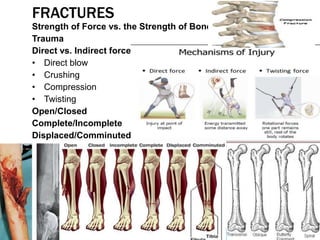
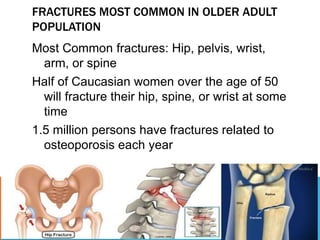
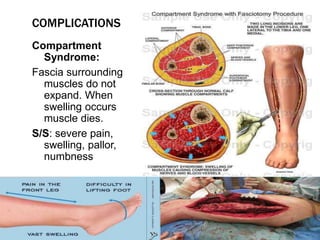
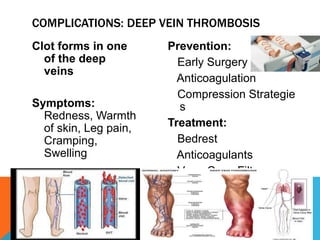
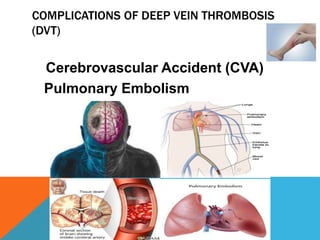
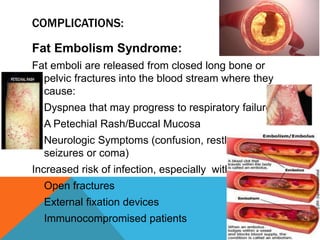
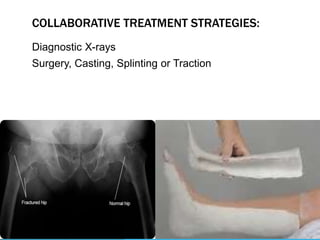
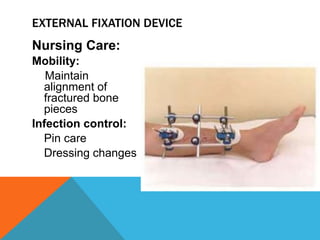
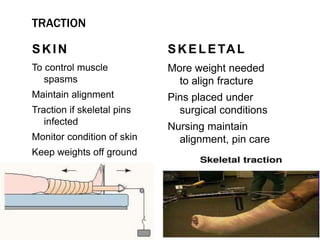
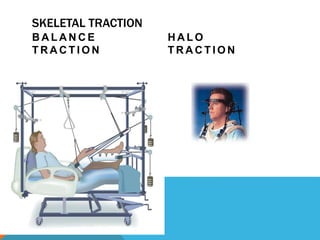
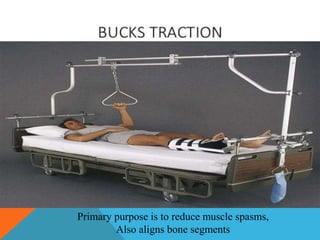
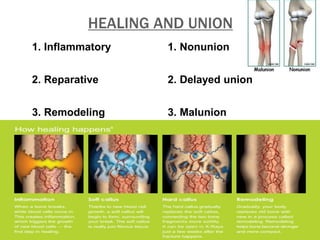
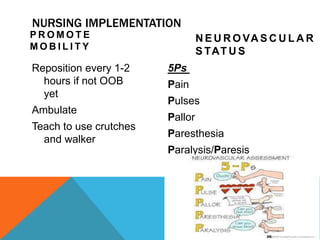
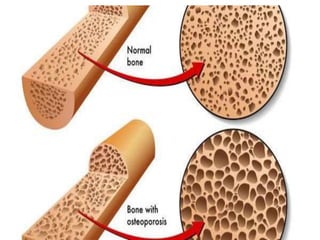
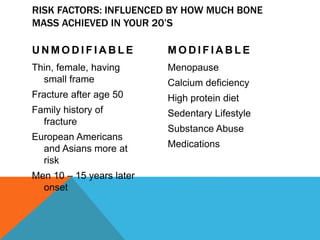
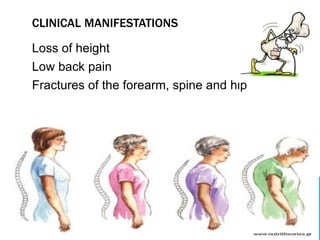
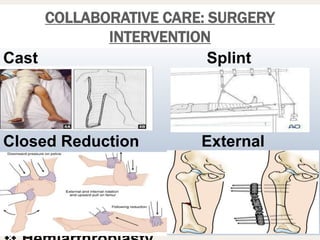
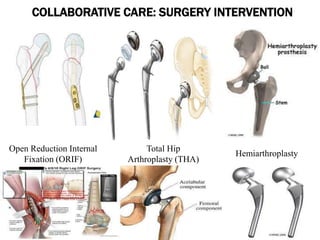
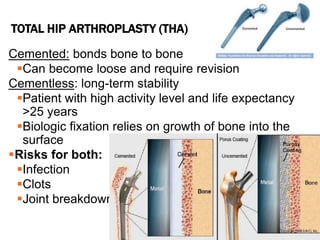
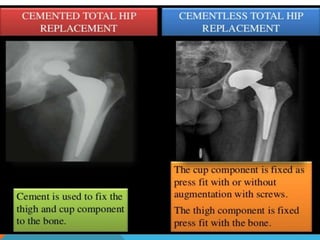
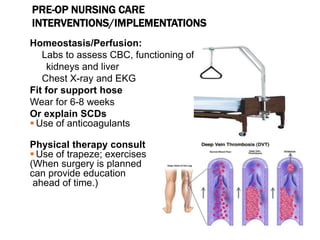
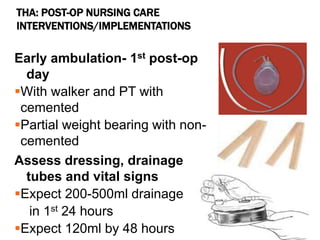
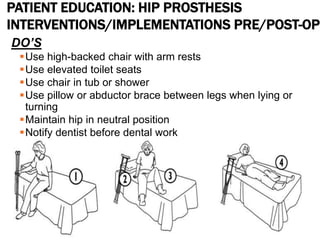
This document discusses fracture objectives related to mobility and the musculoskeletal system. It examines the relationship between mobility and fractures and identifies common fractures and their therapies. Specific objectives cover assessing risk factors for fractures, applying clinical knowledge to fracture care, improving patient safety, and using collaborative interventions to promote bone healing and minimize complications. Additional objectives focus on discussing how hip fractures impact older adults and describing approaches to diagnosing, treating, and providing culturally competent care for patients undergoing surgical repair of a hip fracture.