The document discusses several standardized assessments used to evaluate cognitive functioning:
- The Allen's Cognitive Level Screen evaluates visual-motor tasks of increasing complexity to assess learning potential and cognitive processing.
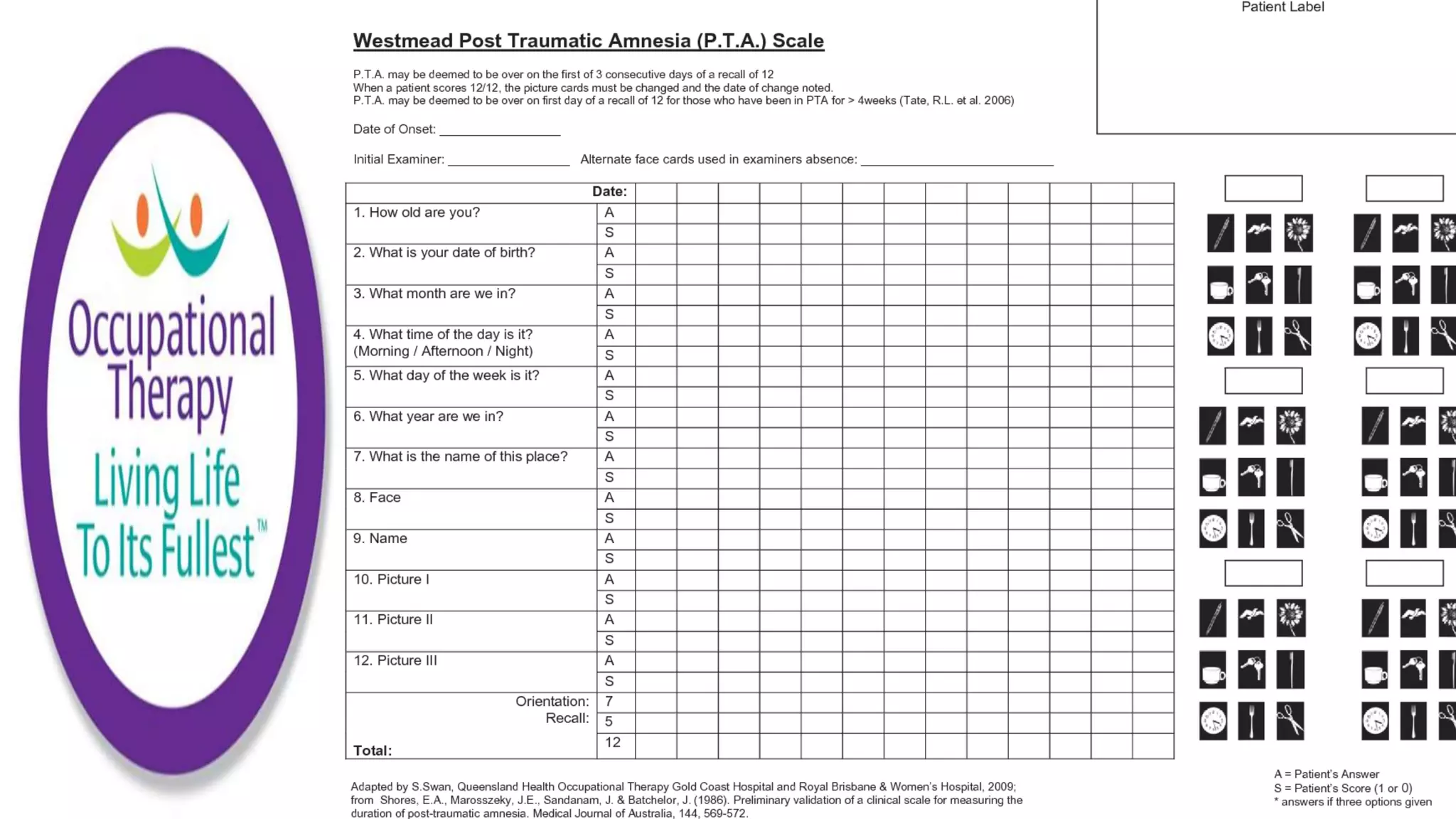
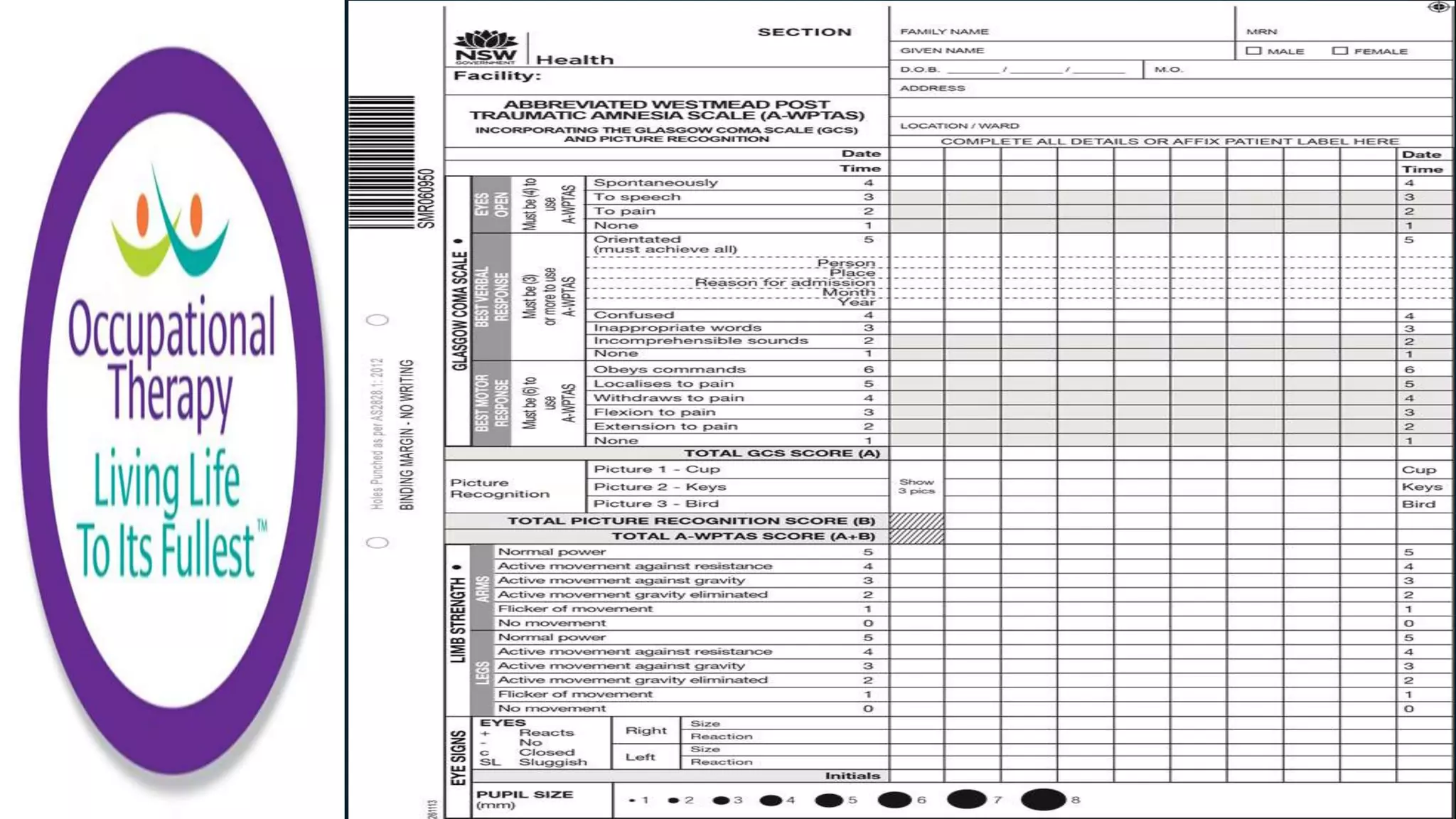
- The Westmead Post Traumatic Amnesia Scale consists of 12 questions to measure orientation and new memory in those with traumatic brain injuries and monitors recovery from post-traumatic amnesia.
