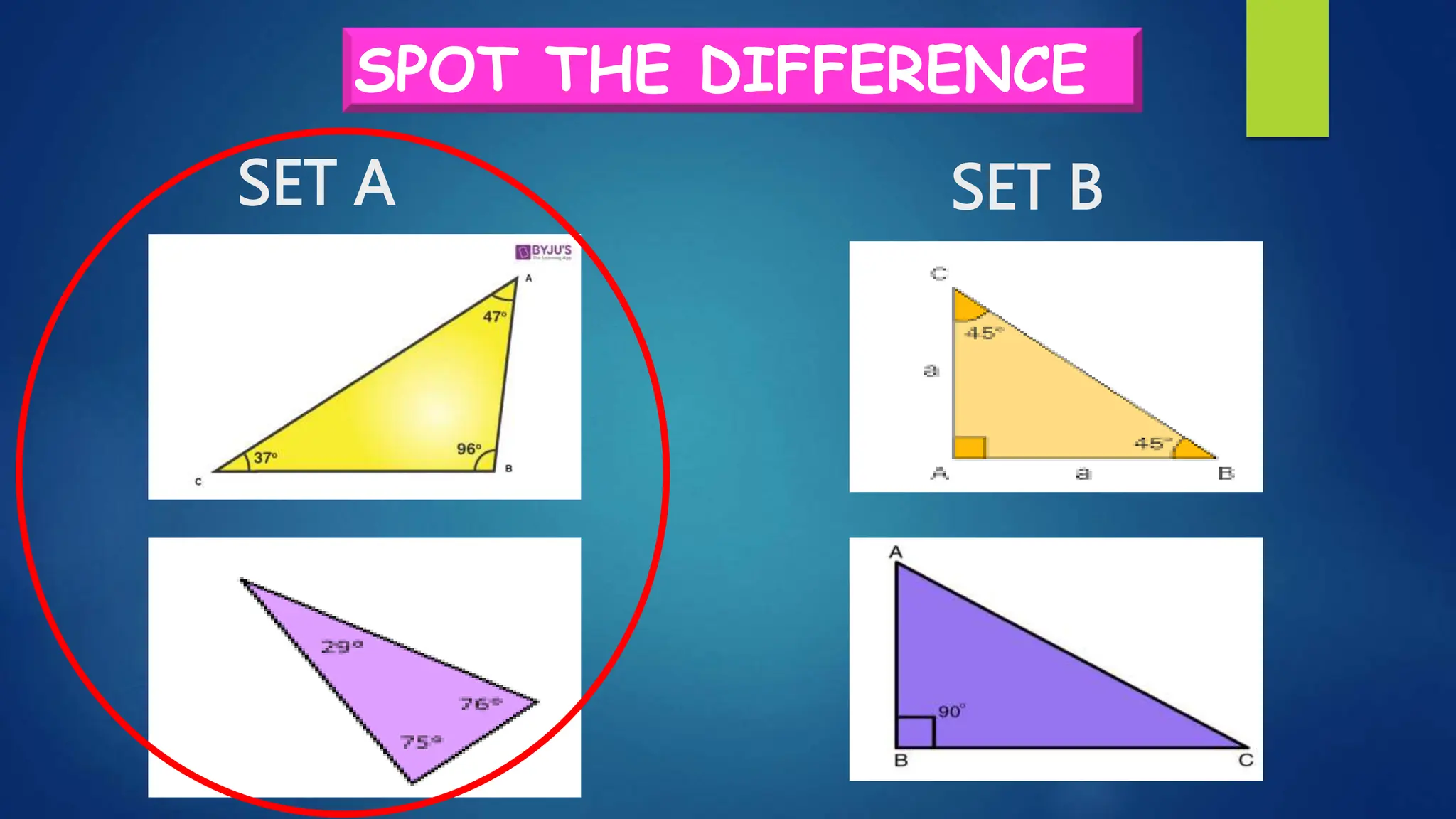
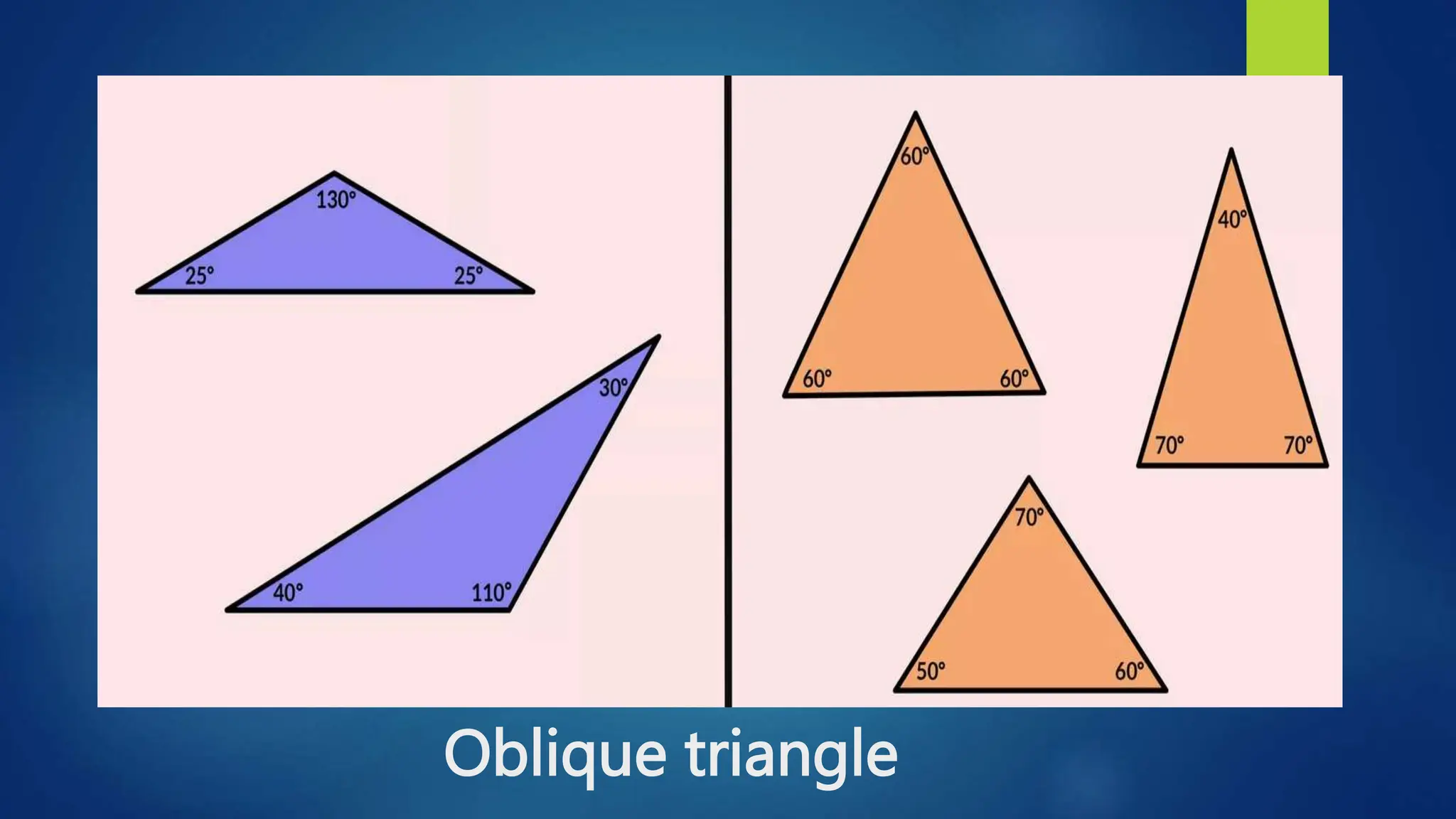
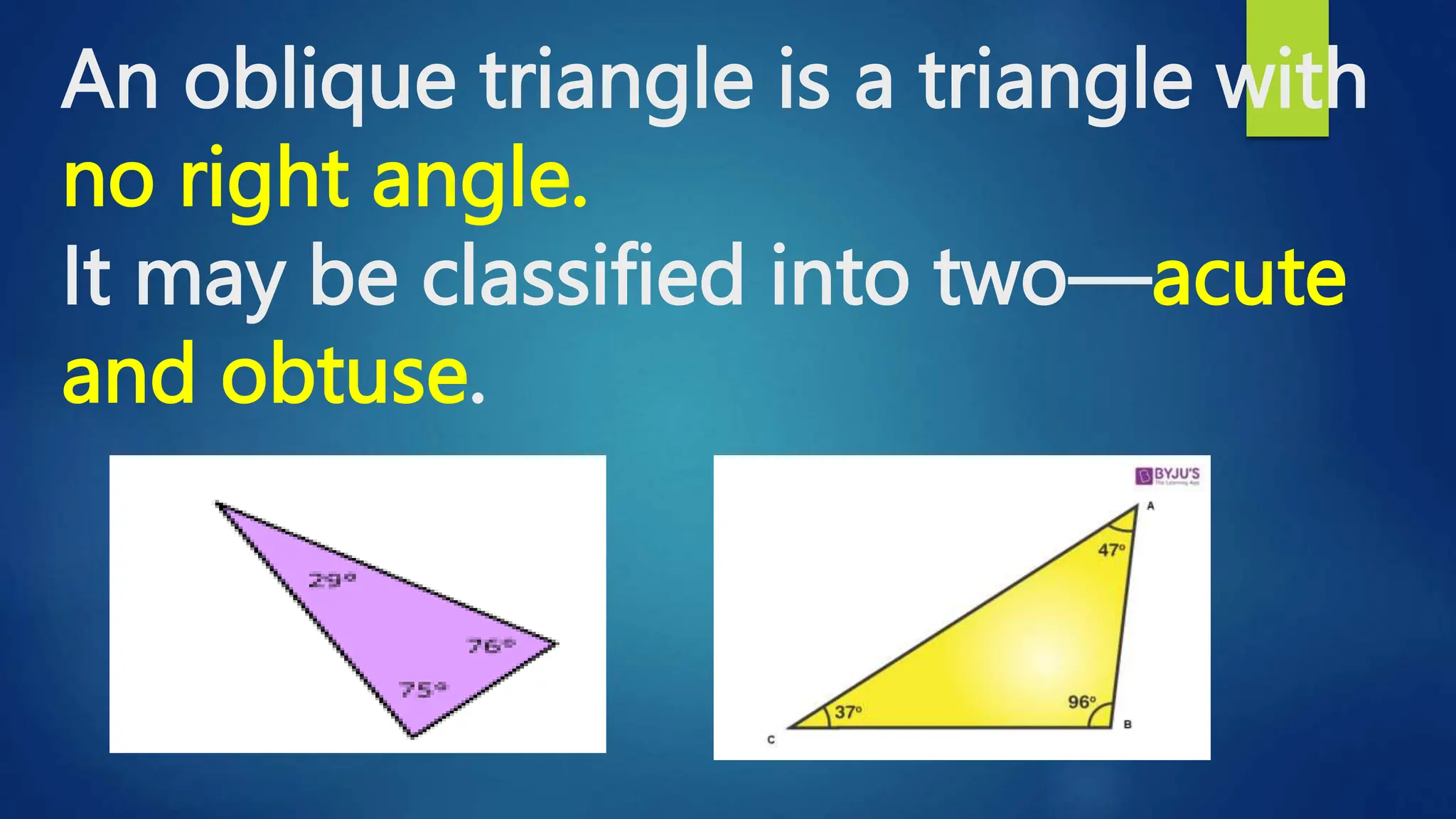
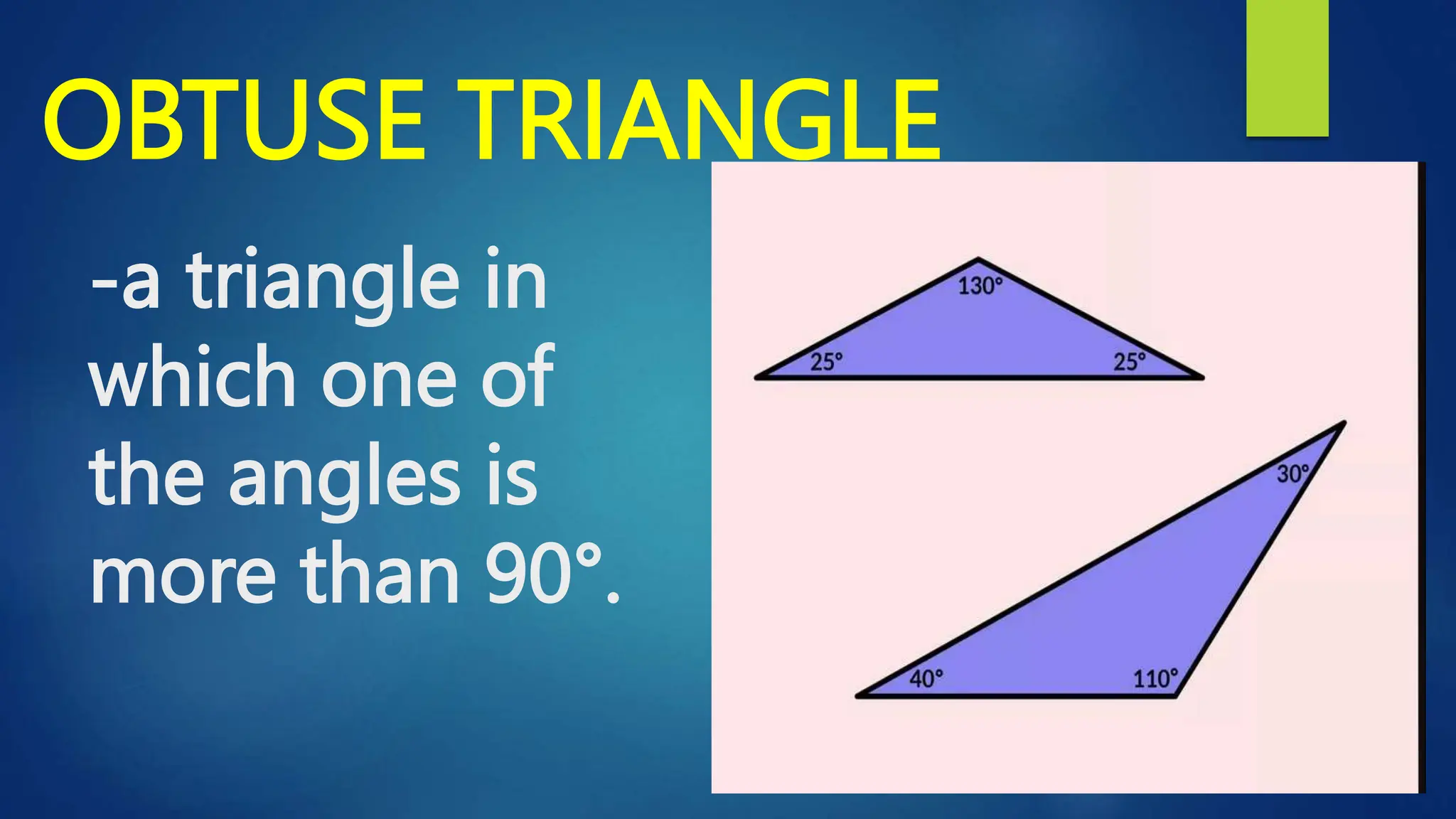
