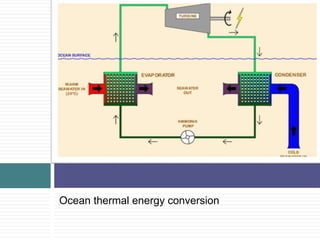
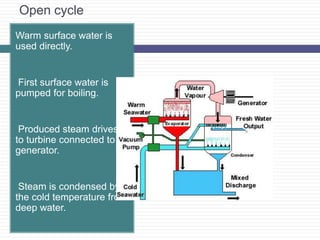
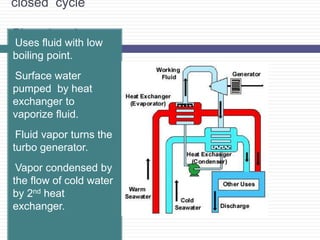
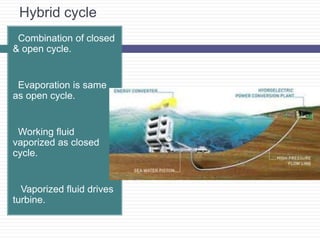
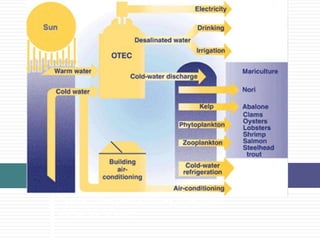
Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) uses the temperature difference between cooler deep water and warmer surface water to generate electricity through various cycles, including open, closed, and hybrid. This technology has evolved since its first attempt in 1880, with several plants built around the world, including recent developments in India. OTEC offers a renewable energy source with low cost and minimal waste, making it a promising solution for energy needs.