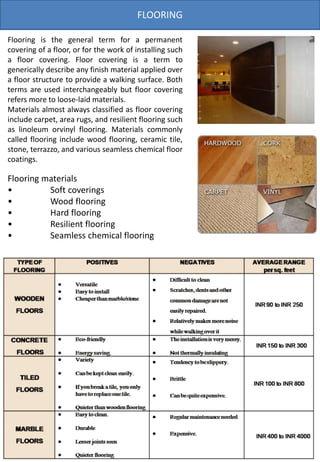
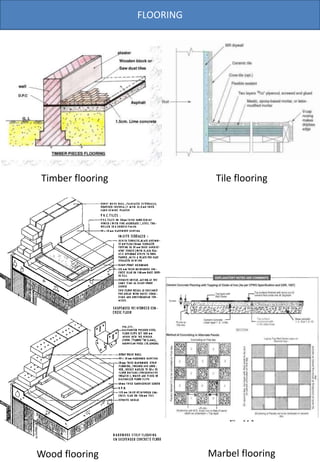
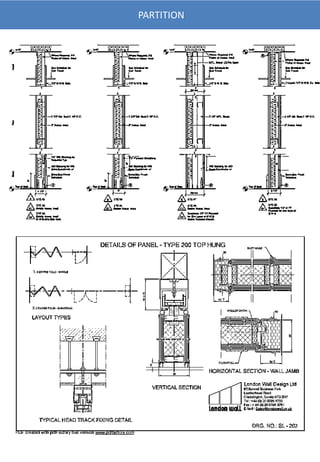
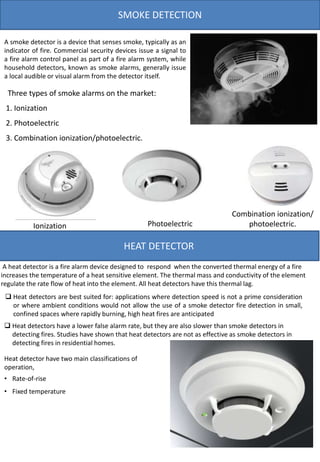
The document provides information on various types of office interiors components including flooring, ceilings, walls, partitions, lighting and smoke detection. It discusses different material options for floors including soft coverings, wood, tile and resilient flooring. It also outlines different ceiling types such as dropped, glass, POP, gypsum and coffered ceilings. Various wall finishes like wood panels, plywood, plaster and laminate are also summarized.