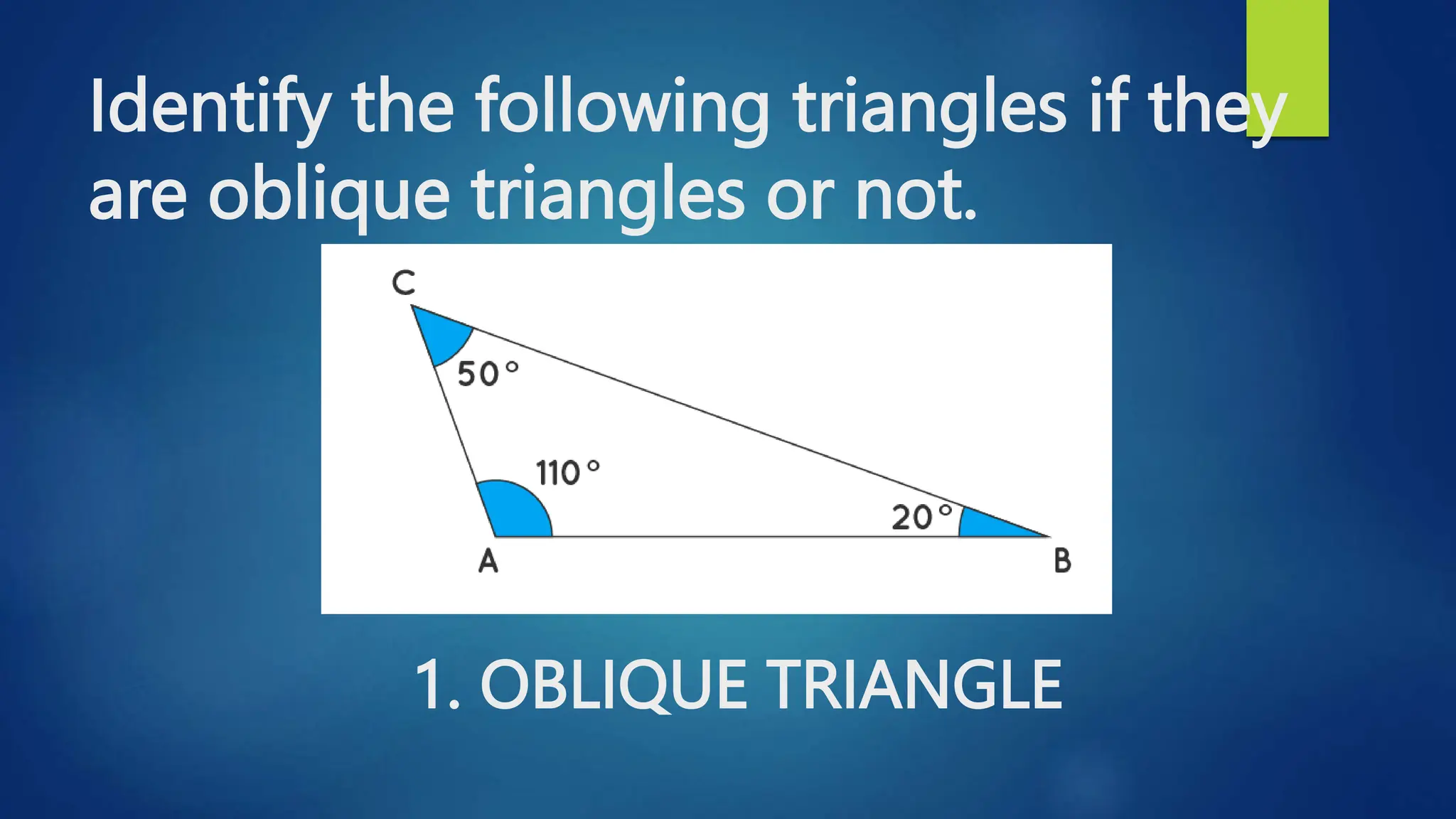
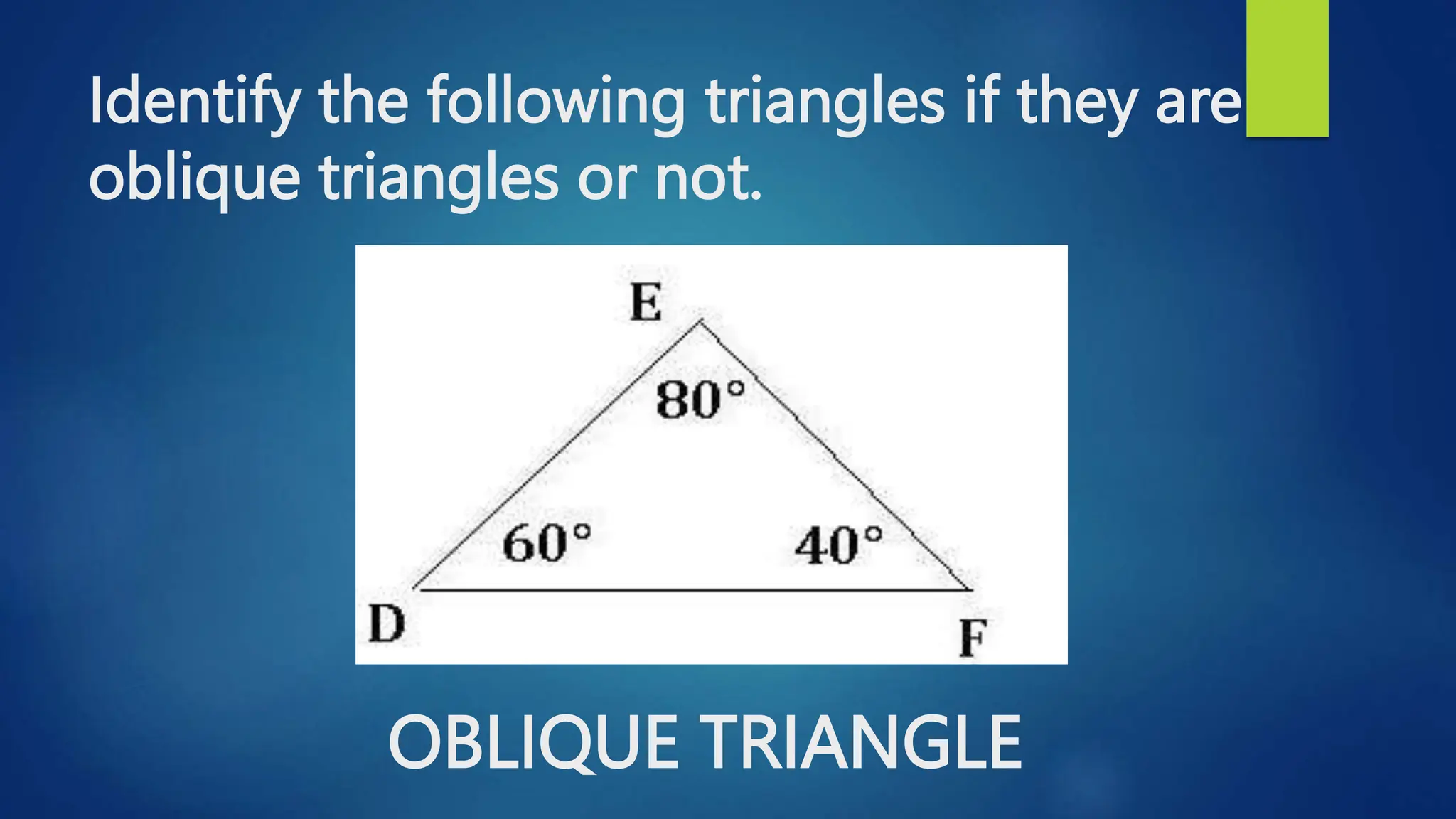
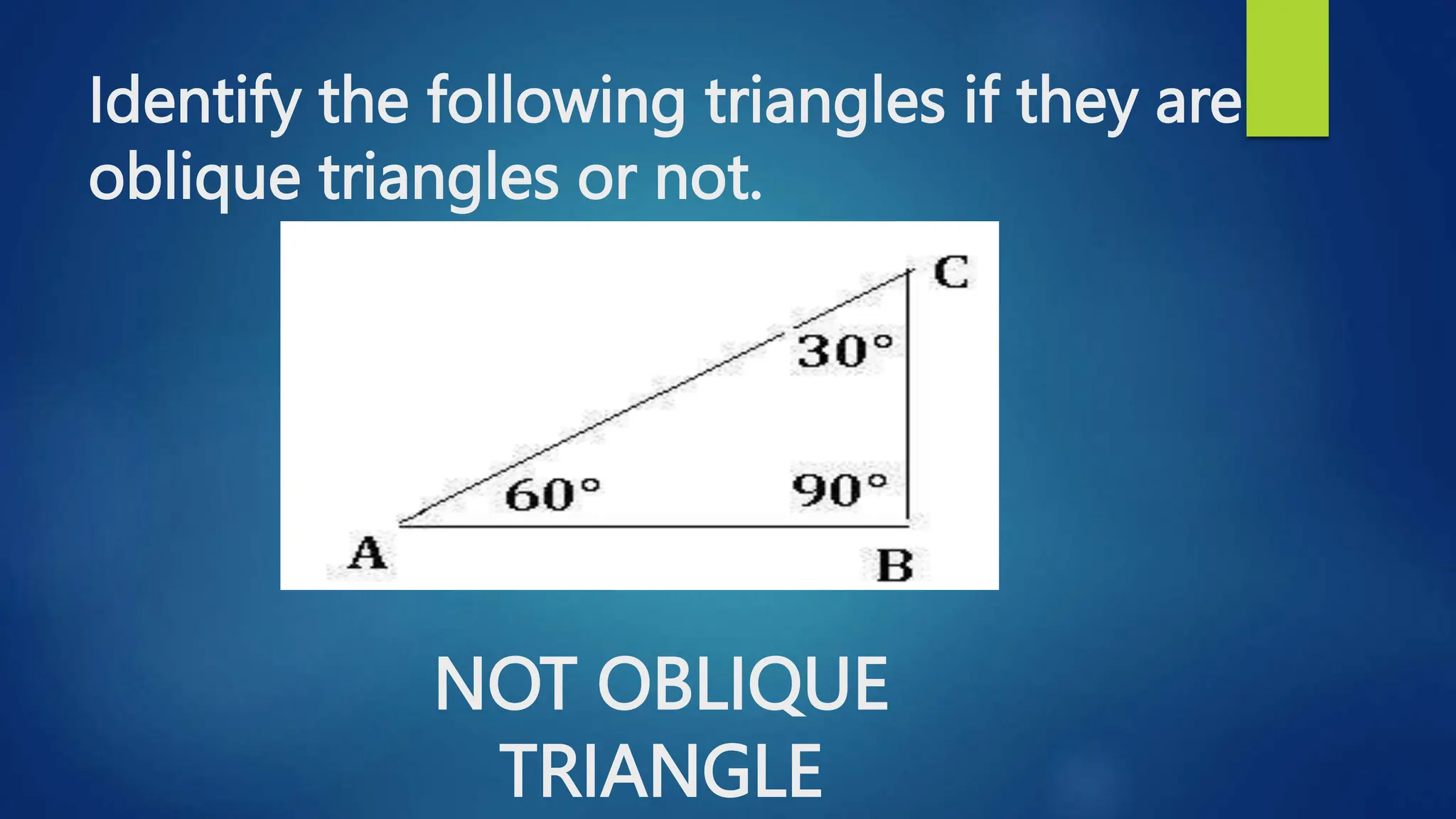
