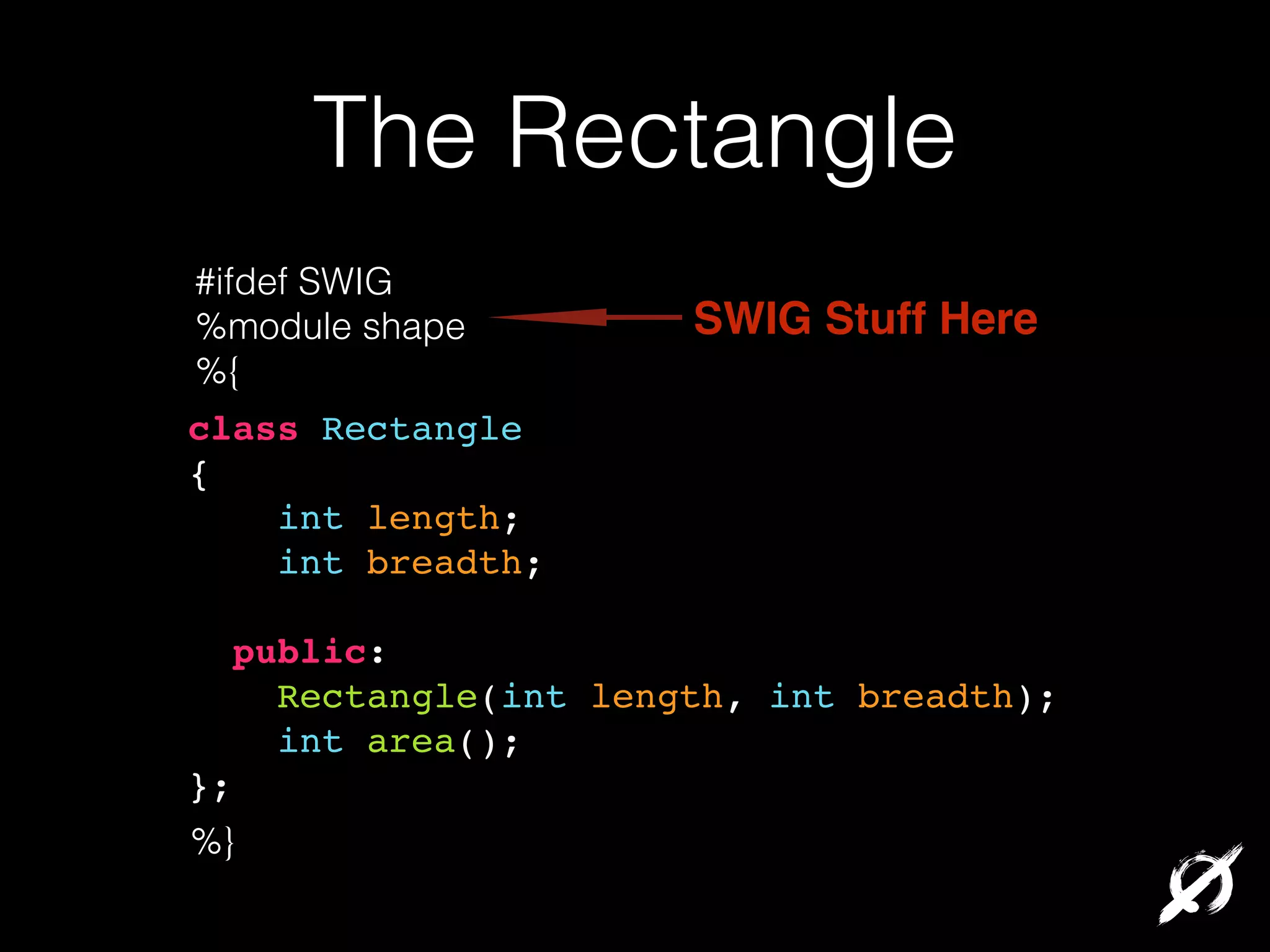
The document discusses various approaches to integrating native code with Ruby:
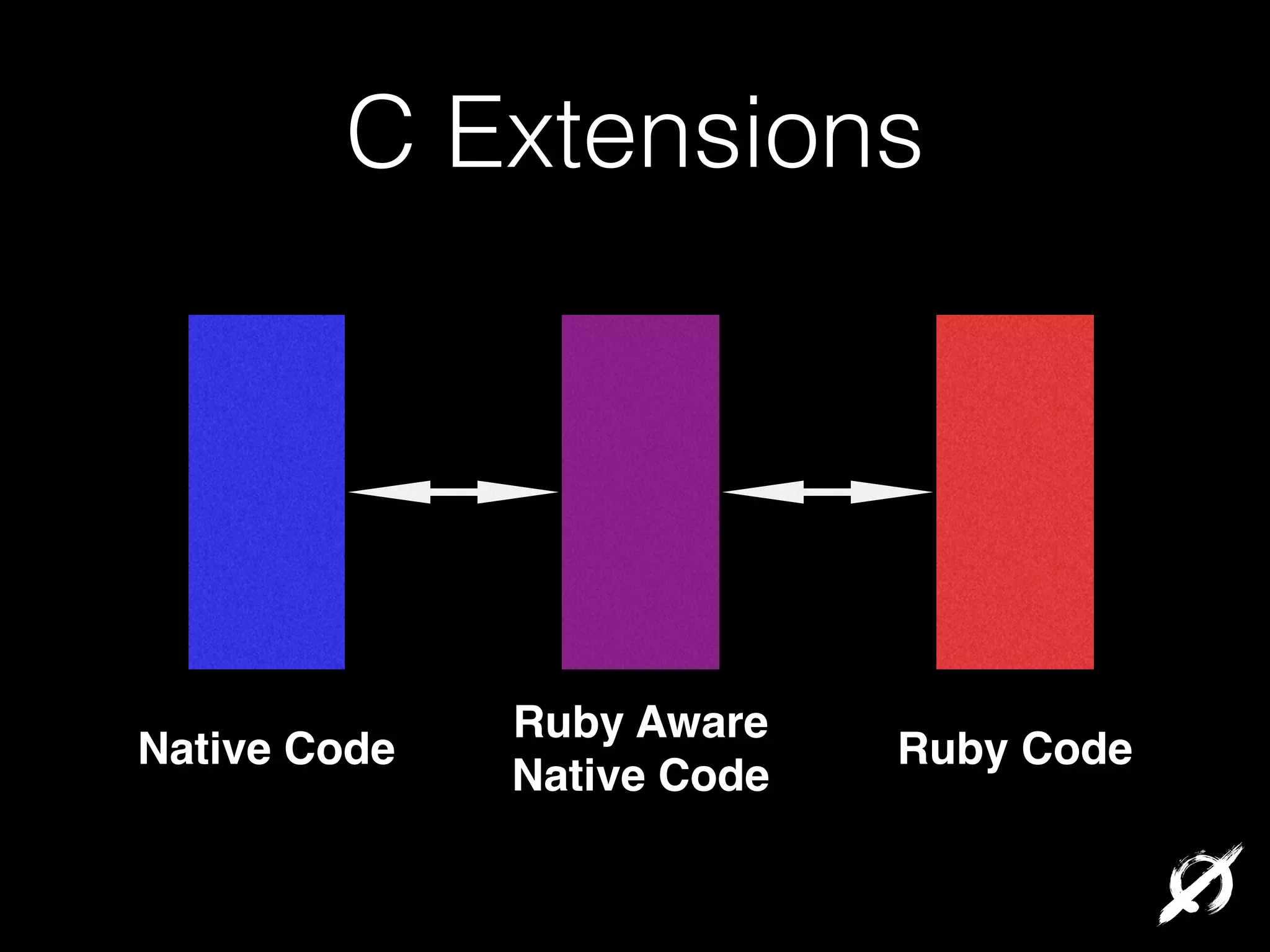
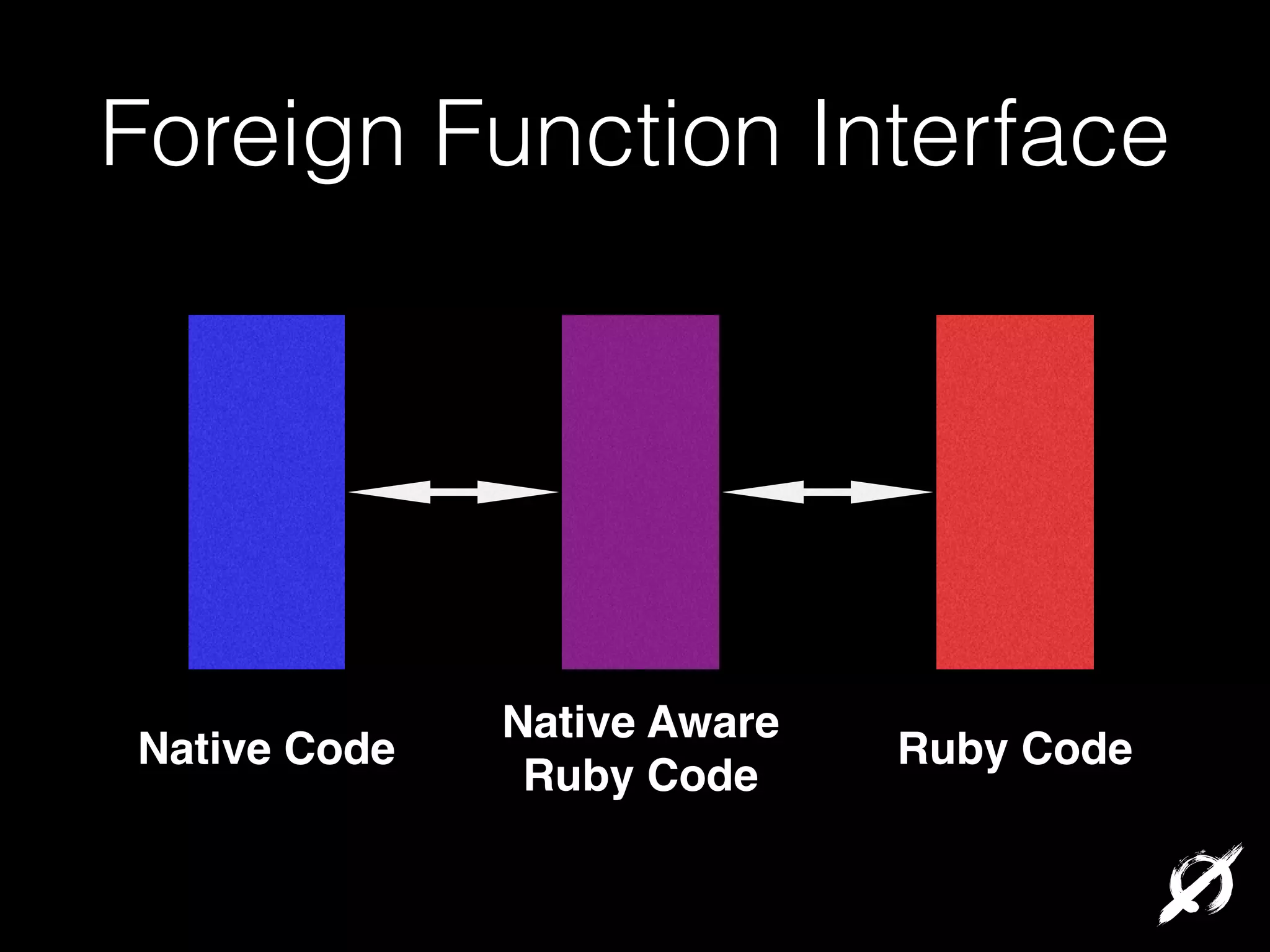
Native extensions allow Ruby code to directly call C/C++ functions for improved performance or to interface with existing libraries. This can be done through writing C extensions, using the Foreign Function Interface (FFI) gem, or the Simplified Wrapper and Interface Generator (SWIG). FFI provides an easy Ruby DSL for interfacing with native code while handling data conversions. SWIG can generate bindings to interface Ruby and other languages with C/C++ code. Memory management must still be considered when using native extensions.