- Cognistat screens five ability areas through tasks administered by an examiner to identify cognitive impairments.
- The Wessex Head Injury Matrix can assess patients from coma through minimally conscious states to set rehabilitation goals.
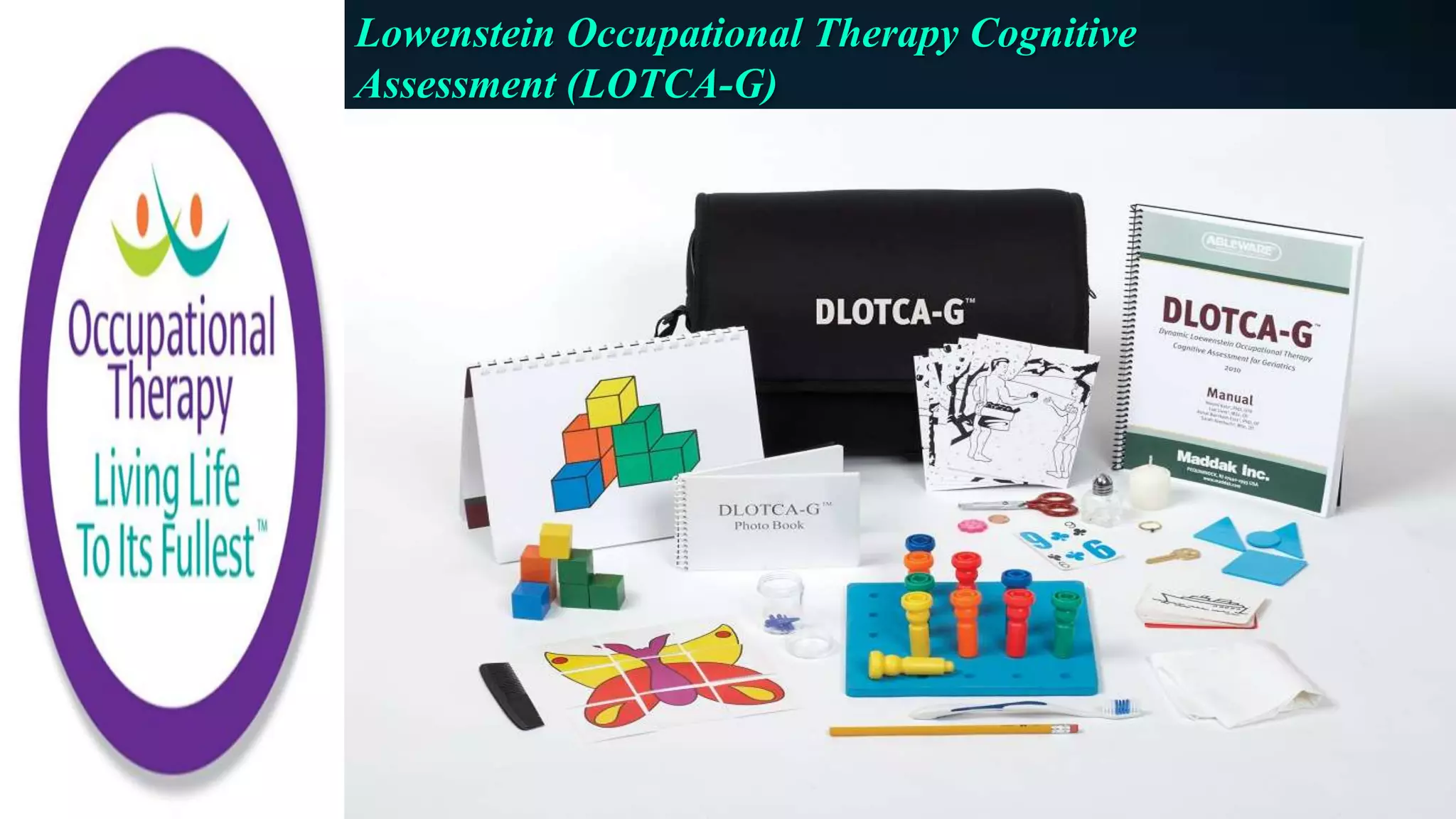
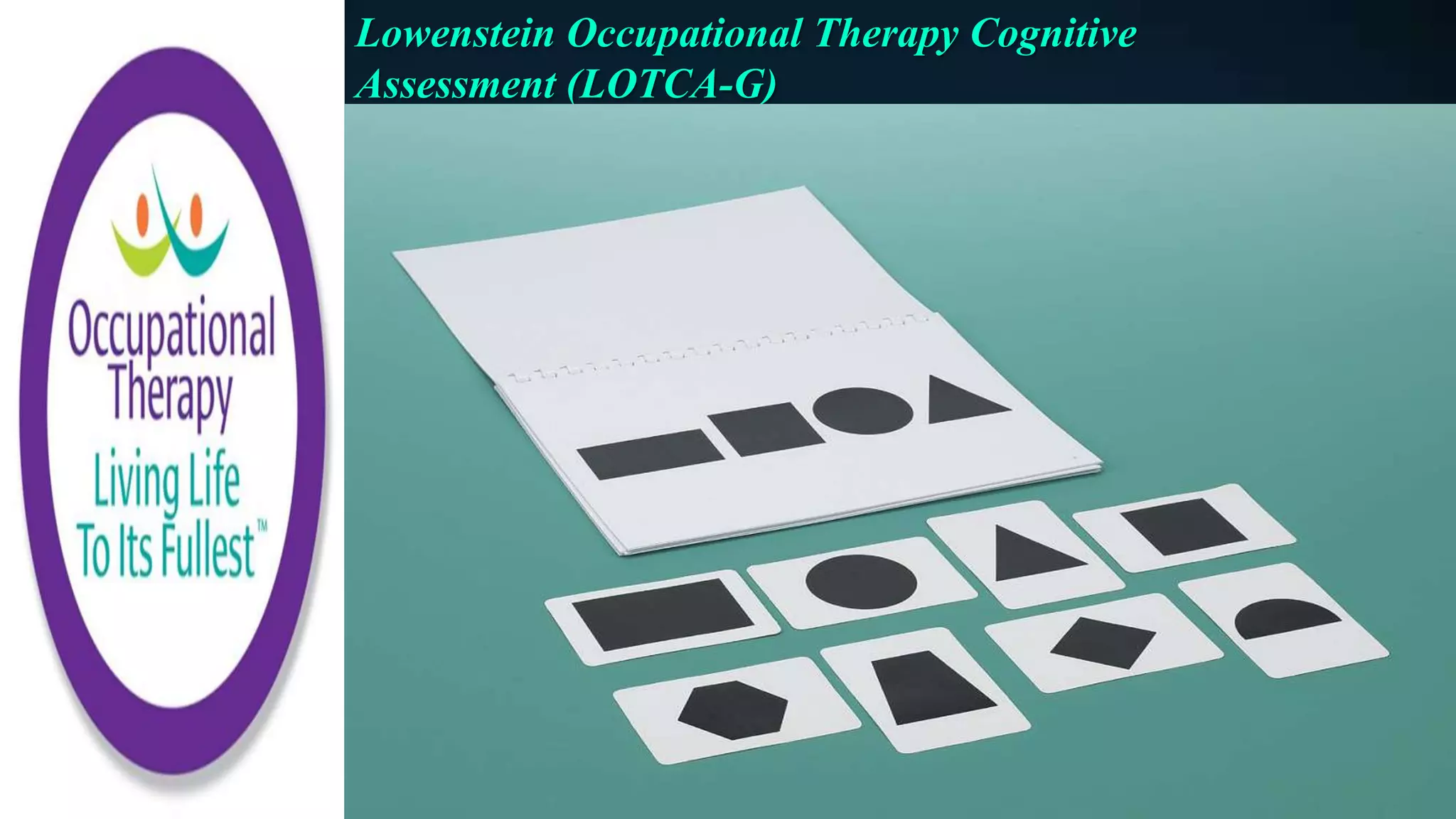
- The Lowenstein Occupational Therapy Cognitive Assessment uses 25 subtests in areas