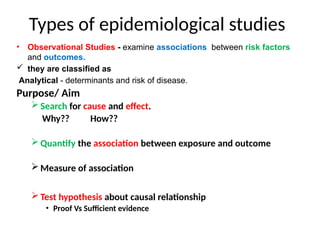
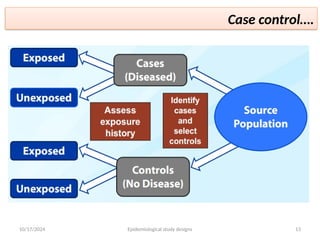
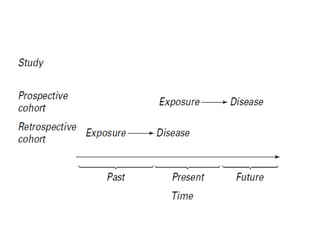
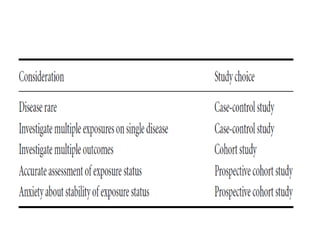
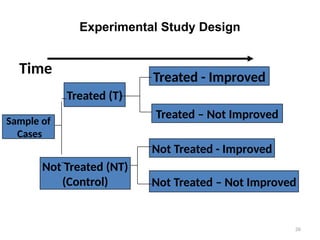
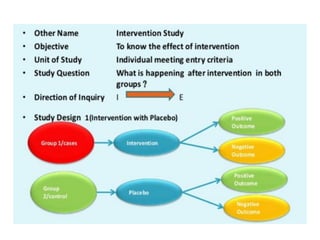
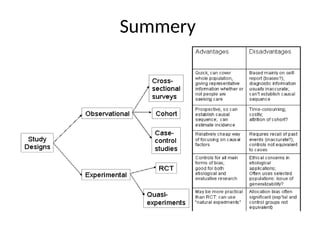
The document discusses various types of epidemiological studies, including observational (cross-sectional, ecological, case-control, cohort) and experimental studies, highlighting their purposes, advantages, and limitations. It emphasizes the importance of measuring disease frequency through incidence and prevalence rates to understand disease dynamics and inform public health planning. Additionally, it outlines the role of health information systems in collecting, managing, and analyzing health data to support effective decision-making and resource allocation.