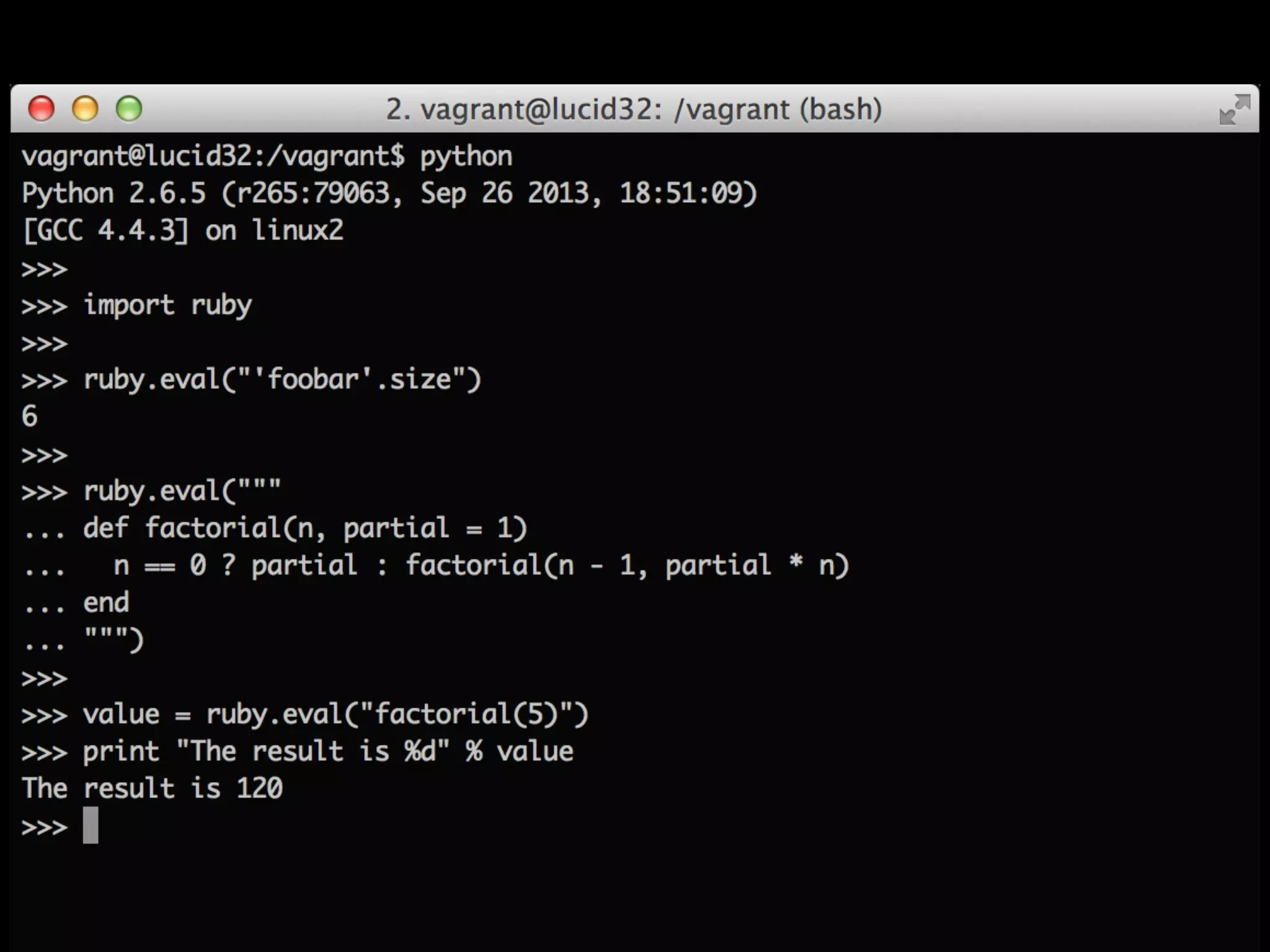
![#include "Python.h"
#include "ruby.h"
!
