The document summarizes various topics related to power in organizations, including:
1) It defines influence as a basic organizational process and describes common tactics for exerting influence.
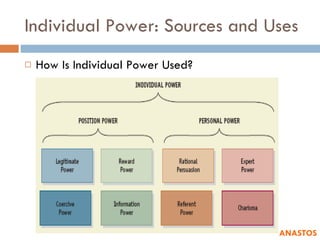
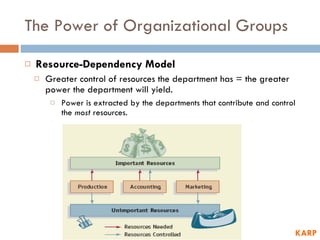
2) It discusses sources of individual power including position and personal power.
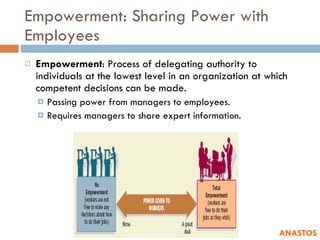
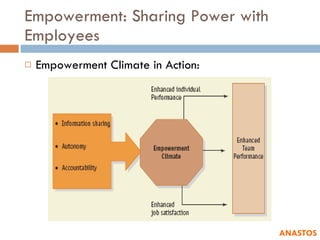
3) It describes empowerment as sharing power with employees through information sharing, autonomy, and team accountability.
4) It addresses abuses of power like sexual harassment and organizational politics for self-interest.