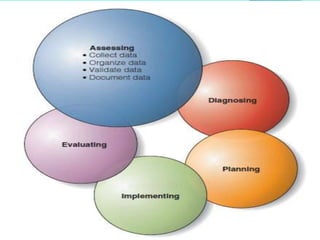
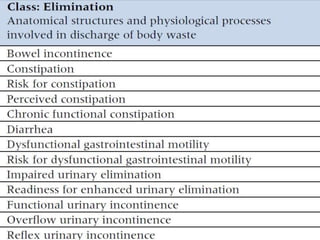
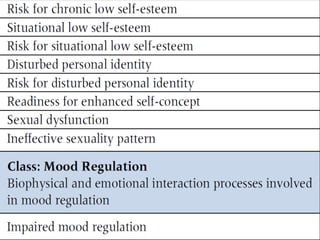
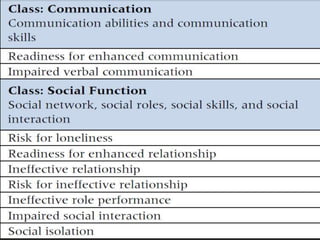
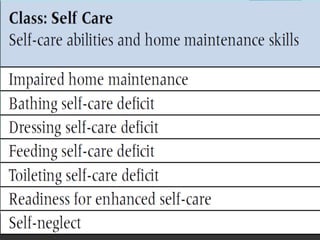
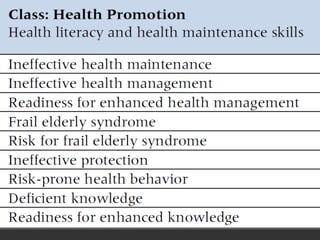
The nursing process involves 5 steps: assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. It is a systematic method used by nurses to identify issues, develop care plans, provide care, and evaluate outcomes. Assessment involves collecting client data through various methods. Diagnosis identifies actual or potential problems based on assessment findings. Planning establishes goals and selects interventions. Implementation carries out the care plan. Evaluation assesses progress towards goals and effectiveness of the plan. The nursing process is cyclic and ensures individualized, evidence-based care.