static PyObject *python_ruby_eval(PyObject *self, PyObject *string)
{
VALUE val = rb_eval_string(PyString_AsString(string));
switch(TYPE(val)) {
case T_FIXNUM: return PyInt_FromLong(FIX2INT(val));
case T_STRING: return PyString_FromString(StringValuePtr(val));
default: return Py_None; // Can handle these cases later
}
}
!
static PyMethodDef module_functions[] = {
{ "eval", python_ruby_eval, METH_O, "Evaluate Ruby Code" },
{ NULL }
};
!
void initruby(void)
{
ruby_init();
Py_InitModule3("ruby", module_functions, "A ruby module for python.");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcrc-talk-140103004958-phpapp02/75/Gcrc-talk-7-2048.jpg)
![#include "Python.h"
#include "ruby.h"
!
static PyObject *python_ruby_eval(PyObject *self, PyObject *string)
{
VALUE val = rb_eval_string(PyString_AsString(string));
switch(TYPE(val)) {
case T_FIXNUM: return PyInt_FromLong(FIX2INT(val));
case T_STRING: return PyString_FromString(StringValuePtr(val));
default: return Py_None; // Can handle these cases later
}
}
!
static PyMethodDef module_functions[] = {
{ "eval", python_ruby_eval, METH_O, "Evaluate Ruby Code" },
{ NULL }
};
!
void initruby(void)
{
ruby_init();
Py_InitModule3("ruby", module_functions, "A ruby module for python.");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcrc-talk-140103004958-phpapp02/75/Gcrc-talk-8-2048.jpg)
![#include "Python.h"
#include "ruby.h"
!
static PyObject *python_ruby_eval(PyObject *self, PyObject *string)
{
VALUE val = rb_eval_string(PyString_AsString(string));
switch(TYPE(val)) {
case T_FIXNUM: return PyInt_FromLong(FIX2INT(val));
case T_STRING: return PyString_FromString(StringValuePtr(val));
default: return Py_None; // Can handle these cases later
}
}
!
static PyMethodDef module_functions[] = {
{ "eval", python_ruby_eval, METH_O, "Evaluate Ruby Code" },
{ NULL }
};
!
void initruby(void)
{
ruby_init();
Py_InitModule3("ruby", module_functions, "A ruby module for python.");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcrc-talk-140103004958-phpapp02/75/Gcrc-talk-9-2048.jpg)
![#include "Python.h"
#include "ruby.h"
!
static PyObject *python_ruby_eval(PyObject *self, PyObject *string)
{
VALUE val = rb_eval_string(PyString_AsString(string));
switch(TYPE(val)) {
case T_FIXNUM: return PyInt_FromLong(FIX2INT(val));
case T_STRING: return PyString_FromString(StringValuePtr(val));
default: return Py_None; // Can handle these cases later
}
}
!
static PyMethodDef module_functions[] = {
{ "eval", python_ruby_eval, METH_O, "Evaluate Ruby Code" },
{ NULL }
};
!
void initruby(void)
{
ruby_init();
Py_InitModule3("ruby", module_functions, "A ruby module for python.");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcrc-talk-140103004958-phpapp02/75/Gcrc-talk-10-2048.jpg)
![#include "Python.h"
#include "ruby.h"
!
