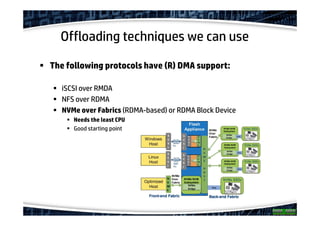
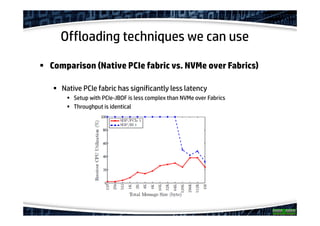
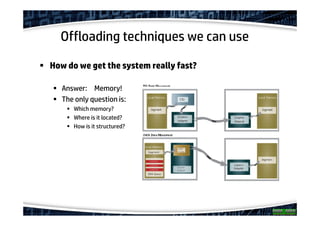
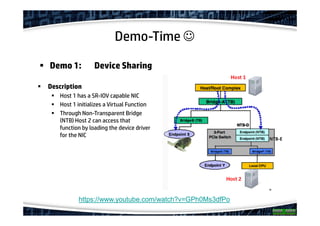
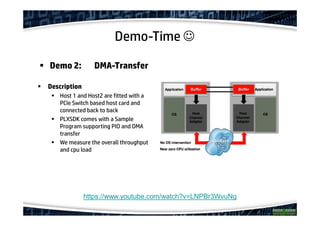
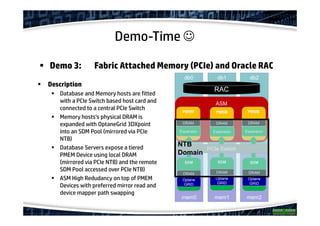
The document explores the concept of offloading in database management, showcasing various techniques and implementations that can help save resources on database servers. It includes discussions of hardware setups, such as DMA engines, and protocols like RDMA for improving data transfer efficiency. The presentation concludes with findings about generic offloading capabilities and the performance potential of fabric-attached memory in database contexts.