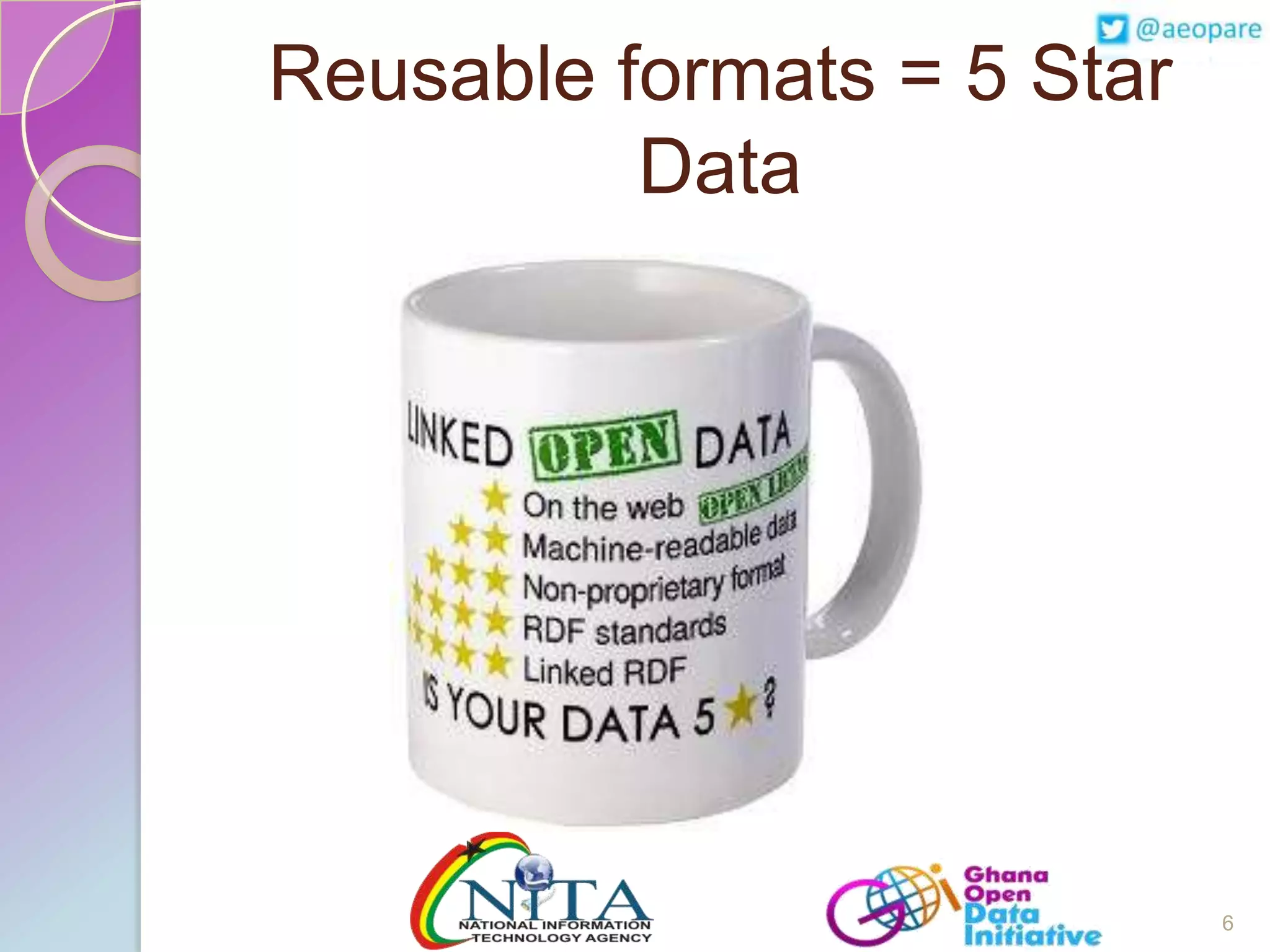
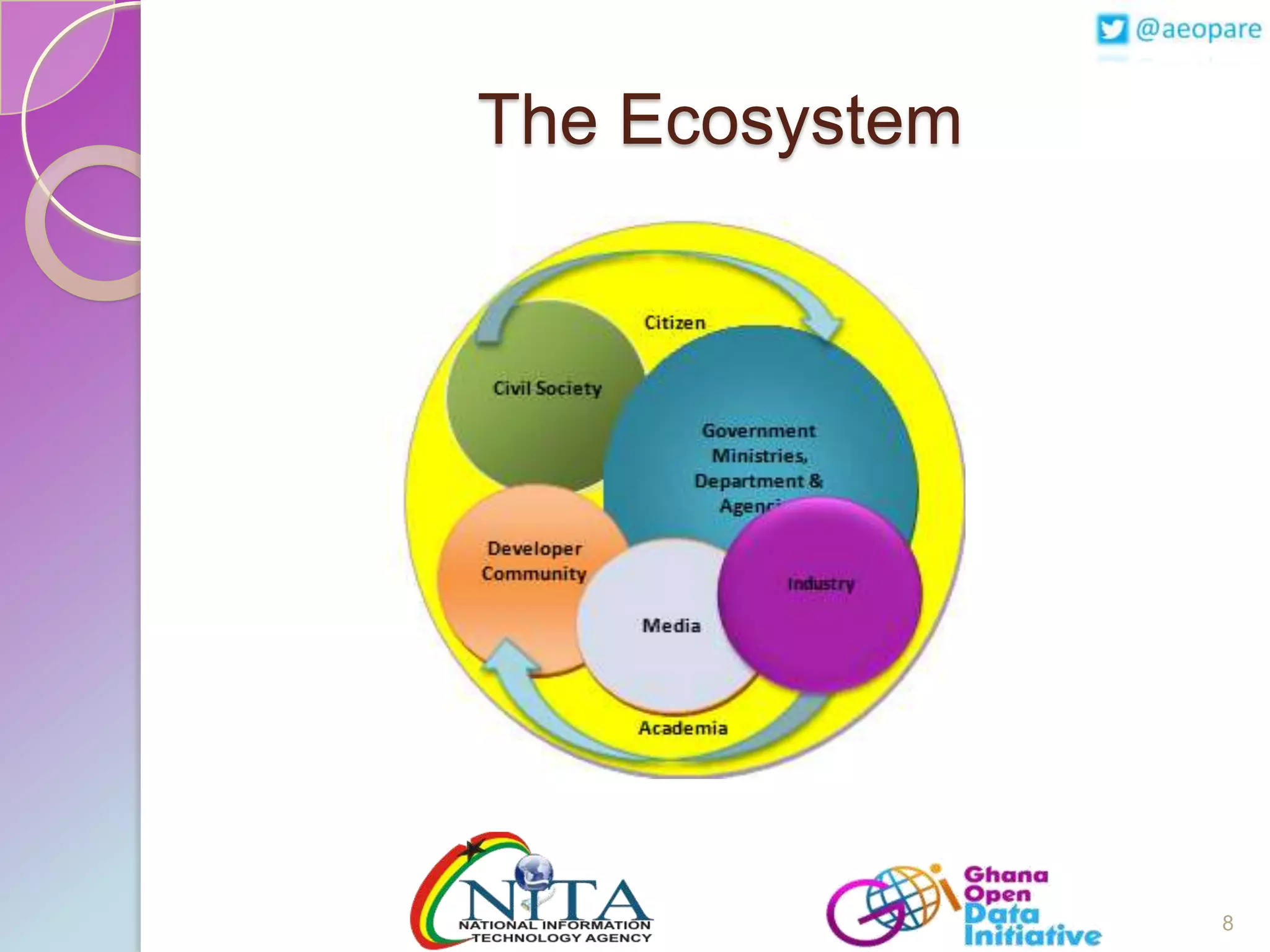
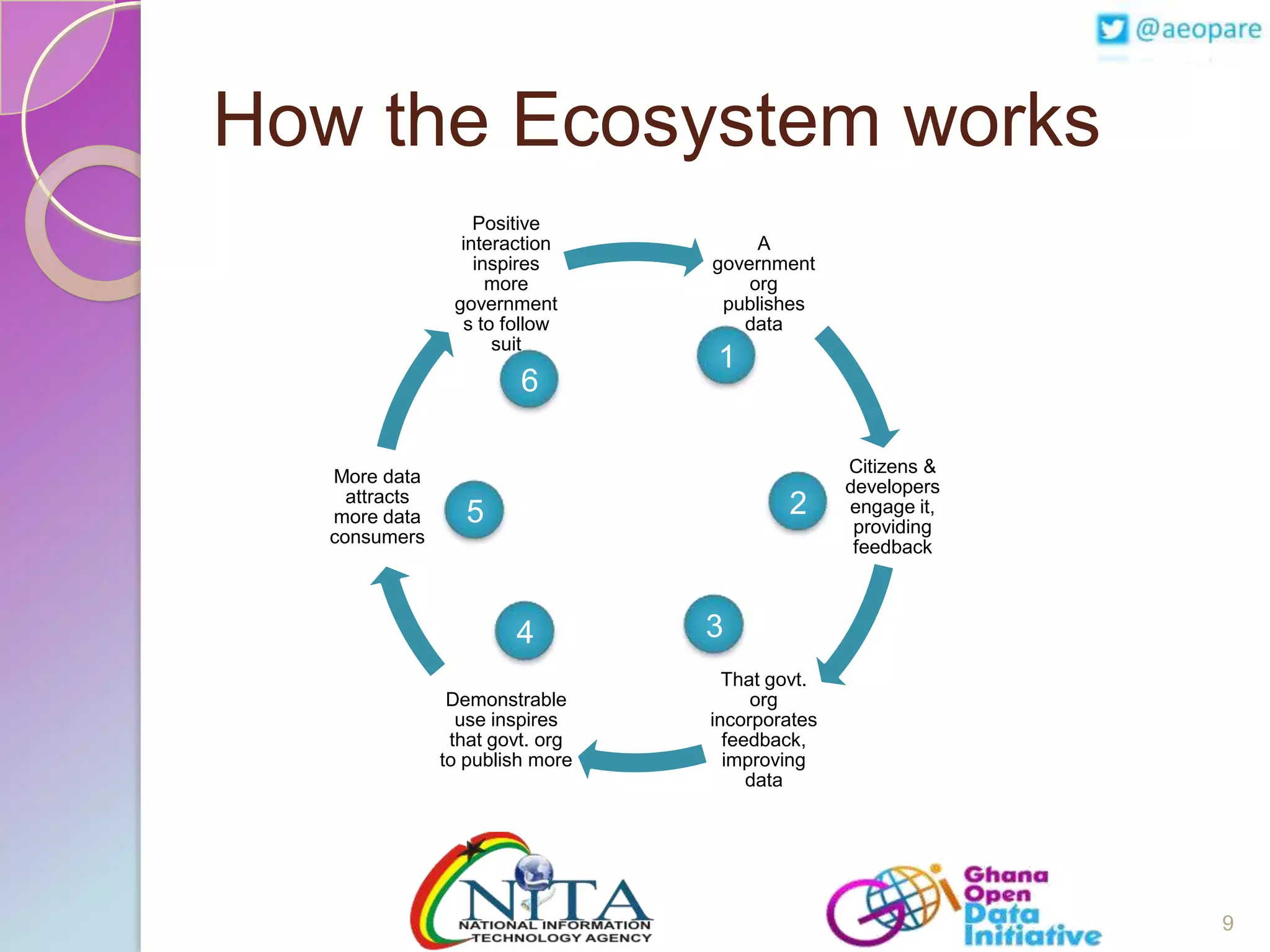
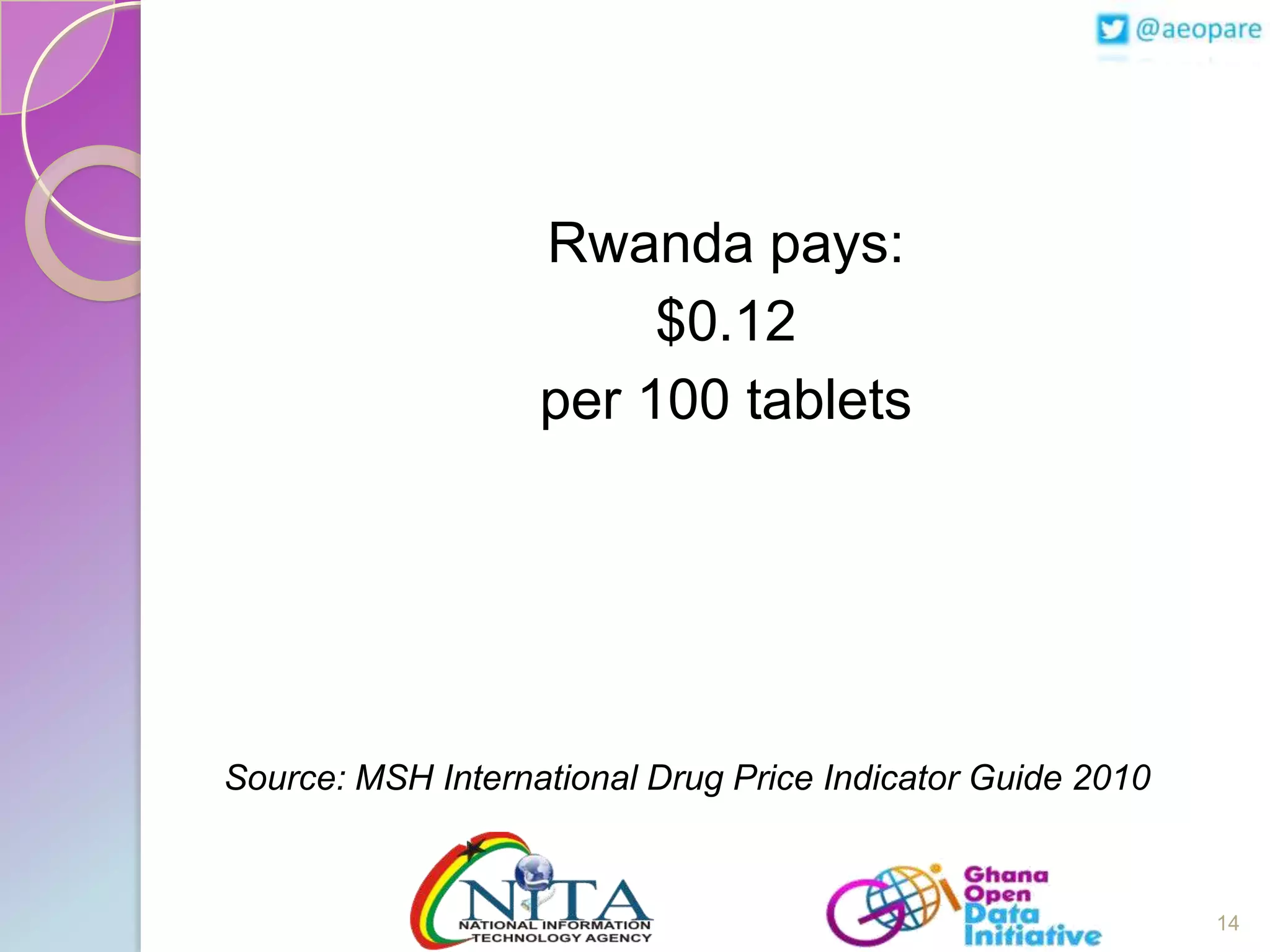
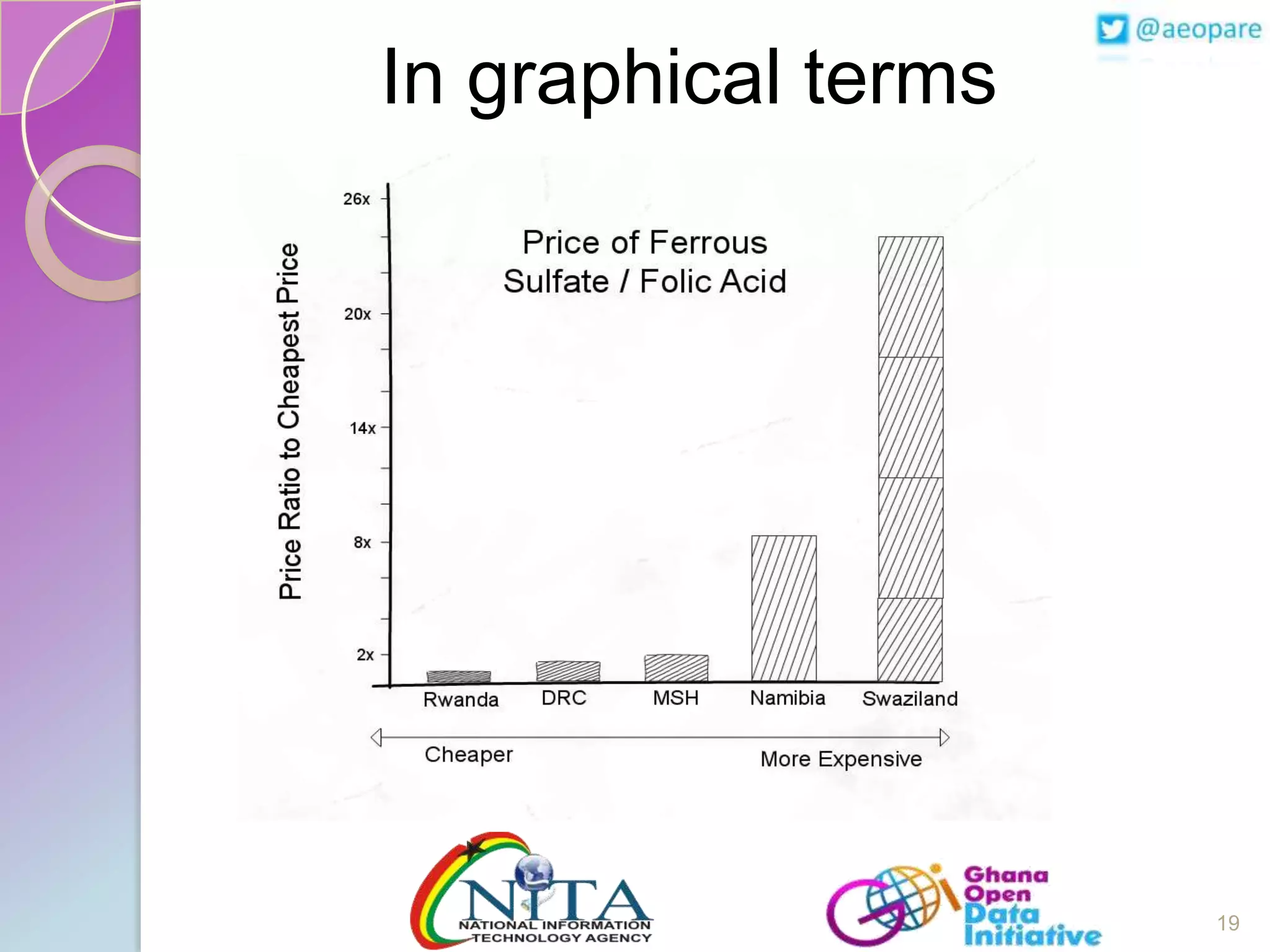
This document discusses the creation of an Africa Open Data Community (AfrODC). It defines open data as freely available public data in reusable formats without restrictions. Open data comes from a wide variety of sources and excludes personal, sensitive, incomplete or misleading information. The benefits of open data include economic development, efficient services, evidence-based decisions, and improved data quality. An open data ecosystem involves governments publishing data, citizens and developers using and providing feedback on data, and more data and users attracting each other. The document advocates for an AfrODC to promote economic growth, innovation, and sharing across Africa. Current African open data publishers include Ghana, Kenya, Morocco, and Tunisia.