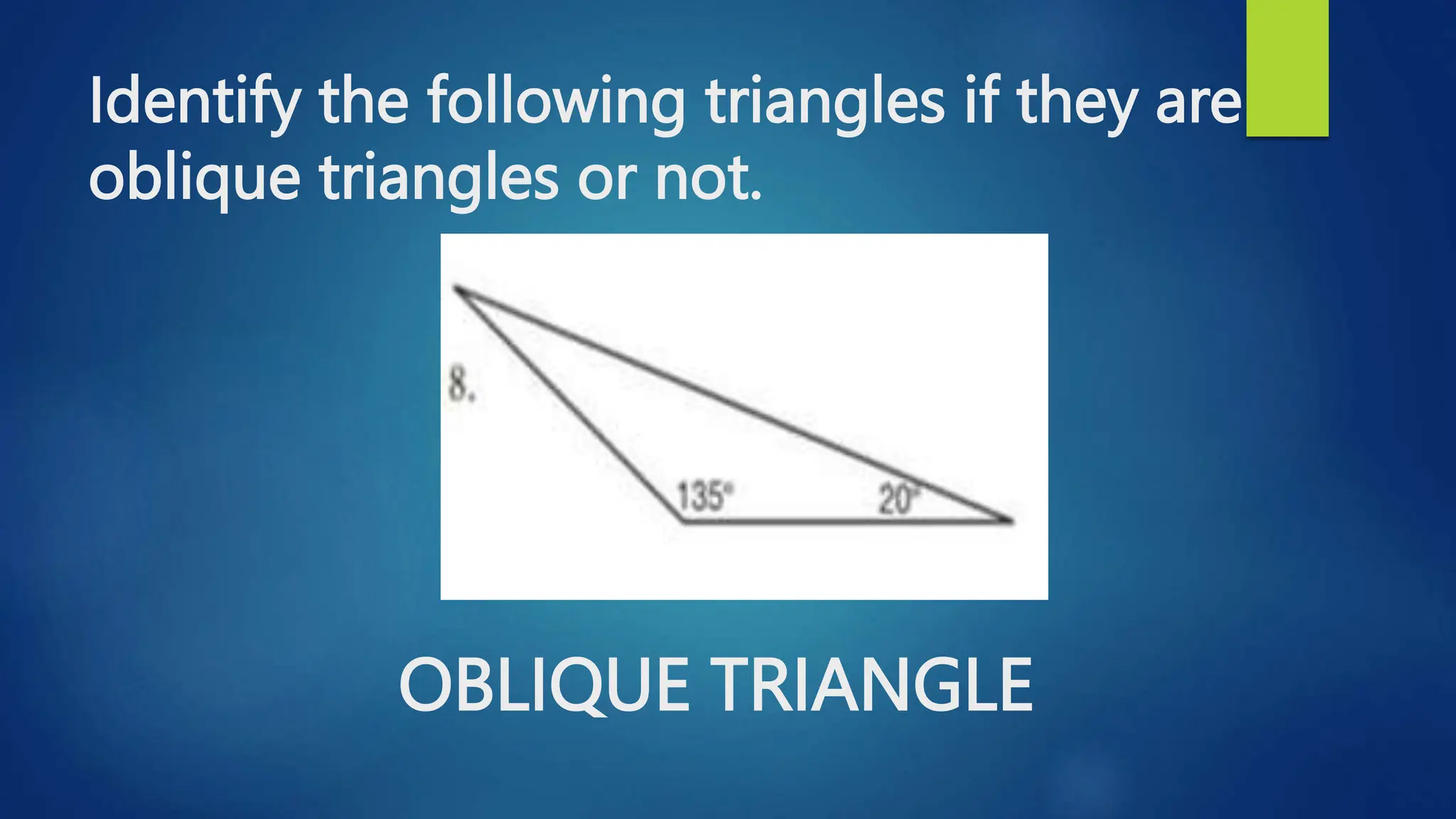
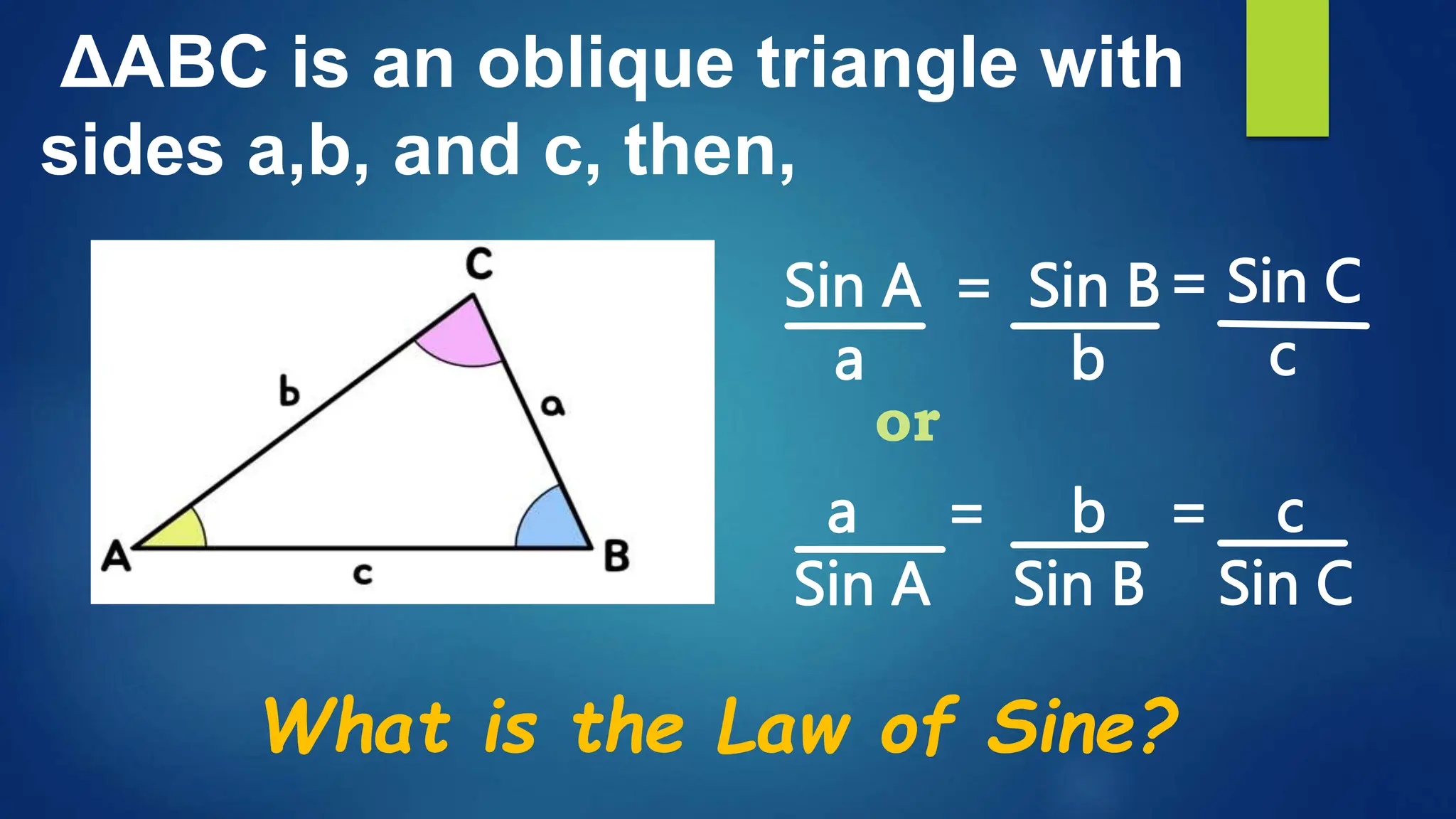
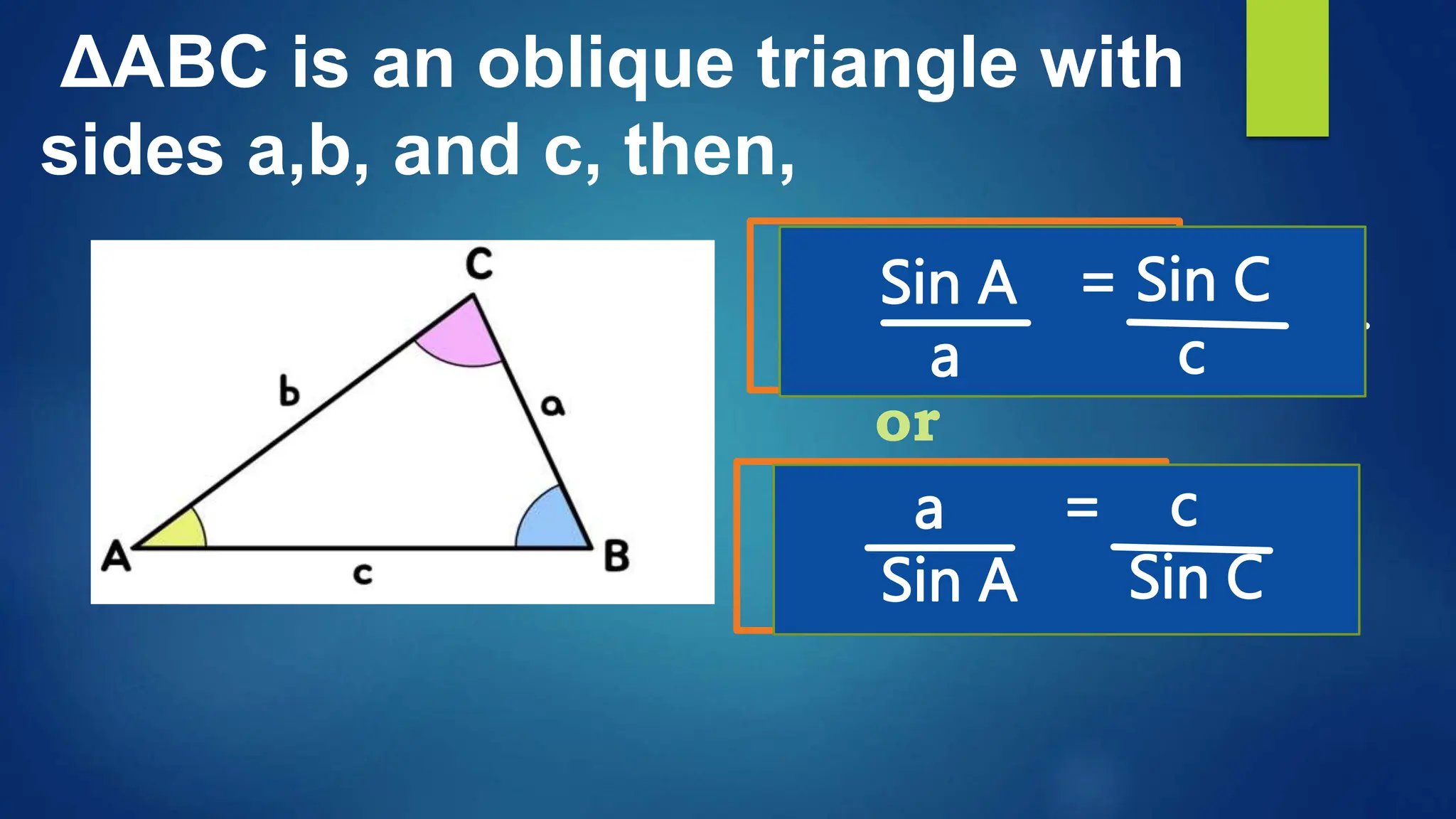
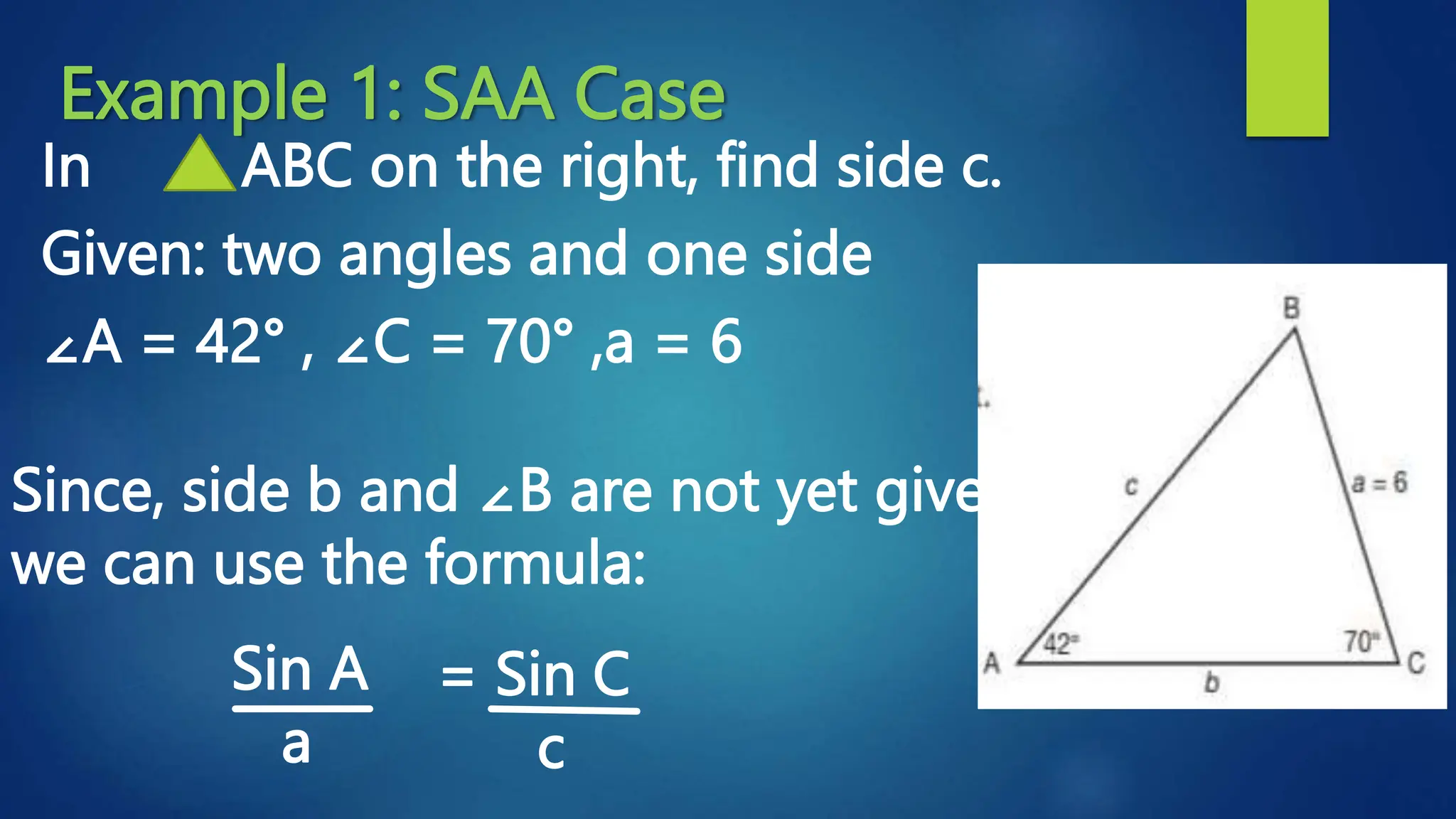