static PyObject *python_ruby_eval(PyObject *self, PyObject *string)
{
VALUE val = rb_eval_string(PyString_AsString(string));
switch(TYPE(val)) {
case T_FIXNUM: return PyInt_FromLong(FIX2INT(val));
case T_STRING: return PyString_FromString(StringValuePtr(val));
default: return Py_None; // Can handle these cases later
}
}
!
static PyMethodDef module_functions[] = {
{ "eval", python_ruby_eval, METH_O, "Evaluate Ruby Code" },
{ NULL }
};
!
void initruby(void)
{
ruby_init();
Py_InitModule3("ruby", module_functions, "A ruby module for python.");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcrc-talk-140103004958-phpapp02/75/Gcrc-talk-11-2048.jpg)
![#include "Python.h"
#include "ruby.h"
!
static PyObject *python_ruby_eval(PyObject *self, PyObject *string)
{
VALUE val = rb_eval_string(PyString_AsString(string));
switch(TYPE(val)) {
case T_FIXNUM: return PyInt_FromLong(FIX2INT(val));
case T_STRING: return PyString_FromString(StringValuePtr(val));
default: return Py_None; // Can handle these cases later
}
}
!
static PyMethodDef module_functions[] = {
{ "eval", python_ruby_eval, METH_O, "Evaluate Ruby Code" },
{ NULL }
};
!
void initruby(void)
{
ruby_init();
Py_InitModule3("ruby", module_functions, "A ruby module for python.");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcrc-talk-140103004958-phpapp02/75/Gcrc-talk-12-2048.jpg)
![#include "Python.h"
#include "ruby.h"
!
static PyObject *python_ruby_eval(PyObject *self, PyObject *string)
{
VALUE val = rb_eval_string(PyString_AsString(string));
switch(TYPE(val)) {
case T_FIXNUM: return PyInt_FromLong(FIX2INT(val));
case T_STRING: return PyString_FromString(StringValuePtr(val));
default: return Py_None; // Can handle these cases later
}
}
!
static PyMethodDef module_functions[] = {
{ "eval", python_ruby_eval, METH_O, "Evaluate Ruby Code" },
{ NULL }
};
!
void initruby(void)
{
ruby_init();
Py_InitModule3("ruby", module_functions, "A ruby module for python.");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcrc-talk-140103004958-phpapp02/75/Gcrc-talk-13-2048.jpg)
![#include "Python.h"
#include "ruby.h"
!
static PyObject *python_ruby_eval(PyObject *self, PyObject *string)
{
VALUE val = rb_eval_string(PyString_AsString(string));
switch(TYPE(val)) {
case T_FIXNUM: return PyInt_FromLong(FIX2INT(val));
case T_STRING: return PyString_FromString(StringValuePtr(val));
default: return Py_None; // Can handle these cases later
}
}
!
static PyMethodDef module_functions[] = {
{ "eval", python_ruby_eval, METH_O, "Evaluate Ruby Code" },
{ NULL }
};
!
void initruby(void)
{
ruby_init();
Py_InitModule3("ruby", module_functions, "A ruby module for python.");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcrc-talk-140103004958-phpapp02/75/Gcrc-talk-14-2048.jpg)








![example
require 'ffi'!
!
module MyLib!
extend FFI::Library!
ffi_lib 'c'!
attach_function :puts, [:string], :int!
end!
!
MyLib.puts 'Hello, World using libc!'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcrc-talk-140103004958-phpapp02/75/Gcrc-talk-27-2048.jpg)
![another example
require 'ffi'!
!
module MyMathLib!
extend FFI::Library!
ffi_lib 'm'!
attach_function :pow, [:double, :double],!
:double!
end!
!
MyMathLib.pow(4, 5) # => 1024.0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcrc-talk-140103004958-phpapp02/75/Gcrc-talk-28-2048.jpg)