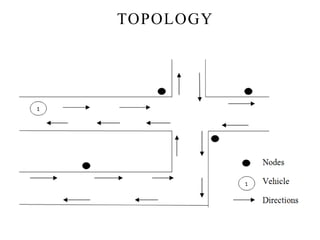
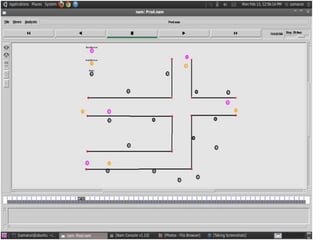
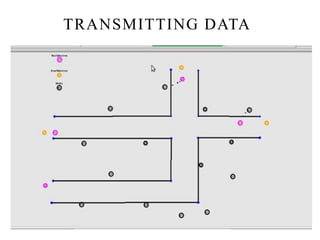
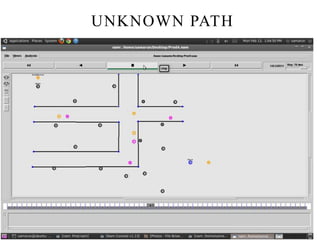
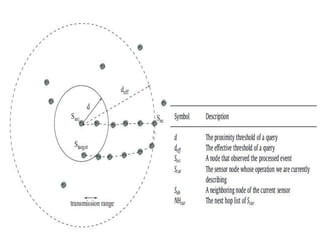
This document discusses detecting proximity events in sensor networks. It introduces the concept of proximity queries, which allows sensor nodes to report interesting events observed within a certain distance of each other. It describes how sensor nodes scattered in a sensor field can detect proximity events using local routing indices and transmit data along predefined or unknown paths. It addresses problems that can occur, such as wasted messages when no matching events are nearby, and presents solutions like rumor-based approaches and incrementally updating local routing indices.