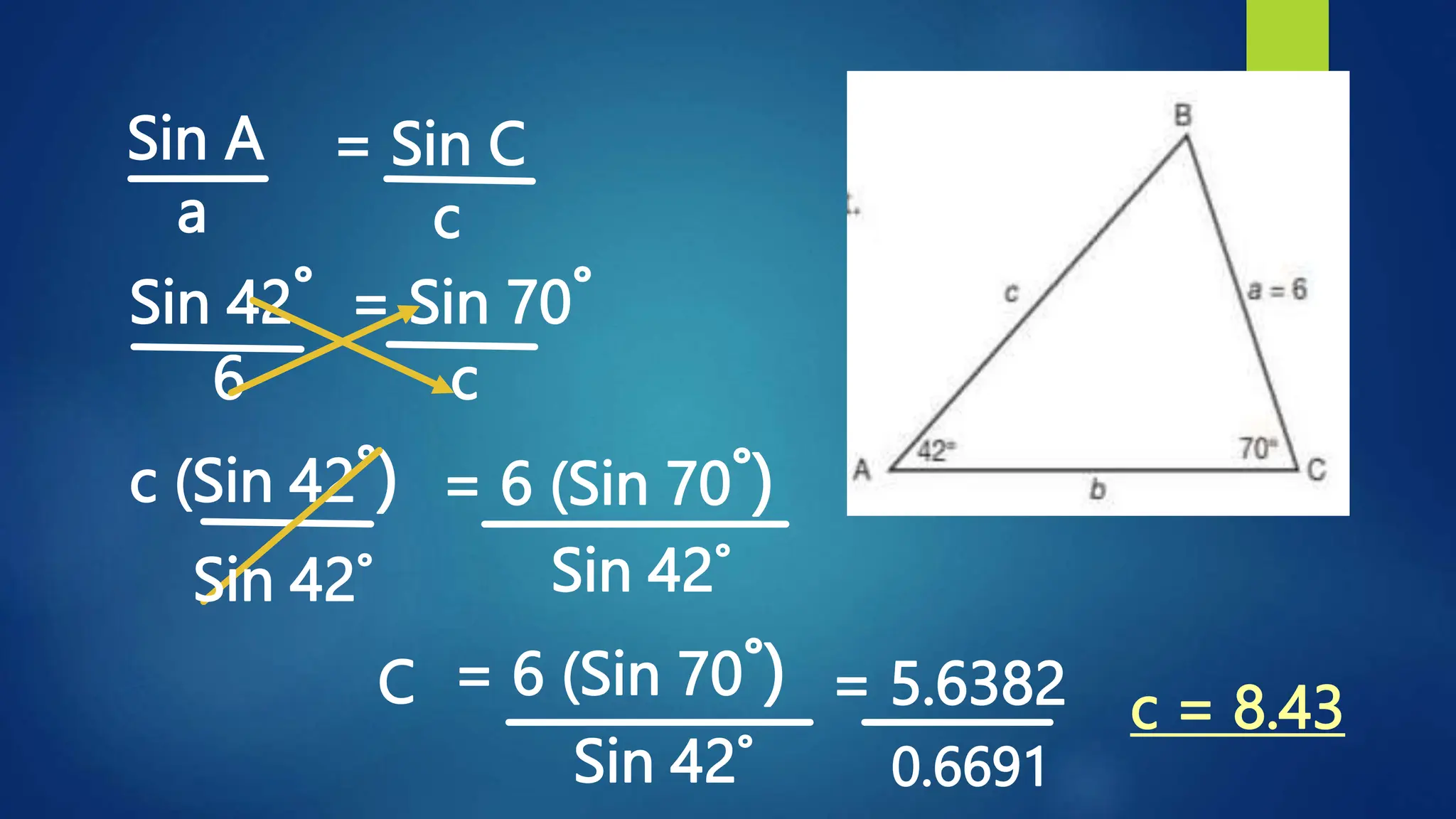
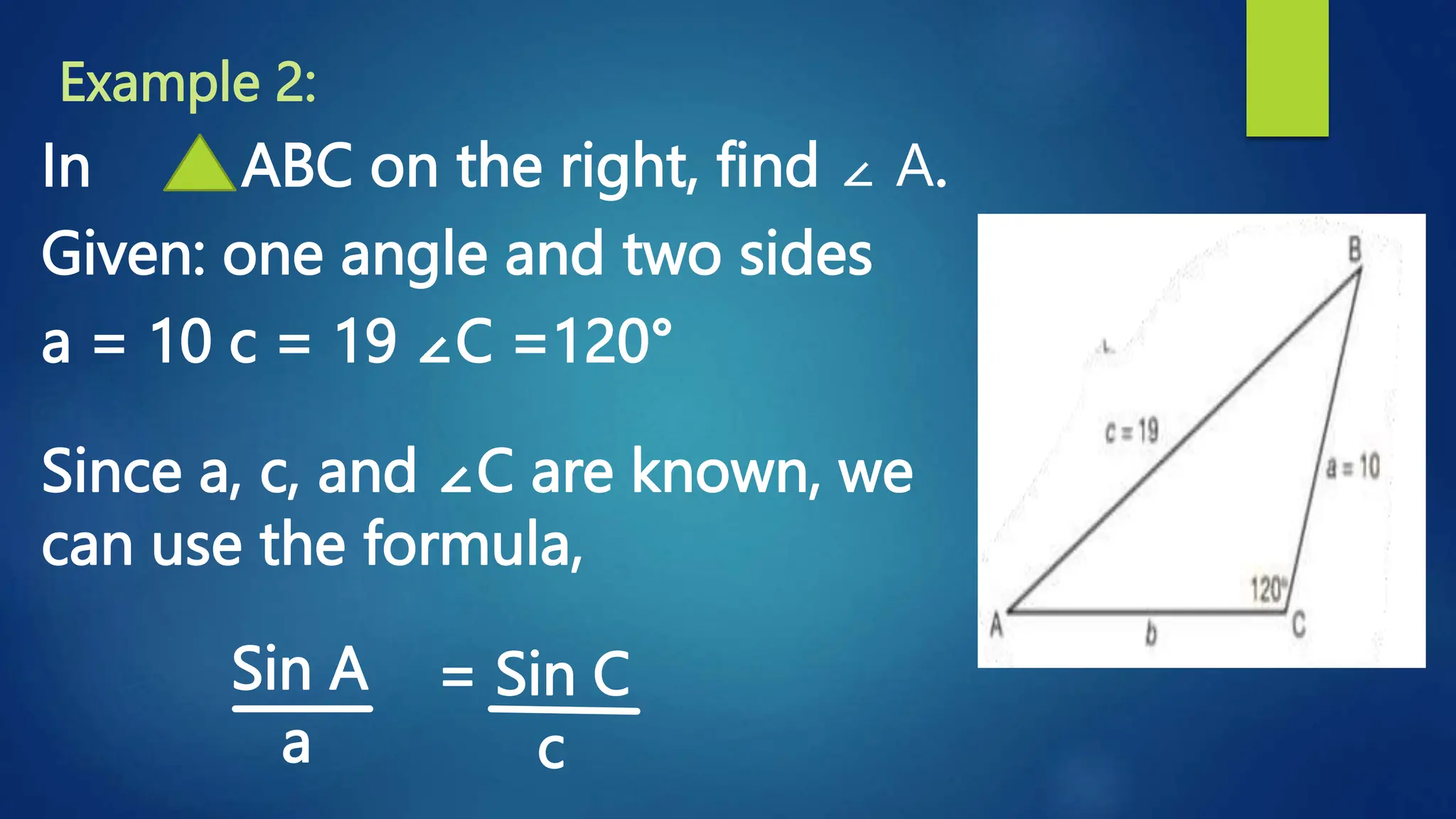
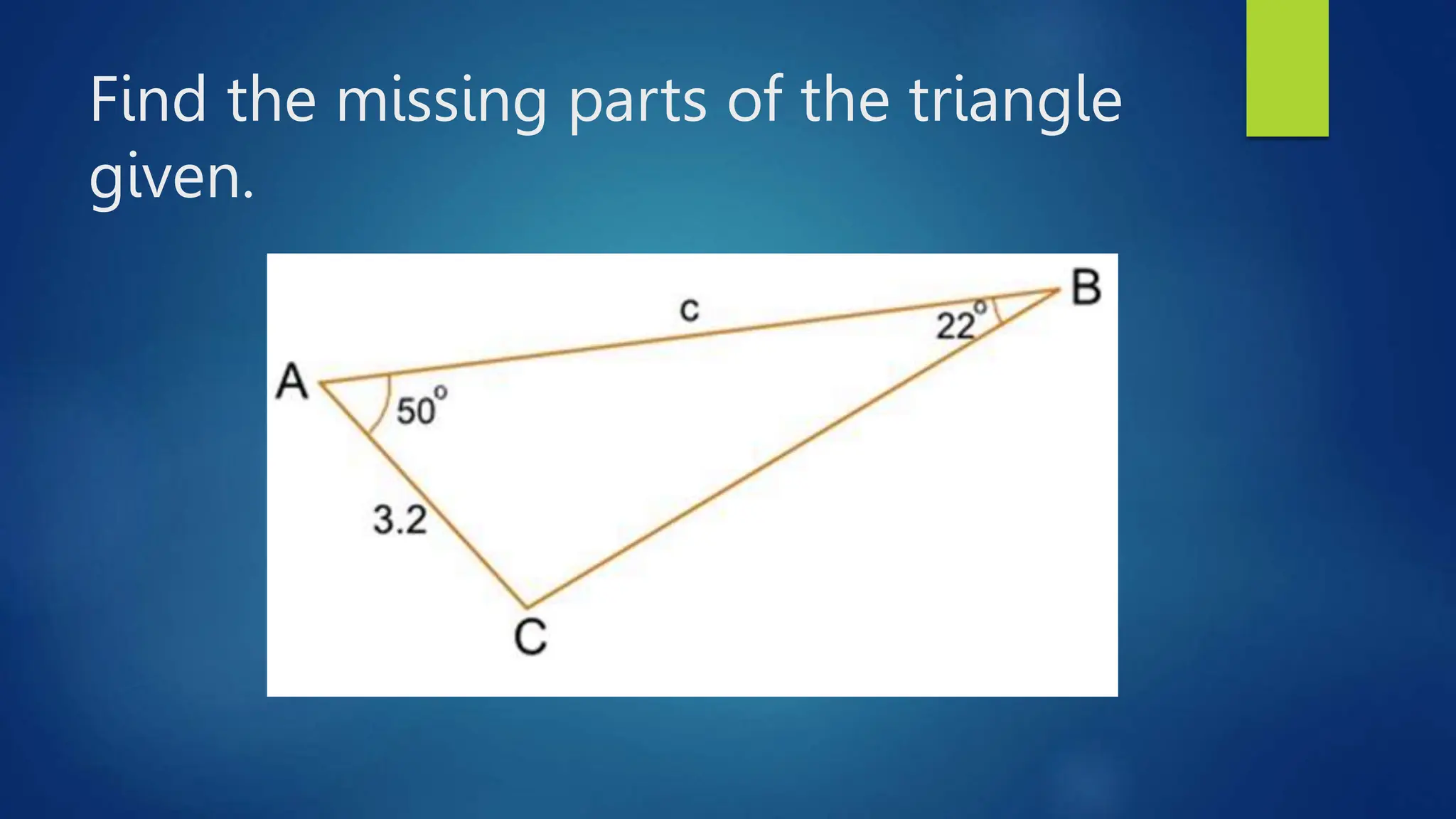
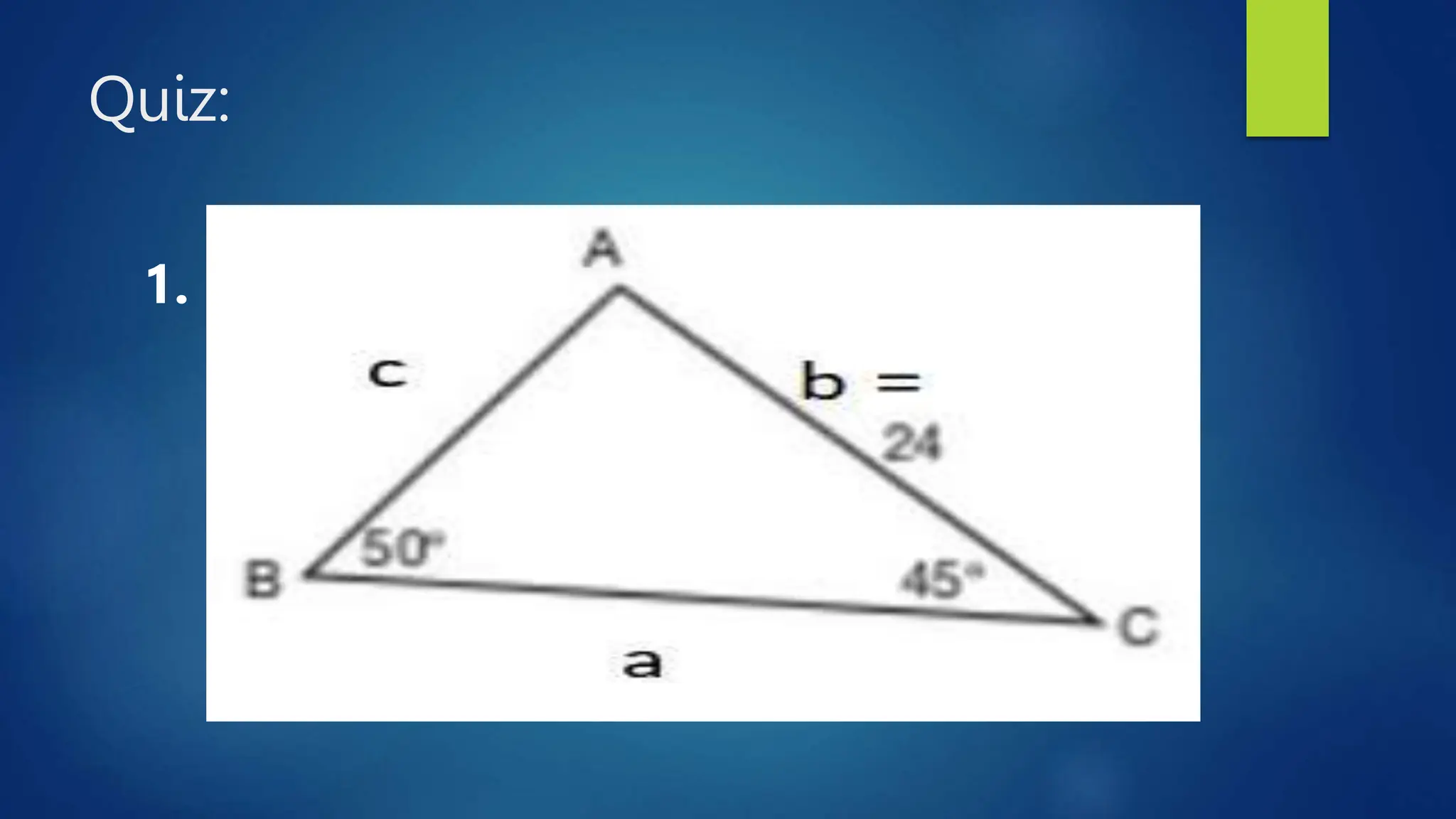
This document discusses oblique triangles and the Law of Sines. It begins by defining oblique triangles as triangles that do not have a right angle. It then introduces the Law of Sines, which states that the ratio of the sine of an angle to its opposite side is equal to the ratio of the sine of any other angle to its opposite side. Examples are given to demonstrate how to use the Law of Sines to solve for missing sides and angles of oblique triangles when given certain information like two angles and a side. Real-world applications of the Law of Sines are also mentioned.